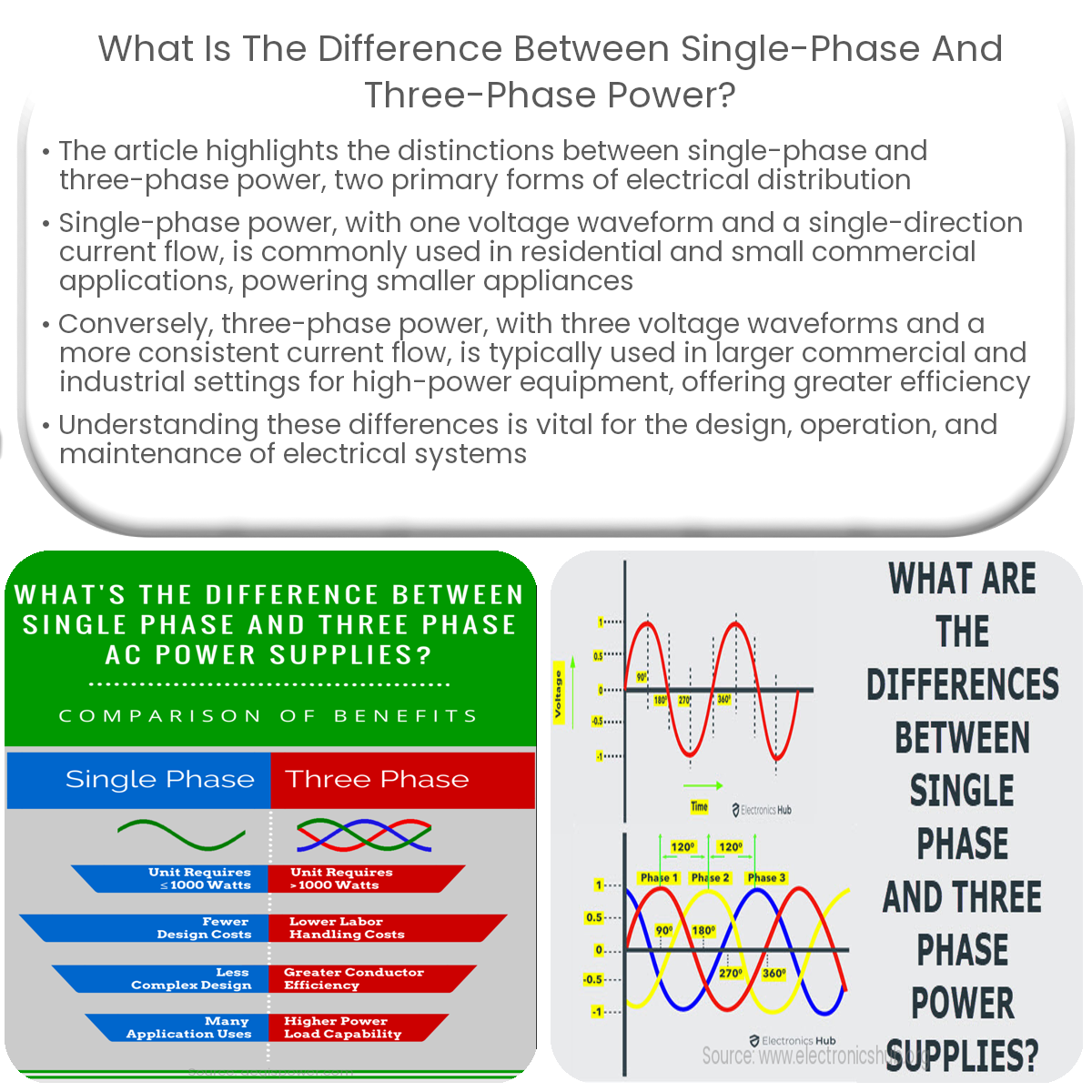
Single-phase power has one voltage waveform, while three-phase power has three, making the latter more efficient and suitable for larger applications.
Difference Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power
Electricity is primarily distributed in two forms: single-phase and three-phase power. Each form has its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. This article will explore the differences between single-phase and three-phase power, along with their uses in various contexts.
Single-Phase Power
Single-phase power is an electrical distribution system with only one voltage waveform. It is the most common type of electrical service used in residential and small commercial applications. In a single-phase system, the voltage reaches its peak value at one point in each cycle, with the current flowing in only one direction. This type of power is suitable for smaller loads and is often used for lighting, heating, and powering smaller appliances.
Three-Phase Power
Three-phase power is an electrical distribution system with three voltage waveforms, each offset by 120 degrees from the others. This type of power distribution is typically used for larger commercial and industrial applications, where higher power levels are required. In a three-phase system, the voltage reaches its peak value at three different points in each cycle, providing a more consistent and continuous flow of power. This results in higher efficiency, smoother operation, and increased reliability for equipment such as motors, generators, and transformers.
Key Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power
Single-phase and three-phase power differ in several ways:
- Voltage waveforms: Single-phase power has one voltage waveform, while three-phase power has three voltage waveforms, offset by 120 degrees from each other.
- Current flow: Single-phase power has a single-direction current flow, while three-phase power has a more consistent and continuous flow of current.
- Efficiency: Three-phase power is generally more efficient than single-phase power, particularly for large electrical loads.
- Applications: Single-phase power is typically used for residential and small commercial applications, while three-phase power is used for larger commercial and industrial applications.
Applications of Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power
Both single-phase and three-phase power have specific applications:
- Single-phase power is commonly used in homes, small businesses, and rural areas, where power requirements are relatively low. It is suitable for lighting, heating, and running small appliances.
- Three-phase power is used in larger commercial and industrial settings, where higher power levels are needed for equipment such as motors, generators, and transformers. It provides a more stable and efficient power supply for these applications.
Conclusion
Single-phase and three-phase power are the two primary types of electrical distribution systems, each with its own characteristics and applications. Understanding the differences between these two forms of power is essential for designing, operating, and maintaining electrical systems in various contexts, from residential to large-scale industrial applications.