Explore the functionality, construction, benefits, and limitations of capacitive humidity sensors, and understand their role in various industries.
Introduction to Capacitive Humidity Sensors
Humidity, or the amount of water vapor present in the air, plays a significant role in numerous fields such as meteorology, agriculture, health and wellness, HVAC systems, and many more. To accurately measure this critical parameter, a variety of sensors are employed, one of the most common being capacitive humidity sensors.
Understanding Capacitive Humidity Sensors
Capacitive humidity sensors operate based on the principle of capacitance. Capacitance is the ability of a system to store an electric charge. In the case of these sensors, a variable capacitor is employed. The capacitance value changes with fluctuations in humidity levels, providing a measure of the current humidity.
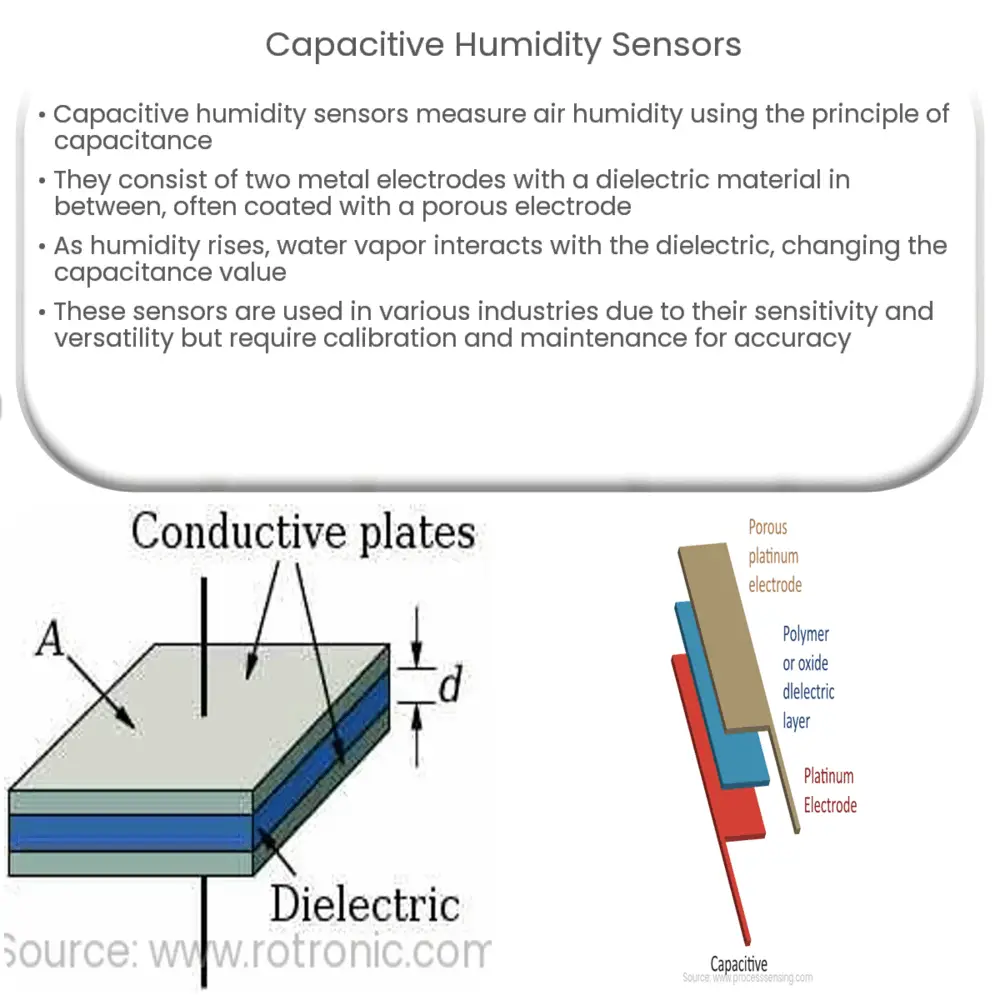
Construction of Capacitive Humidity Sensors
Capacitive humidity sensors typically comprise of two metal electrodes with a thin film of polymer or metal oxide as a dielectric material sandwiched between them. The sensing surface is usually coated with a porous metal electrode to protect it and to allow the passage of humidity.
- Metal Electrodes: These are the conductive plates which hold the charge in the capacitor.
- Dielectric Material: This non-conductive layer affects the capacitor’s ability to hold a charge, with the amount of charge it can hold being dependent on the relative permittivity of the material.
- Porous Metal Electrode: The electrode is porous to allow water vapor to pass through and interact with the dielectric material.
Working Principle
As the humidity increases, more water vapor permeates through the porous metal electrode and is absorbed by the dielectric material. This alters the dielectric constant, and consequently the capacitance. The change in capacitance is then measured, and this value is used to determine the relative humidity in the environment. It’s worth noting that these sensors do not measure absolute humidity but relative humidity – a ratio expressed in percentage.
Most capacitive humidity sensors can measure humidity from 0 to 100% RH, making them versatile for different applications. Their accuracy is typically within ±2% to ±5% RH.
Benefits and Applications
Capacitive humidity sensors offer several advantages including high sensitivity, fast response times, and long-term stability. They also feature a linear output corresponding to the relative humidity, which simplifies the interface to reading devices.
- Weather Stations: These sensors help in providing accurate humidity measurements, critical for weather prediction and climatology studies.
- Agriculture: Monitoring humidity is essential for crop growth and to prevent diseases and pests.
- Healthcare: In hospitals, maintaining a specific humidity level is crucial for patient comfort and to inhibit bacterial growth.
- Industrial Processes: Many industries like textile, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals require specific humidity levels for optimal operation.
Drawbacks and Considerations
Despite their many advantages, capacitive humidity sensors are not without their limitations. They are sensitive to temperature variations, which can affect the sensor’s reading. This requires careful calibration or additional circuitry to compensate for temperature effects. Additionally, while they are robust against most chemical vapors, certain chemicals can lead to the degradation of the dielectric material, resulting in sensor drift or failure.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Capacitive sensors are often integrated with temperature sensors for precise, temperature-compensated humidity measurements.
- Chemical Interference: Environments with high concentrations of chemicals such as chlorine, ammonia, or acidic vapors can degrade the sensor over time.
Advancements and Future Prospects
The development of nanotechnology and advanced materials science has led to the emergence of more accurate and reliable capacitive humidity sensors. For instance, sensors using polymer-based dielectric materials have shown excellent sensitivity and stability. There’s also active research in the use of nanoscale and composite materials to enhance the performance of these sensors.
Maintenance and Calibration
Like any other sensor, capacitive humidity sensors require regular calibration and maintenance to ensure accurate readings. They are typically calibrated against a known humidity source in controlled conditions. Moreover, protective measures such as regular cleaning, avoiding excessive condensation, and staying within the recommended temperature and humidity range, can significantly enhance their lifespan and reliability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, capacitive humidity sensors have found widespread application in numerous industries due to their sensitivity, stability, and versatility. Despite some challenges related to temperature sensitivity and chemical interference, ongoing advancements in technology are constantly improving their performance. Proper understanding, calibration, and maintenance are key to leveraging these devices for accurate humidity measurements, contributing significantly to fields ranging from meteorology to healthcare.

