To find the resonant frequency of an RLC circuit, use the formula f_r = (1 / (2π√(LC))), where L is inductance and C is capacitance in the circuit.
Finding the Resonant Frequency of an RLC Circuit
An RLC circuit is an electrical circuit that consists of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C) connected in series or parallel. One of the essential properties of these circuits is their ability to resonate at a specific frequency, known as the resonant frequency. At this frequency, the inductive and capacitive reactances cancel each other out, resulting in the maximum or minimum response of the circuit. This article will discuss the process of determining the resonant frequency for both series and parallel RLC circuits.
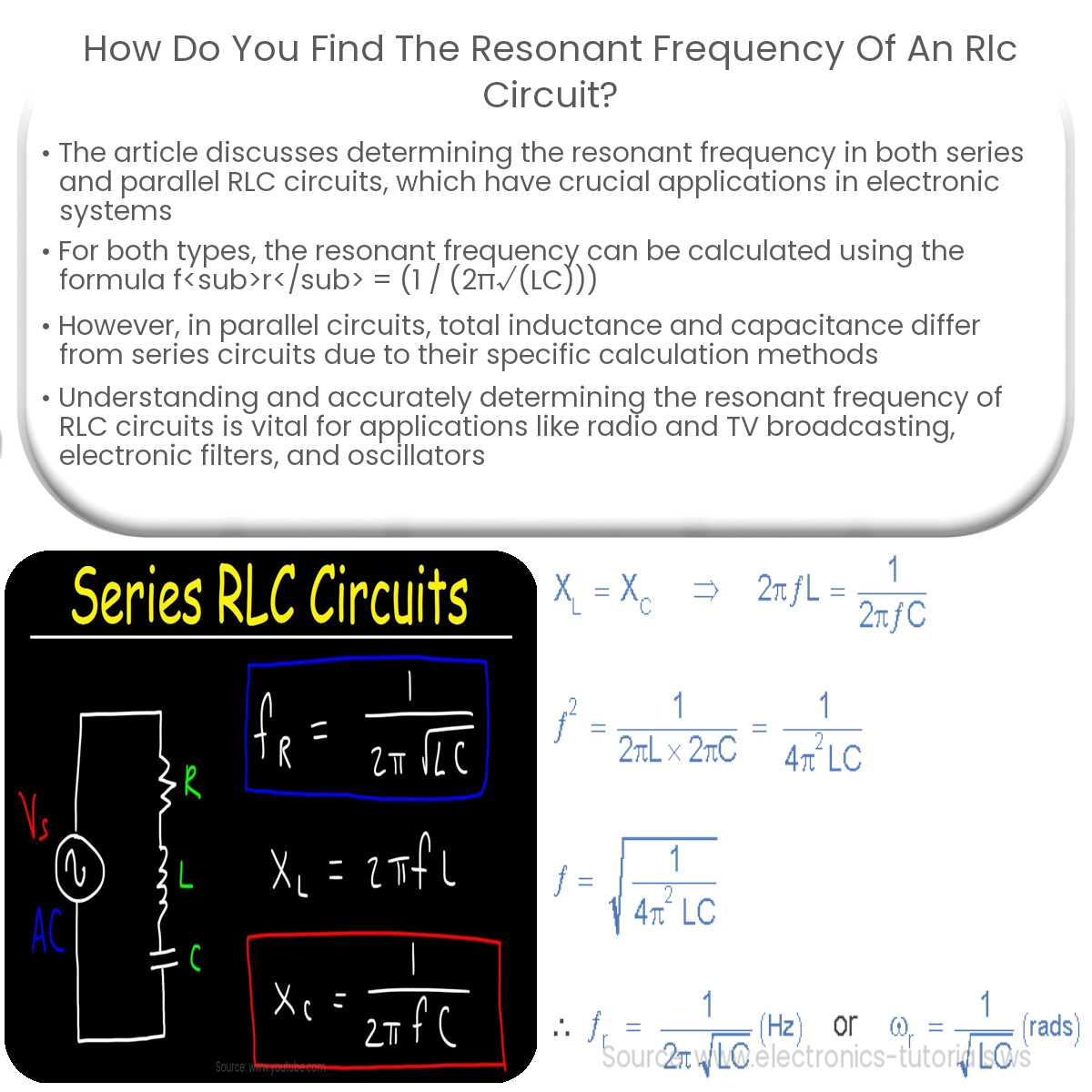
Resonant Frequency in Series RLC Circuits
In a series RLC circuit, the resonant frequency (fr) can be calculated using the following formula:
fr = (1 / (2π√(LC)))
Where L represents the inductance of the inductor (in henries), and C is the capacitance of the capacitor (in farads). To find the resonant frequency, you simply need to plug the values of L and C into the equation and solve for fr.
Resonant Frequency in Parallel RLC Circuits
In a parallel RLC circuit, the resonant frequency can also be calculated using the same formula as for the series RLC circuit:
fr = (1 / (2π√(LC)))
However, it is important to note that the total inductance (L) and total capacitance (C) in a parallel RLC circuit are different from those in a series RLC circuit. In a parallel RLC circuit, the total inductance is the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of each inductor’s inductance, and the total capacitance is the sum of each capacitor’s capacitance. Once you have calculated the total inductance and capacitance, you can use the formula to find the resonant frequency.
Applications of Resonant Frequency in RLC Circuits
Resonant frequency plays a crucial role in various applications, such as:
- Radio and television broadcasting, where RLC circuits help tune into specific channels.
- Filters in electronic circuits, where RLC circuits selectively allow certain frequencies to pass through while blocking others.
- Oscillators, where RLC circuits generate sinusoidal waveforms at specific frequencies.
Understanding the resonant frequency of RLC circuits is essential for designing and analyzing electronic systems that rely on frequency-dependent behavior. By applying the appropriate formula and considering the characteristics of the individual components, engineers and hobbyists can accurately determine the resonant frequency for various RLC circuit configurations.