Explore the importance, types, and selection process of board-to-board connectors in electronic assemblies, along with future trends.
Understanding Board-to-Board Connectors
When it comes to electronic assemblies, an often overlooked but crucial component is the board-to-board connector. These connectors are fundamental to the architecture of many modern electronic devices, enabling them to perform their tasks efficiently and reliably.
Board-to-board connectors are used to facilitate connections between different printed circuit boards (PCBs) within a system. They provide a flexible interface that often allows for variation in board spacing and alignment, offering designers the versatility required in today’s complex electronic environments.
The Importance of Board-to-Board Connectors
As electronic devices become more complex and compact, the demand for reliable, efficient, and flexible connection solutions has grown exponentially. Board-to-board connectors play a critical role in this development, providing key benefits such as:
- Space Efficiency: By allowing for direct connection between PCBs, these connectors eliminate the need for excessive wiring, conserving valuable space within the device.
- Design Flexibility: Board-to-board connectors come in a variety of formats, pitches, and orientations, providing a high degree of flexibility for designers.
- Reliability and Durability: These connectors are designed to withstand a range of environmental conditions and operational stresses, ensuring long-lasting, reliable connections.
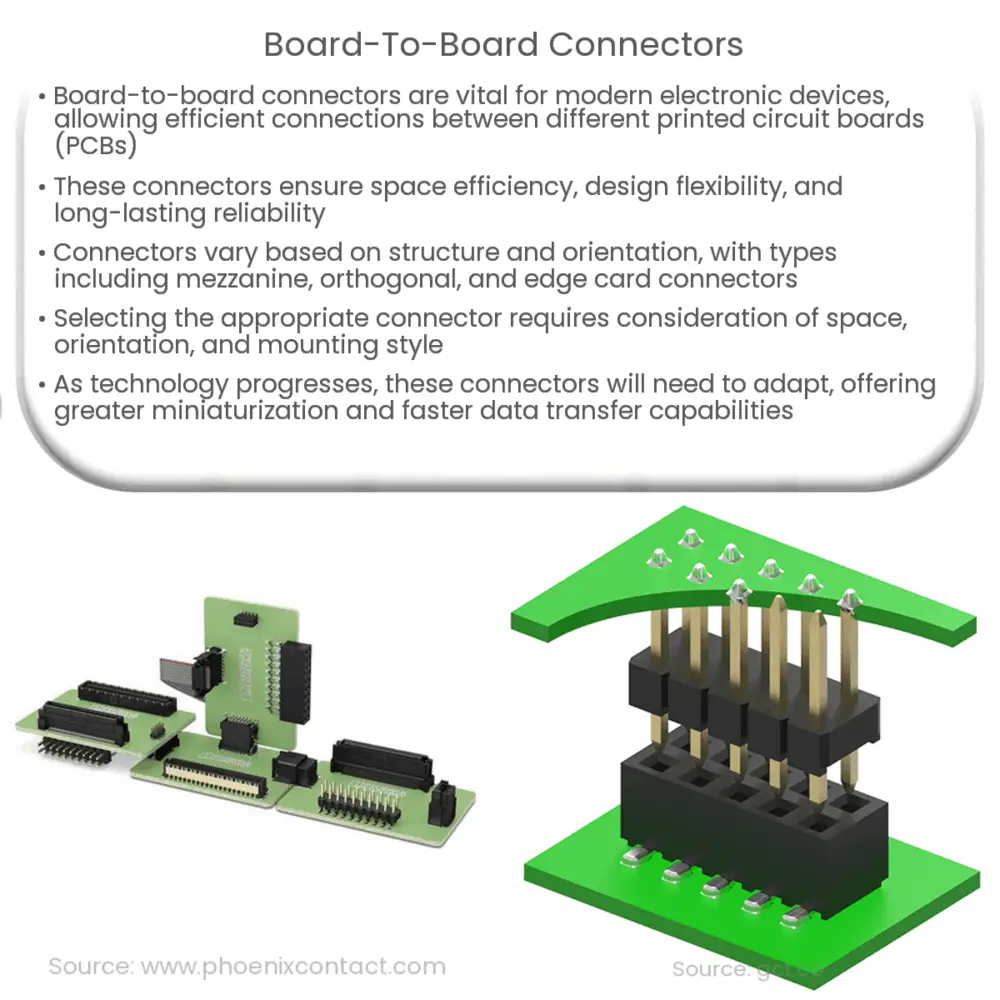
Types of Board-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-board connectors are categorized based on various parameters such as their structure, mounting style, and orientation. Some common types include:
- Mezzanine Connectors: These connectors are designed to connect two parallel PCBs in a stacked configuration. They are typically used in applications where space is at a premium.
- Orthogonal Connectors: These connectors allow for perpendicular connections between PCBs, typically found in backplane applications.
- Edge Card Connectors: These connectors enable connection to the edge of a PCB, typically used in pluggable or removable applications.
Each type of board-to-board connector has its unique advantages and use cases, enabling designers to tailor their PCB architecture to the specific needs of their application. Understanding the differences and capabilities of these connectors is fundamental to selecting the right connector for any given situation.
Selecting the Right Board-to-Board Connector
Given the wide range of board-to-board connectors available, making the right choice can be challenging. A good starting point is to consider the specific requirements of the application in question.
- Space Constraints: The available space within the device can greatly influence the type of connector required. Mezzanine connectors, for instance, are excellent for high-density applications where board space is limited.
- Orientation: The desired orientation of the PCBs should also be considered. Orthogonal connectors, for example, allow for perpendicular connections, making them ideal for certain backplane applications.
- Mounting Style: Whether the connector needs to be surface mounted or through-hole mounted can also dictate the type of connector required.
Understanding these factors can guide the decision-making process and help designers select the most suitable board-to-board connector for their specific application.
The Future of Board-to-Board Connectors
As technology continues to evolve, board-to-board connectors are expected to adapt and change to meet emerging needs. With advances in miniaturization, we can expect connectors to become smaller, without compromising their performance or reliability. Additionally, with the rise of new technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G, board-to-board connectors will need to support faster data transfer rates, pushing the boundaries of connector design and innovation.
Conclusion
Board-to-board connectors are an essential yet often overlooked component in modern electronics. They provide the critical interface between different printed circuit boards, enabling these components to work together seamlessly. While the variety of connectors available can seem overwhelming, understanding the unique requirements of each application can simplify the selection process. As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate these connectors to evolve in kind, becoming ever more capable and versatile, and continuing to underpin the functionality and performance of our electronic devices.

