Explore the fundamentals of optical delay lines, their working principles, applications, components, challenges, and future prospects in photonics and telecommunications.
Introduction to Optical Delay Lines
An optical delay line is a critical component used in various areas of optical communications and photonics. Its primary purpose is to delay the optical signal passing through it, hence the name. This delay is critical in many applications, such as optical coherence tomography, signal processing, laser scanning microscopy, and interferometry, to name a few.
Working Principle of Optical Delay Lines
Optical delay lines work by manipulating the path that an optical signal takes. The path’s length and the medium’s refractive index through which the signal passes determine the delay achieved. When the light path is extended, it takes more time for the light signal to traverse it, thus causing a delay.
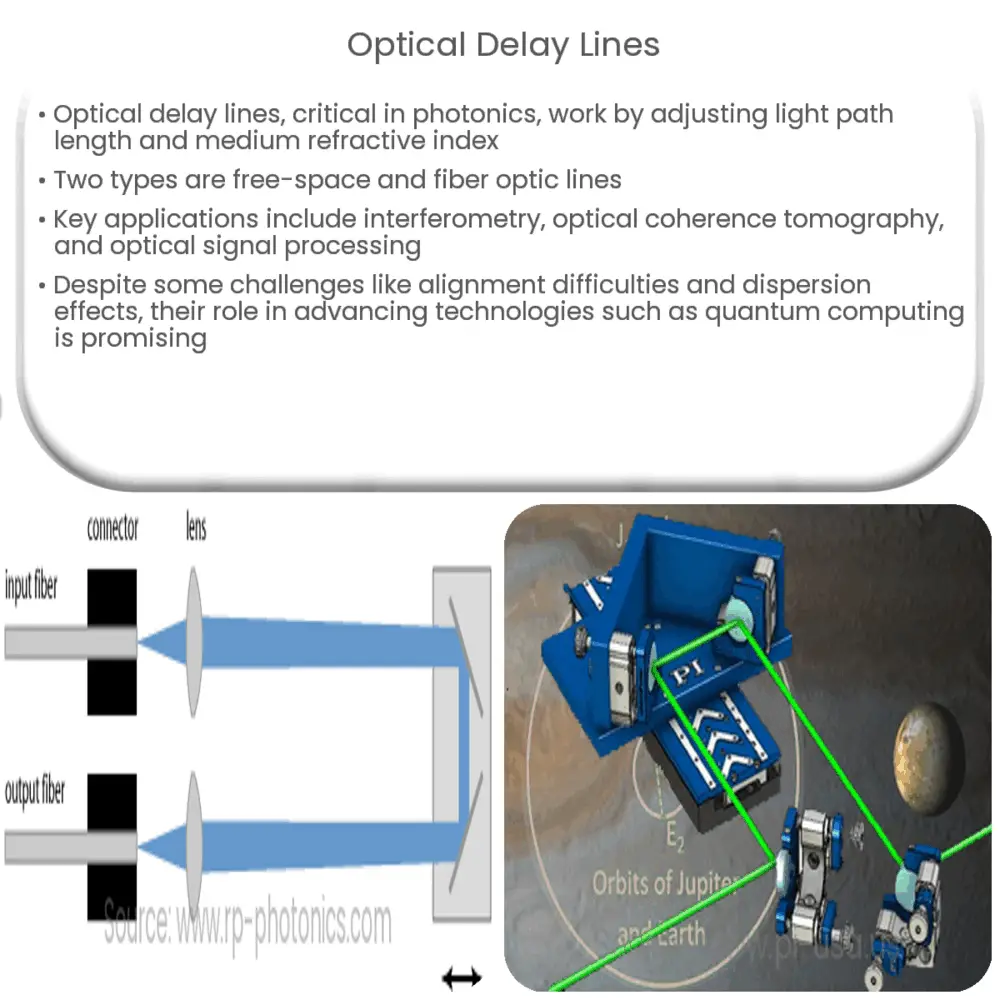
- Free-space delay lines: This type involves the use of mirrors to reflect the signal multiple times, thereby lengthening the path that light takes. These can be fixed or adjustable in design, depending on the application’s requirement.
- Fiber optic delay lines: These use optical fiber as the medium, where light is delayed due to its reflection and refraction within the fiber. Fiber optic delay lines are more compact compared to their free-space counterparts.
Applications of Optical Delay Lines
Optical delay lines find usage in a wide range of applications:
- Interferometry: They are a fundamental component in interferometers, used to create a path difference between two or more light beams. This difference in path is critical in creating interference fringes that are the basis of interferometric measurements.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT): In OCT, a low-coherence light source is split into two beams – one is directed at the sample, and the other is sent through an optical delay line. The interference pattern generated when the beams are recombined allows imaging of the internal structure of the sample.
- Optical signal processing: Optical delay lines play an integral role in advanced optical signal processing, helping to create filters and tune phase relations between different signal components.
The Role of Refractive Index in Optical Delay Lines
The delay in an optical delay line is also influenced by the refractive index of the medium through which the light passes. The refractive index is the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to its speed in a given medium. A higher refractive index means slower light propagation, leading to a longer delay.
Components of Optical Delay Lines
Most optical delay lines are made up of similar components, regardless of their type. These include:
- Optical elements: These are the key elements that manipulate the path of the light. They can be mirrors in free-space delay lines or optical fibers in fiber-optic delay lines.
- Mounts and stages: These components hold and adjust the position of the optical elements. For variable delay lines, the stages can be motorized to adjust the path length of the light.
- Controllers: In variable delay lines, controllers are used to regulate the motorized stages, enabling precise control of the delay.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the versatility and broad utility of optical delay lines, they are not without their challenges. These include alignment difficulties, especially in free-space delay lines, and dispersion effects in fiber optic delay lines. However, ongoing research and development efforts are paving the way for solutions to these problems, such as the use of dispersion-compensating fibers and the development of integrated photonic delay lines.
In the future, optical delay lines are expected to play an even more significant role in advanced photonics and telecommunications systems. They are fundamental to the development of all-optical networks and will be key in advancing technologies such as quantum computing and communication.
Conclusion
In conclusion, optical delay lines are a vital tool in photonics and optical communications, offering the ability to control the timing of light signals with high precision. Their working principle is simple yet powerful, relying on path length adjustment and refractive index modulation to achieve the desired delay. Despite some challenges, the future of optical delay lines looks promising, with their role set to become even more central in the advent of all-optical networks and quantum technologies.



