Electric current can cause tingling, muscle contractions, respiratory issues, cardiac problems, burns, and internal organ damage, depending on factors.
Effects of Electric Current on the Human Body
Electricity plays a crucial role in modern society, but it can be harmful when not handled properly. This article will explore the effects of electric current on the human body and the factors that influence these effects.
Effects of Electric Current
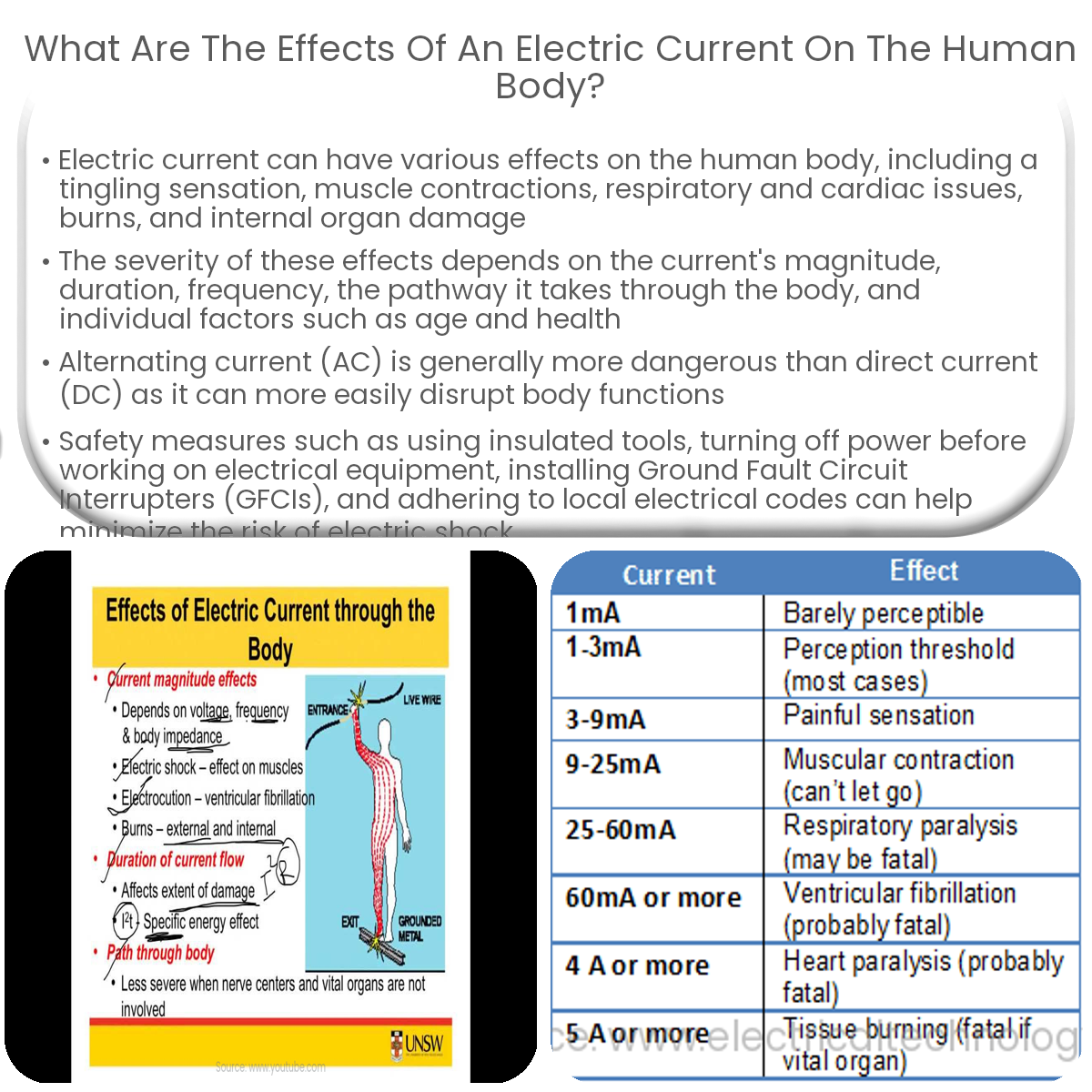
When electric current passes through the human body, it can cause a range of effects, depending on factors such as current magnitude, duration, frequency, and the body’s resistance. Some common effects include:
- Tingling sensation: Mild electric current can cause a tingling sensation, usually experienced when touching a live wire or device with a small leakage current.
- Muscle contractions: As current increases, it can cause involuntary muscle contractions, which may lead to difficulty in letting go of an energized object.
- Respiratory issues: Stronger currents can affect the respiratory system, causing difficulty in breathing or even respiratory paralysis.
- Cardiac issues: High currents can disrupt the normal functioning of the heart, potentially leading to ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest.
- Burns: Electric current can cause burns, ranging from mild to severe, at the points of contact with the body.
- Internal organ damage: Current passing through the body can damage internal organs and tissues, leading to long-term health issues.
Factors Influencing Effects
Several factors determine the severity of electric current’s effects on the human body:
- Current magnitude: Higher current levels generally cause more severe effects.
- Duration: The longer the current flows through the body, the more significant the potential damage.
- Frequency: Alternating current (AC) is typically more dangerous than direct current (DC) due to its ability to disrupt normal body functions more easily.
- Pathway: The route the current takes through the body can impact the severity of the effects, with current passing through vital organs being more dangerous.
- Individual factors: Age, health, and body composition can influence the body’s resistance to electric current and the severity of its effects.
Prevention and Safety Measures
Adhering to safety guidelines and taking precautions when working with electricity can minimize the risk of electric shock:
- Use insulated tools and personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Turn off power before working on electrical equipment.
- Install Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) in high-risk areas.
- Follow local electrical codes and regulations.
- Stay informed about electrical safety practices.
By understanding the effects of electric current on the human body and taking appropriate safety measures, the risk of injury or fatality can be significantly reduced.