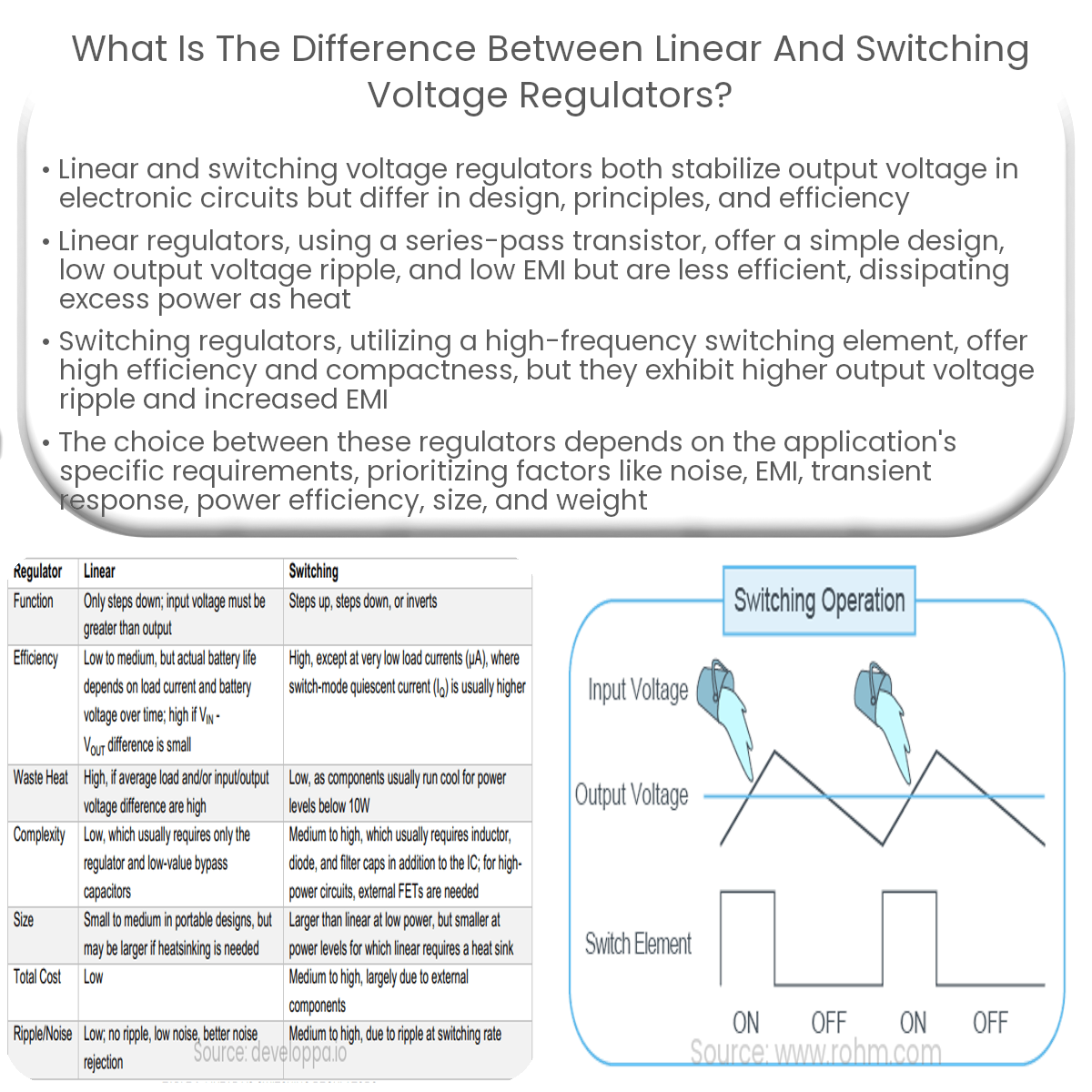
Linear regulators maintain voltage using a series-pass transistor, while switching regulators use high-frequency switching elements for higher efficiency.
Linear vs. Switching Voltage Regulators
Both linear and switching voltage regulators are used to maintain a stable output voltage in electronic circuits. However, they differ in their design, operating principles, and efficiency.
Linear Voltage Regulators
Linear voltage regulators work by using a series-pass transistor to drop the excess voltage between the input and output. The transistor’s resistance changes as needed to maintain a constant output voltage. Some key characteristics of linear regulators are:
- Simple design and easy implementation
- Low output voltage ripple and low electromagnetic interference (EMI)
- Fast transient response
- Highly accurate output voltage
However, linear regulators are less efficient than switching regulators, as they dissipate excess power as heat. This can lead to high power losses, especially when the difference between the input and output voltages is large or when the current drawn is high.
Switching Voltage Regulators
Switching voltage regulators use a different approach to regulate voltage. They use a high-frequency switching element, typically a transistor, to rapidly switch the input voltage on and off. This creates a pulsating output voltage, which is then filtered and smoothed to obtain a stable output. Key features of switching regulators include:
- High efficiency, as they do not dissipate excess power as heat
- Ability to step-up (boost), step-down (buck), or invert the input voltage
- Compact size and lighter weight compared to linear regulators
However, switching regulators have a few disadvantages, such as higher output voltage ripple and increased EMI due to their high-frequency operation. Additionally, they are more complex in design and may require additional components.
Choosing the Right Voltage Regulator
The choice between linear and switching voltage regulators depends on the specific requirements of the application. If low noise, low EMI, and fast transient response are critical, a linear regulator may be the best choice. However, if power efficiency, size, and weight are more important, a switching regulator would be a better option.