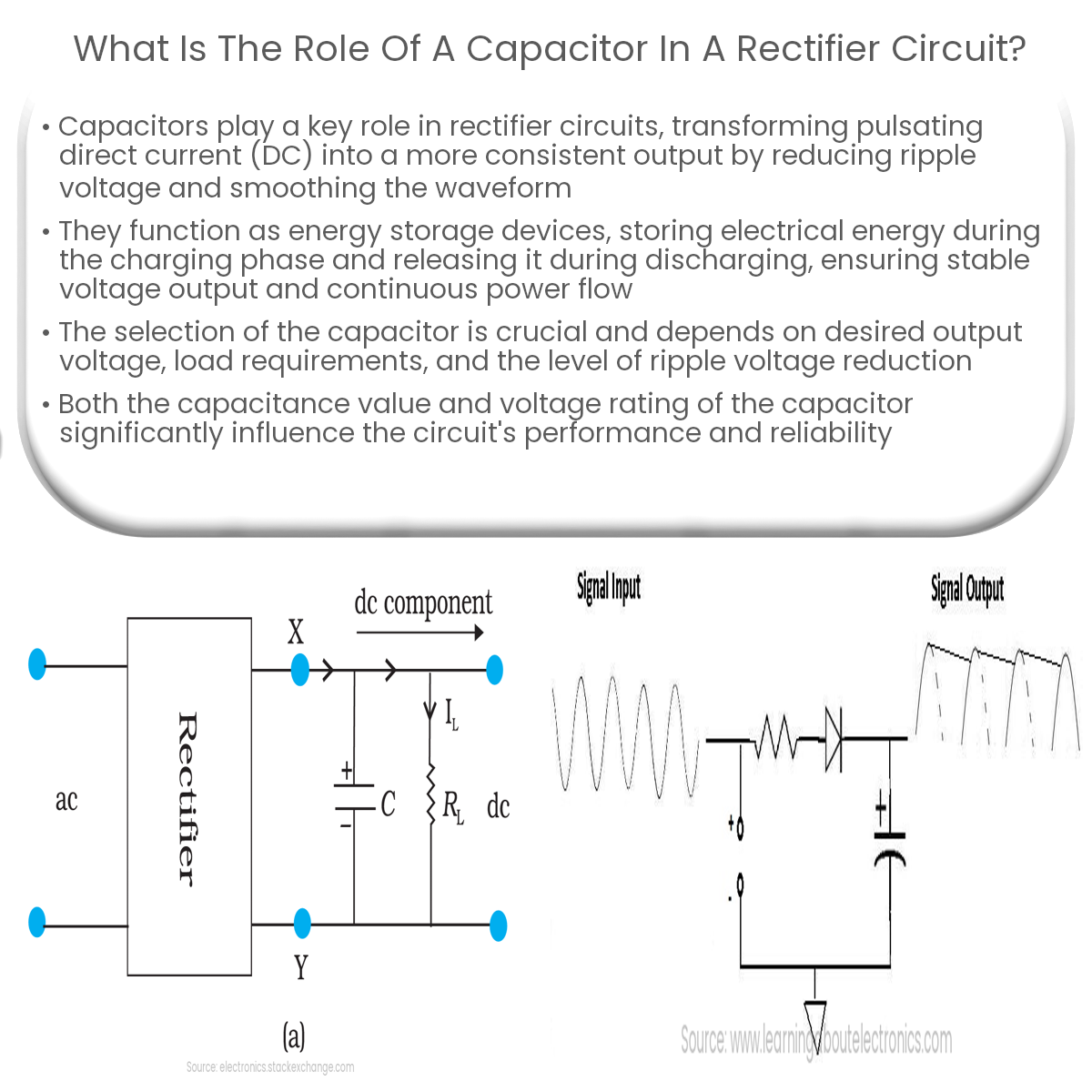
A capacitor in a rectifier circuit smooths the pulsating DC output, reduces ripple voltage, and provides continuous power to the load.
Role of a Capacitor in a Rectifier Circuit
A rectifier circuit is designed to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). This conversion process often results in a pulsating DC output that varies with time. To obtain a smoother and more constant DC output, a capacitor is introduced into the rectifier circuit. In this article, we will explore the role of a capacitor in a rectifier circuit and how it improves the performance of the system.
Smoothing the Output Voltage
The primary function of a capacitor in a rectifier circuit is to smooth the pulsating DC output. After the AC input has been converted to a pulsating DC waveform, the capacitor is connected in parallel with the output load to filter out the ripple voltage. The capacitor charges during the peak of the pulsating waveform and discharges during the troughs, providing a constant voltage across the load.
Reducing Ripple Voltage
Ripple voltage is the residual AC component in the DC output of a rectifier circuit. The capacitor plays a crucial role in minimizing this ripple voltage. The larger the capacitor, the more effective it is at reducing the ripple voltage. The capacitance value is chosen based on the desired level of output voltage regulation and the load requirements.
Energy Storage and Release
A capacitor acts as an energy storage device in a rectifier circuit. During the charging phase, it stores electrical energy in its electric field. During the discharging phase, it releases the stored energy to the load, maintaining a stable voltage output. This energy storage and release process helps maintain a continuous flow of power to the load even when the input AC waveform is at its lowest point.
Capacitor Selection
Choosing the right capacitor for a rectifier circuit depends on factors such as the desired output voltage, load requirements, and the level of ripple voltage reduction. The capacitance value and the voltage rating of the capacitor are crucial parameters to consider. A higher capacitance value results in better smoothing performance but may also increase the size and cost of the capacitor. The voltage rating of the capacitor should be greater than the peak voltage of the rectifier output to avoid capacitor failure.
Conclusion
In summary, capacitors play a vital role in rectifier circuits by smoothing the output voltage, reducing ripple voltage, and providing continuous power to the load. The selection of the appropriate capacitor is essential to ensure the desired performance and reliability of the rectifier circuit.