Explore the world of brushless generators: their working principle, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and comparison with brushed generators.
Introduction to Brushless Generators
A brushless generator is a type of electrical machine that uses electromagnetic induction to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The primary advantage of a brushless generator, as the name suggests, is the absence of brushes, which can wear out over time and require maintenance. Instead, brushless generators rely on a more modern and efficient system.
Working Principle of Brushless Generators
The working principle of brushless generators lies in Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. This law states that a change in magnetic field within a closed loop of wire induces an electromotive force (EMF), producing an electric current. Brushless generators use this principle to create electricity, with the rotor spinning within a magnetic field to induce current.
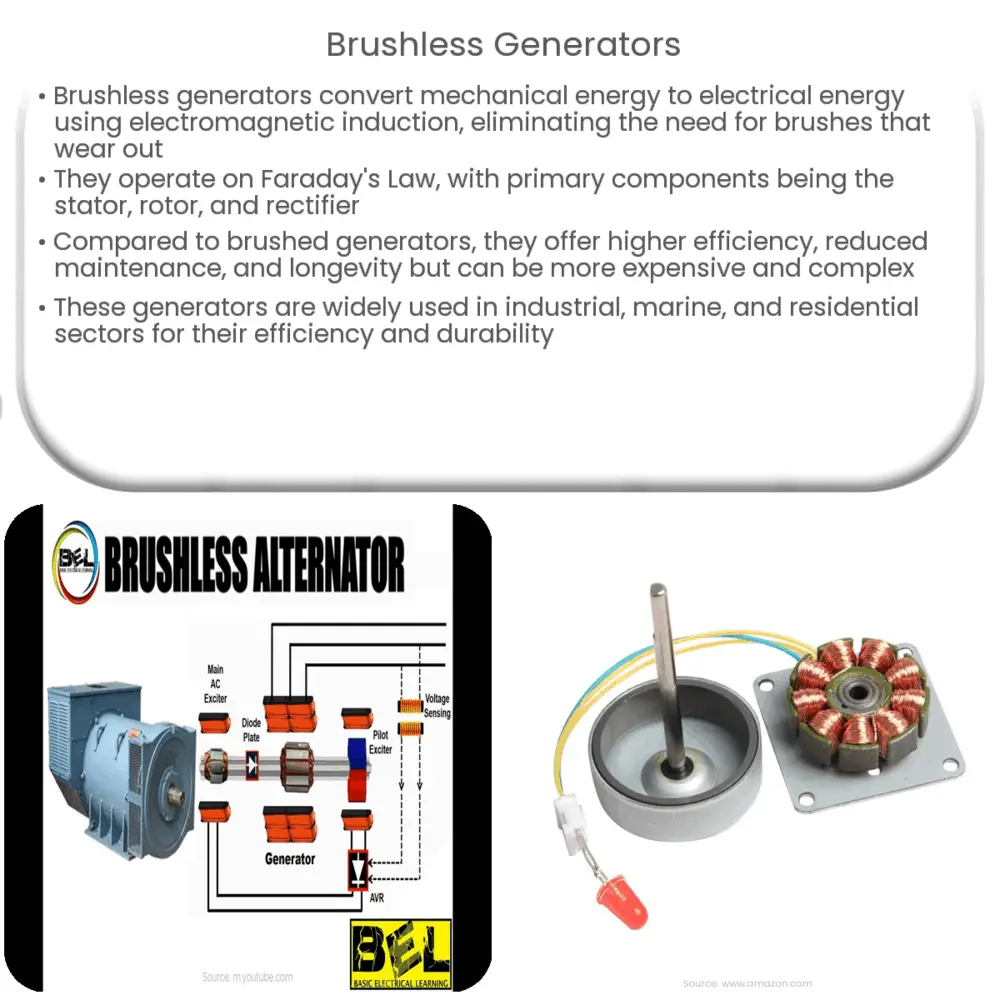
Components of a Brushless Generator
Brushless generators have three primary components:
- Stator: This is the stationary part of the generator which houses the windings. It is usually the outer shell.
- Rotor: The rotor, also known as the armature, is the part of the generator that rotates. It contains the magnetic field that interacts with the stator to produce electricity.
- Rectifier: This component is essential in converting the alternating current (AC) produced by the generator into direct current (DC).
Brushless Generators vs. Brushed Generators
One might wonder about the difference between brushless generators and traditional brushed generators. The key differences lie in their construction, efficiency, and maintenance requirements.
- Construction: Brushed generators have brushes that connect the rotor to the external circuit, whereas brushless generators eliminate these brushes, relying on a rectifier for the conversion of AC to DC.
- Efficiency: Brushless generators are generally more efficient than brushed generators. This is because brushless generators eliminate energy losses due to friction and wear and tear of the brushes.
- Maintenance: Brushless generators require less maintenance since they do not have brushes that can wear out. This means less downtime and lower maintenance costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Brushless Generators
While brushless generators offer several advantages over their brushed counterparts, they also come with certain drawbacks.
Advantages
- Longevity: Without brushes that can wear out, brushless generators tend to have a longer lifespan.
- Efficiency: By eliminating losses from friction and the wear and tear of brushes, brushless generators tend to operate more efficiently.
- Maintenance: The lack of brushes means less maintenance is required, reducing downtime and overall operational costs.
Disadvantages
- Cost: Brushless generators are typically more expensive upfront than brushed generators due to their complex construction.
- Complexity: The complex design of brushless generators can make them more challenging to repair if a problem arises.
Applications of Brushless Generators
Brushless generators are widely used in various sectors due to their efficiency and durability. They are frequently employed in:
- Industrial sector: They are used in factories and industrial plants that require a reliable and efficient power source.
- Marine sector: In marine vessels, brushless generators are essential due to their resistance to harsh conditions and their long lifespan.
- Residential sector: They are also used in homes as a backup power source during power outages.
Conclusion
In conclusion, brushless generators represent a significant evolution in generator technology. Their high efficiency, reduced maintenance requirements, and longevity make them a preferred choice for many applications, despite their higher initial cost and complexity. As technology continues to advance, the use of brushless generators is expected to become more prevalent, providing reliable and efficient power solutions for various sectors.

