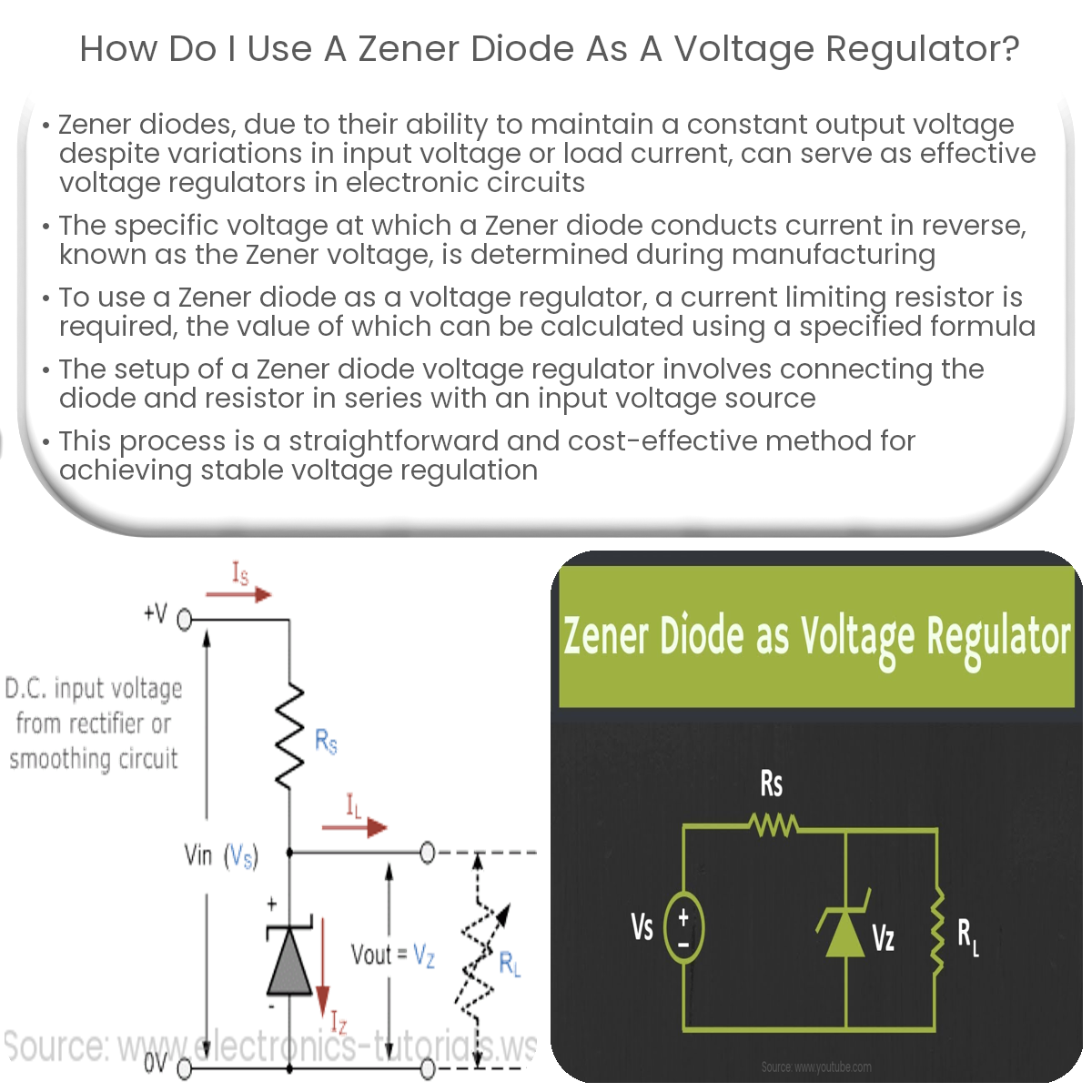
To use a Zener diode as a voltage regulator, connect it in reverse-biased mode with a current-limiting resistor and apply the input voltage.
Using a Zener Diode as a Voltage Regulator
Zener diodes are semiconductor devices that can be used as voltage regulators in electronic circuits. They maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load current. This article will guide you through using a Zener diode as a voltage regulator in your circuit.
Understanding Zener Diodes
A Zener diode is designed to conduct current in reverse when a specific voltage, called the Zener voltage, is reached. This voltage is determined by the diode’s doping characteristics and is chosen during manufacturing. Zener diodes are widely used for voltage regulation because they can maintain a constant voltage across their terminals, providing a stable reference voltage.
Components Required
- Zener diode with the desired Zener voltage
- Current limiting resistor (R1)
- Load resistor (RL, optional)
- Input voltage source
Calculating the Resistor Value
To use a Zener diode as a voltage regulator, you must first determine the value of the current limiting resistor, R1. This resistor is connected in series with the diode and is used to limit the current through the diode. To calculate R1, use the following formula:
R1 = (Vin – VZ) / IZ
Where Vin is the input voltage, VZ is the Zener voltage, and IZ is the desired Zener current. Ensure that the chosen resistor can handle the power dissipation calculated using P = I2R.
Setting Up the Circuit
Follow these steps to set up a Zener diode voltage regulator:
- Connect the input voltage source to one end of the current limiting resistor, R1.
- Connect the other end of R1 to the anode (the terminal with a shorter lead or marked with a band) of the Zener diode.
- Connect the cathode (the longer lead) of the Zener diode to the ground or common reference point.
- If desired, connect the load resistor, RL, between the Zener diode’s cathode and ground.
When the input voltage is applied, the Zener diode will maintain the desired Zener voltage across its terminals, effectively regulating the output voltage. The load resistor, RL, is optional, but it can be used to simulate the actual load of your circuit and ensure the regulation is effective under varying load conditions.
Conclusion
Using a Zener diode as a voltage regulator is a simple and cost-effective solution for maintaining a constant output voltage in electronic circuits. By choosing the appropriate Zener diode and current limiting resistor, you can effectively regulate voltage for a wide range of applications.