Explore the world of Bias Tees, their components, functions, applications, and selection criteria in our comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Bias Tees
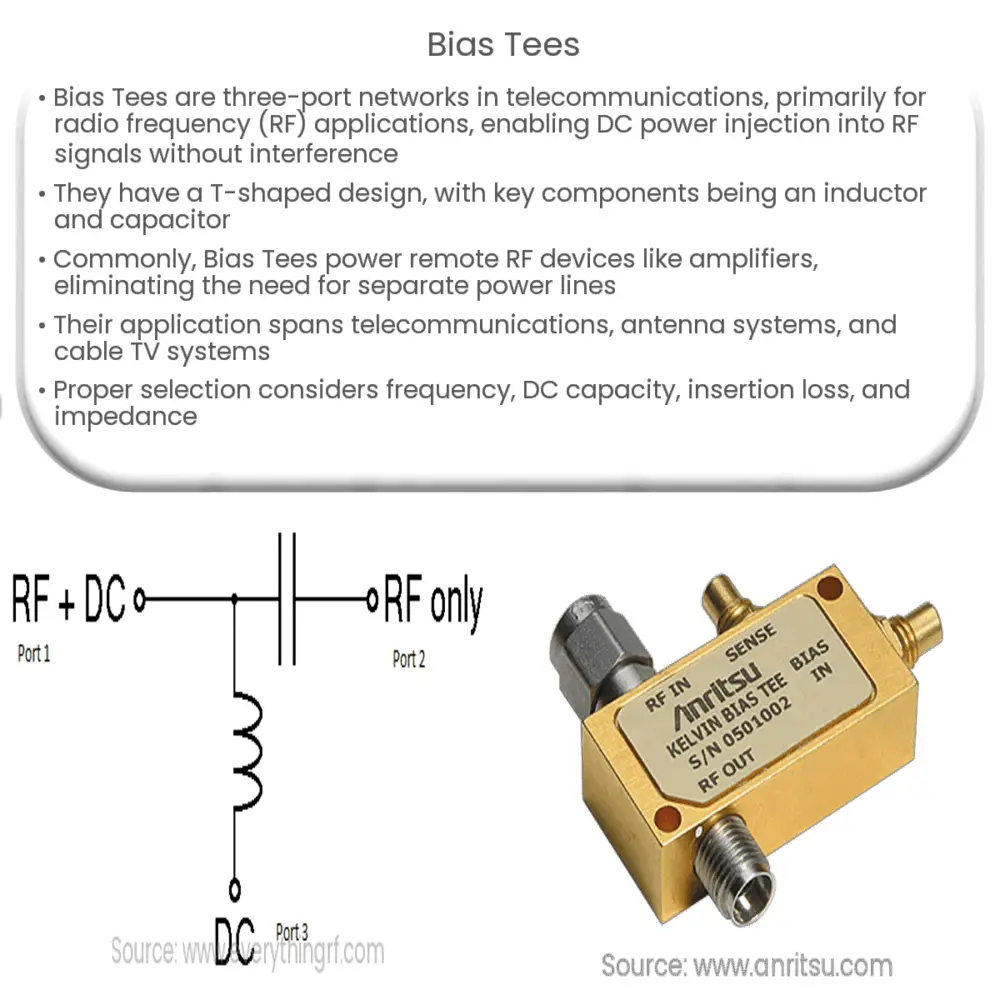
A Bias Tee is a three-port network used in telecommunications, particularly in radio frequency (RF) applications. Its primary function is to inject DC power into an RF signal to power remote RF devices while allowing the RF signal to pass through with minimal loss or interference.
Understanding the Principle
Bias Tees are named for their T-shaped design, which has an isolated port for DC power injection and two ports for RF input and output. The ‘tee’ shape is essential for maintaining isolation between the DC and RF circuits. An inductor (also known as a choke) and a capacitor form the primary components of a Bias Tee, and these two components are the core facilitators of its function.
Key Components: Inductor and Capacitor
- Inductor: The inductor acts as a high impedance path for the RF signal, blocking it from reaching the DC port. It is designed to have a very low impedance to DC power, enabling it to flow to the output port and power the remote device.
- Capacitor: The capacitor blocks the DC power from entering the RF signal path, maintaining the integrity of the signal. It allows the RF signal to pass with minimal insertion loss.
Applications of Bias Tees
Bias Tees find use in various applications within the field of telecommunications and electronics. They are most commonly used to supply DC power to remote RF devices, such as low-noise amplifiers (LNAs) or RF photodiodes. By employing a Bias Tee, the need for a separate power supply line can be eliminated, reducing the complexity and cost of the system design.
Another notable application of Bias Tees is in antenna systems. Bias Tees can be used to power remote active antennas, which improves signal strength and coverage. This can be especially useful in scenarios where running a separate power line may be impractical or undesirable, such as in wireless communication systems or large-scale antenna arrays.
Further applications extend to areas like cable TV systems, where Bias Tees are used to provide power to amplifiers or other devices in the signal path.
Selecting the Right Bias Tee
When selecting a Bias Tee, several factors must be considered to ensure it meets the system requirements. These include:
- Frequency Range: The Bias Tee must be compatible with the RF signal’s frequency. Inappropriate selection could lead to signal loss or interference.
- DC Current Capacity: The Bias Tee should be capable of supplying the required DC current to power the remote device. This specification is often determined by the power requirements of the device.
- Insertion Loss: A Bias Tee should introduce as little insertion loss as possible to maintain signal integrity. This factor is especially crucial in high-performance RF systems.
- Impedance: Impedance matching is essential in RF systems to maximize power transfer and minimize signal reflections. Typically, Bias Tees are designed to match a 50 Ohm system, which is standard in many RF applications.
Conclusion
In summary, Bias Tees play a vital role in the realm of telecommunications and electronics. They provide a unique solution for powering remote RF devices without disrupting the RF signal’s integrity or requiring a separate power line. Understanding the basic function and application of Bias Tees equips engineers and system designers with a tool to simplify system design, enhance performance, and potentially reduce costs. However, appropriate selection is crucial, taking into account factors such as the frequency range, DC current capacity, insertion loss, and impedance. As technology continues to evolve, the application of Bias Tees promises to expand and transform alongside it.

