A DC motor works by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of magnetic fields in the stator and rotor.
Principle of Operation of a DC Motor
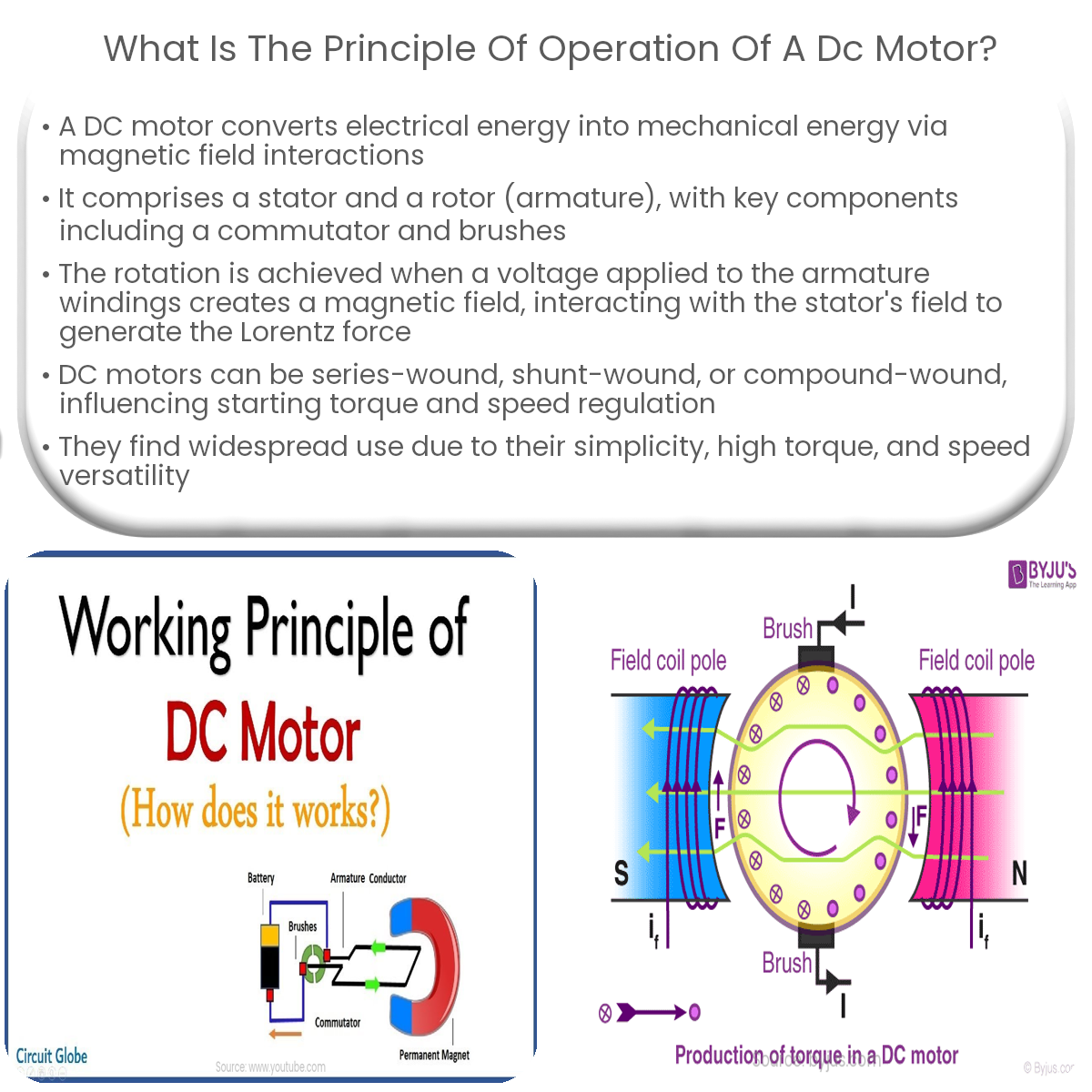
A DC (Direct Current) motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of magnetic fields. The primary components of a DC motor are the stator, which is the stationary part containing a magnetic field, and the rotor, also known as the armature, which rotates inside the stator.
Construction and Components
The main parts of a DC motor include:
Working Principle
When a voltage is applied across the armature windings, a current flows through them, producing a magnetic field around the rotor. The interaction between the rotor’s magnetic field and the stator’s magnetic field generates a force, known as the Lorentz force, which causes the rotor to rotate. The direction of rotation can be determined using the right-hand rule.
As the rotor rotates, the brushes maintain contact with the commutator. The commutator is designed to reverse the current direction in the armature windings as the rotor completes half a rotation. This ensures that the direction of the Lorentz force remains constant, resulting in continuous rotation.
Types of DC Motors
DC motors are primarily classified into three types:
DC motors are widely used in various applications, including electric vehicles, home appliances, and industrial equipment, due to their simplicity, high starting torque, and ability to operate at a wide range of speeds.