Explore the world of Amplitude Modulation (AM) circuits, their components, operation, applications, and their role in communication systems.
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation (AM) Circuits
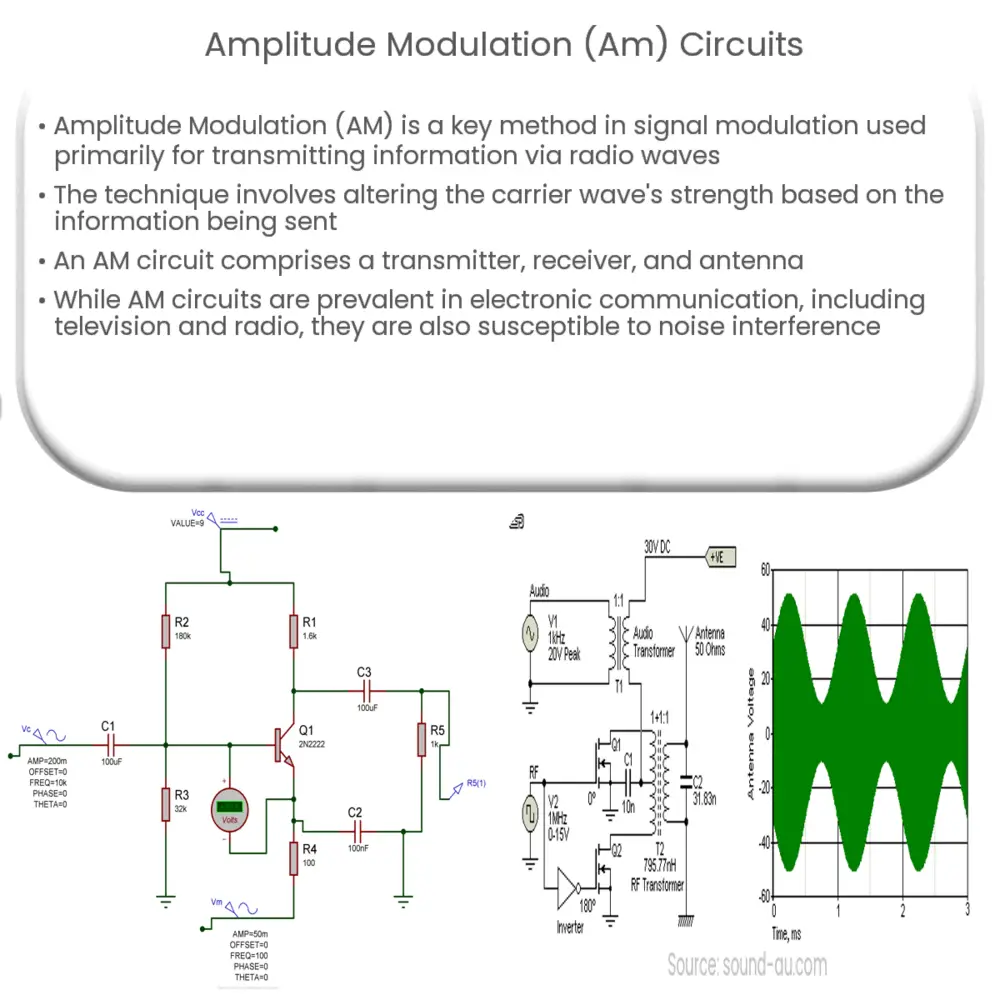
Amplitude Modulation, commonly referred to as AM, is a fundamental method of signal modulation. It is a technique used in electronic communication, predominantly in transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength (amplitude) of the carrier wave in proportion to the waveform being sent, which typically corresponds to sounds to be reproduced by a loudspeaker or light intensity in television.
Working Principle of AM
The basic principle behind AM is quite straightforward. An audio signal is combined with a carrier signal resulting in a change in the overall amplitude of the signal. This change corresponds to the variations in the frequency of the audio signal. The resulting waveform is then transmitted over the airwaves or via other means.
Components of an AM Circuit
- Transmitter: The transmitter is the part of the circuit that sends out the radio signals. In an AM circuit, the transmitter is designed to vary the amplitude of the signal to match the original signal.
- Receiver: The receiver’s role is to detect the radio signal and decode the information. It does this by separating the carrier wave from the modulating signal.
- Antenna: The antenna in an AM circuit is used for transmitting and receiving radio signals. It converts electrical signals into radio waves (during transmission) and vice versa (during reception).
Applications of AM Circuits
AM circuits have a wide range of applications in our daily lives. They are used in television broadcasting, radio broadcasting, and two-way radios. AM signals can also be used for long-distance shortwave broadcasts, including international broadcasting and ship-to-shore communication. Despite the introduction of more advanced modulation techniques like Frequency Modulation (FM), AM continues to be used in many electronic communication systems due to its simplicity and reliability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AM
One of the main advantages of AM is its simplicity. The circuits used for AM modulation and demodulation are relatively simple to design and implement. Furthermore, AM signals can be transmitted over long distances, making them ideal for certain applications. However, AM is also prone to noise interference. Any change in the signal’s amplitude can cause distortion, making the received signal less accurate.
Detailed Operation of AM Circuits
The operation of an AM circuit can be divided into two stages: modulation and demodulation.
- Modulation: This is the process where the information signal modulates the carrier. The carrier wave’s amplitude is varied in accordance with the information signal’s intensity. The modulated signal is then transmitted through the antenna.
- Demodulation: The receiver’s task is to extract the information signal from the received AM signal. This process is known as demodulation. A demodulator is used, which separates the original information signal from the carrier.
Types of AM
There are several types of Amplitude Modulation, including Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC), Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier (SSB-SC), and Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM). These variations offer different trade-offs in terms of complexity, bandwidth efficiency, and power requirements.
Evolution and Future of AM
While AM was the first modulation technique to be used in radio broadcasting, it has been gradually replaced by FM (Frequency Modulation) for music and high-fidelity broadcasting due to FM’s superior noise rejection. However, AM is still widely used for talk shows and news broadcasting, as well as long-distance broadcasting, where its longer wavelength is beneficial. With the advent of digital broadcasting technologies, the use of AM is gradually decreasing, but it still has its place in specific applications due to its simplicity and long-range capabilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Amplitude Modulation (AM) is a fundamental modulation technique that has played a significant role in the evolution of communication systems. Despite the emergence of more advanced technologies, AM remains a vital part of our communication infrastructure. Its simplicity and ability to transmit over long distances continue to make it a reliable choice in many applications. However, as we advance towards a more digital and noise-free era, the use of AM may become more specialized, but its foundational role in the world of communication is undeniable.

