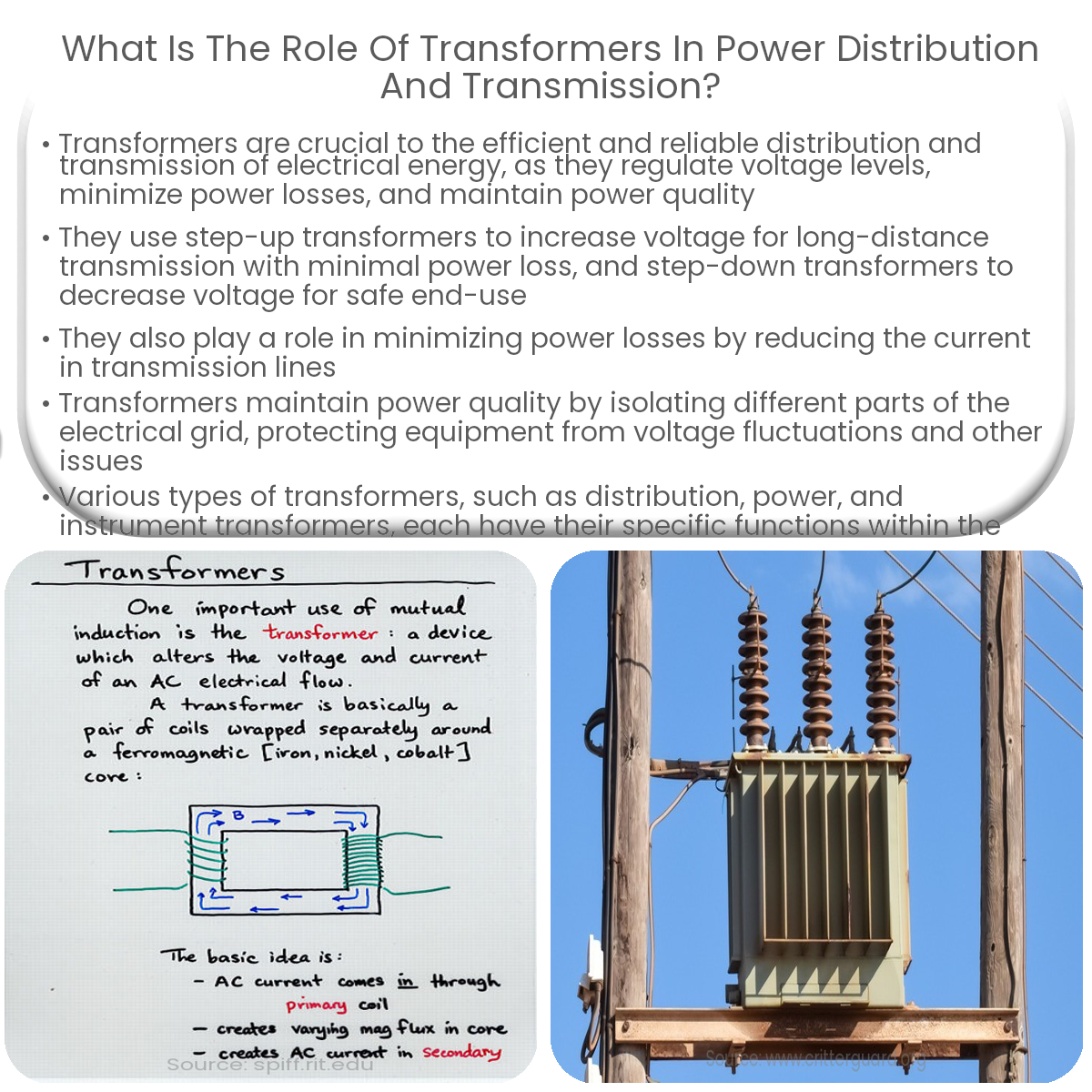
Transformers regulate voltage levels, minimize power losses, and maintain power quality in power distribution and transmission systems.
Role of Transformers in Power Distribution and Transmission
Transformers play a vital role in the efficient and reliable distribution and transmission of electrical energy. They are essential for regulating voltage levels, minimizing power losses, and maintaining power quality. This article will explore the critical functions of transformers in power distribution and transmission systems.
Voltage Regulation
One of the primary roles of transformers is to regulate voltage levels throughout the electrical grid. Transformers are used to step up or step down voltage levels depending on the requirements of the system. This voltage regulation helps to minimize power losses and ensures the efficient transfer of electrical energy from power plants to end-users.
- Step-up transformers: These transformers increase voltage levels at power plants, allowing electricity to be transmitted over long distances with minimal power loss.
- Step-down transformers: These transformers decrease voltage levels for distribution systems and end-users, making the electricity safe and suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Minimizing Power Losses
Transformers contribute to minimizing power losses during transmission and distribution. As voltage levels are increased using step-up transformers, the current in the transmission lines decreases, reducing the power loss due to the resistance of the conductors. This process is crucial for maintaining the efficiency of the electrical grid and minimizing the overall energy losses.
Power Quality and Isolation
Transformers also help maintain power quality by isolating different parts of the electrical grid. They can isolate electrical equipment from voltage fluctuations, harmonic distortion, and other power quality issues, ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electrical devices. Additionally, transformers can provide galvanic isolation, reducing the risk of electrical shock and protecting equipment from potential damage.
Types of Transformers in Power Distribution and Transmission
Various types of transformers are used in power distribution and transmission systems, each with its specific functions:
- Distribution transformers: These transformers are used to step down voltage levels in distribution systems, making the electricity suitable for end-users.
- Power transformers: These large transformers are used in substations and power plants for voltage regulation and long-distance transmission of electrical energy.
- Instrument transformers: These specialized transformers are used for measuring and monitoring voltage and current levels in the electrical grid, ensuring the safe and reliable operation of the system.
Conclusion
Transformers play a crucial role in power distribution and transmission systems by regulating voltage levels, minimizing power losses, and maintaining power quality. They ensure the efficient transfer of electrical energy from power plants to end-users and contribute to the safe and reliable operation of the electrical grid.