Explore the world of capacitive microphones, their operational principle, types, applications, and advantages in this comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Capacitive Microphones
Among the myriad ways to capture sound and convert it into an electrical signal, capacitive microphones, also known as condenser microphones, stand out for their excellent audio quality and sensitivity. They are a popular choice in professional audio recording, broadcasting, and many other fields where sound precision is crucial.
The Basic Principle
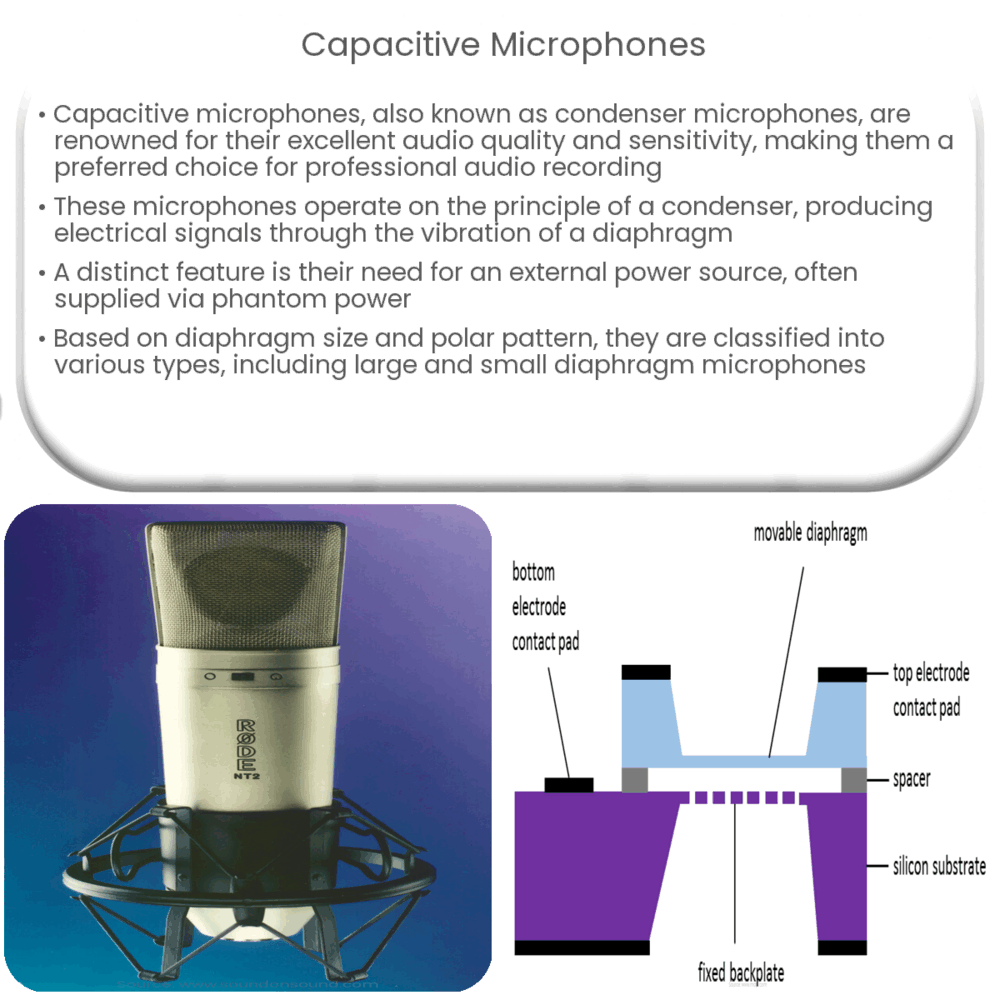
Capacitive microphones work on the principle of a condenser or capacitor, a device that stores energy in an electrostatic field. The capacitor in a capacitive microphone has two plates: one fixed (the backplate) and one movable (the diaphragm). The diaphragm, usually made of a lightweight material, vibrates when it comes into contact with sound waves. This vibration changes the distance between the two plates, altering the capacitance and producing a corresponding electrical signal.
Powering Capacitive Microphones
One distinct feature of capacitive microphones is that they require an external power source or battery to charge the plates of the capacitor. This external power source is often provided through a technique called phantom power, supplied via the same cable that carries the audio signal. The power is essential in creating the electrical field between the two plates and hence, the microphone’s ability to convert sound into an electrical signal.
- Phantom Power: Phantom power is a method used to supply steady direct current (DC) electric power to the active electronic components of the microphone through the balanced audio signal cables. Generally, professional audio interfaces and preamplifiers provide this power.
- Battery Power: Some microphones also offer battery compartments for standalone power, allowing for portable use where an external power source might not be available.
Types of Capacitive Microphones
Based on the diaphragm size and the polar pattern, capacitive microphones can be classified into several types:
- Large Diaphragm Microphones: These are popular in studio recording due to their ability to capture a wide frequency range and their inherent warmth.
- Small Diaphragm Microphones: Also known as pencil mics, these are known for their accurate and uncolored sound representation.
Capacitive microphones provide a level of sound accuracy and detail that is hard to match. They are integral to the world of sound, helping us to communicate, create, and connect. In the next part of this article, we will dive deeper into the operational details and further classifications of capacitive microphones, as well as the applications and advantages they offer.
Further Classifications and Operational Details
Continuing our discussion on the types of capacitive microphones, we have:
- Shotgun Microphones: These are highly directional microphones with a narrow polar pattern (directionality). They are primarily used in situations where sound sources are distant, such as in film and television production.
- Multi-Pattern Microphones: These microphones can switch between different polar patterns, providing the flexibility to record in various situations.
Applications of Capacitive Microphones
Capacitive microphones find usage in a wide variety of applications owing to their superior sound quality and sensitivity. Here are a few notable ones:
- Studio Recording: Their wide frequency response and high sensitivity make them ideal for studio recording.
- Broadcasting: In the broadcasting industry, these microphones are used due to their excellent clarity and voice detail.
- Live Sound: Certain capacitive microphones are used for live performances due to their ability to handle high sound pressure levels.
Advantages of Capacitive Microphones
There are numerous advantages to using capacitive microphones:
- High Sensitivity: They can pick up even the slightest sound nuances, making them a favourite among professionals.
- Excellent High-Frequency Response: Capacitive microphones are known for their wide frequency response, particularly at the high end.
- Little Noise: They introduce little self-noise, hence ensuring a clean and clear sound capture.
Conclusion
Capacitive microphones have significantly shaped the audio recording landscape thanks to their outstanding sound capturing capabilities. Their operational principle, derived from the concept of capacitors, is ingenious and elegant, and has served as a solid foundation for sound recording technology. Despite requiring an external power source, these microphones offer substantial benefits that greatly outweigh this minor inconvenience. From studio recording to broadcasting and live performances, capacitive microphones are instrumental in delivering high-quality sound.
In the realm of sound capture, the importance of understanding how tools like capacitive microphones work cannot be overstated. It not only broadens one’s technical knowledge but also aids in making informed decisions when it comes to audio recording. As the technology evolves, it will be exciting to see how capacitive microphones adapt and continue to serve our auditory needs.

