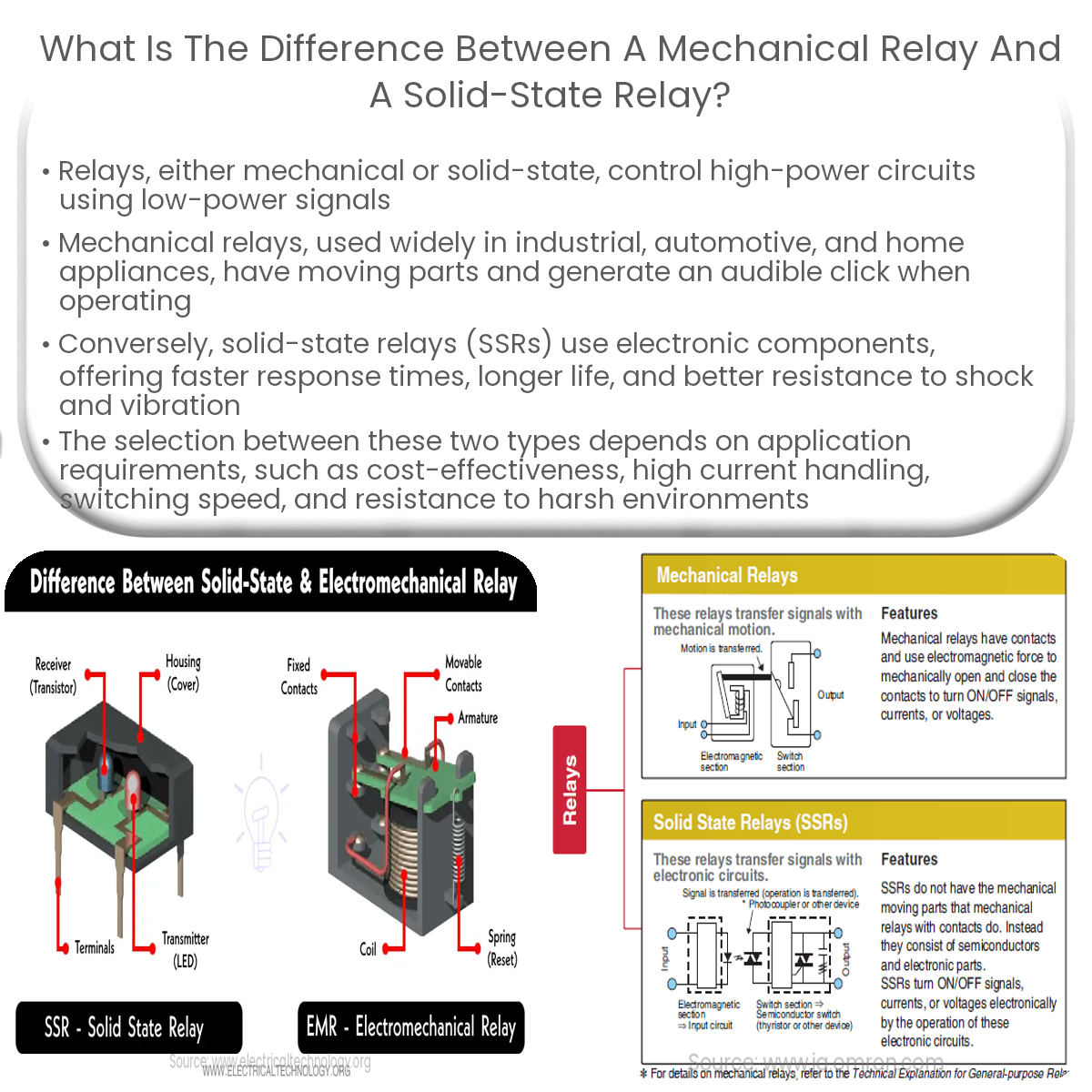
Mechanical relays have moving parts, while solid-state relays use electronic components. SSRs offer faster switching, longer life, and better resistance.
Mechanical Relay vs. Solid-State Relay
Relays are electromechanical or electronic devices that enable the control of high-power circuits using low-power signals. There are two primary types of relays: mechanical relays and solid-state relays. This article will explore the differences between these two types of relays and their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Mechanical Relay
Mechanical relays are electromechanical switches that consist of a coil, a set of contacts, and an armature. When an electric current passes through the coil, a magnetic field is generated, causing the armature to move and open or close the contacts. This operation allows the mechanical relay to control high-power circuits using low-power control signals. Mechanical relays have been widely used for decades in various applications, such as industrial equipment, automotive systems, and home appliances.
Solid-State Relay
Solid-state relays (SSRs) are electronic switches that perform a similar function to mechanical relays but have no moving parts. SSRs use semiconductor components, such as transistors, thyristors, or optocouplers, to switch the high-power circuit. Since SSRs rely on electronic components, they have a faster response time, longer life, and better resistance to shock and vibration compared to mechanical relays.
Key Differences
- Construction: Mechanical relays have moving parts, while solid-state relays rely on electronic components.
- Switching Speed: Solid-state relays have a faster response time than mechanical relays, making them more suitable for applications that require high-speed switching.
- Lifetime: Due to the absence of moving parts, solid-state relays generally have a longer life and higher reliability than mechanical relays.
- Noise: Mechanical relays produce an audible clicking noise during operation, whereas solid-state relays are silent.
- Resistance to Shock and Vibration: Solid-state relays are more resistant to shock and vibration compared to mechanical relays, making them suitable for harsh environments.
Conclusion
Both mechanical and solid-state relays have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on the specific application requirements. Mechanical relays are generally more cost-effective and can handle higher currents, making them suitable for many industrial and automotive applications. On the other hand, solid-state relays offer faster switching speeds, longer life, and better resistance to shock and vibration, making them ideal for applications requiring high reliability and precision control.