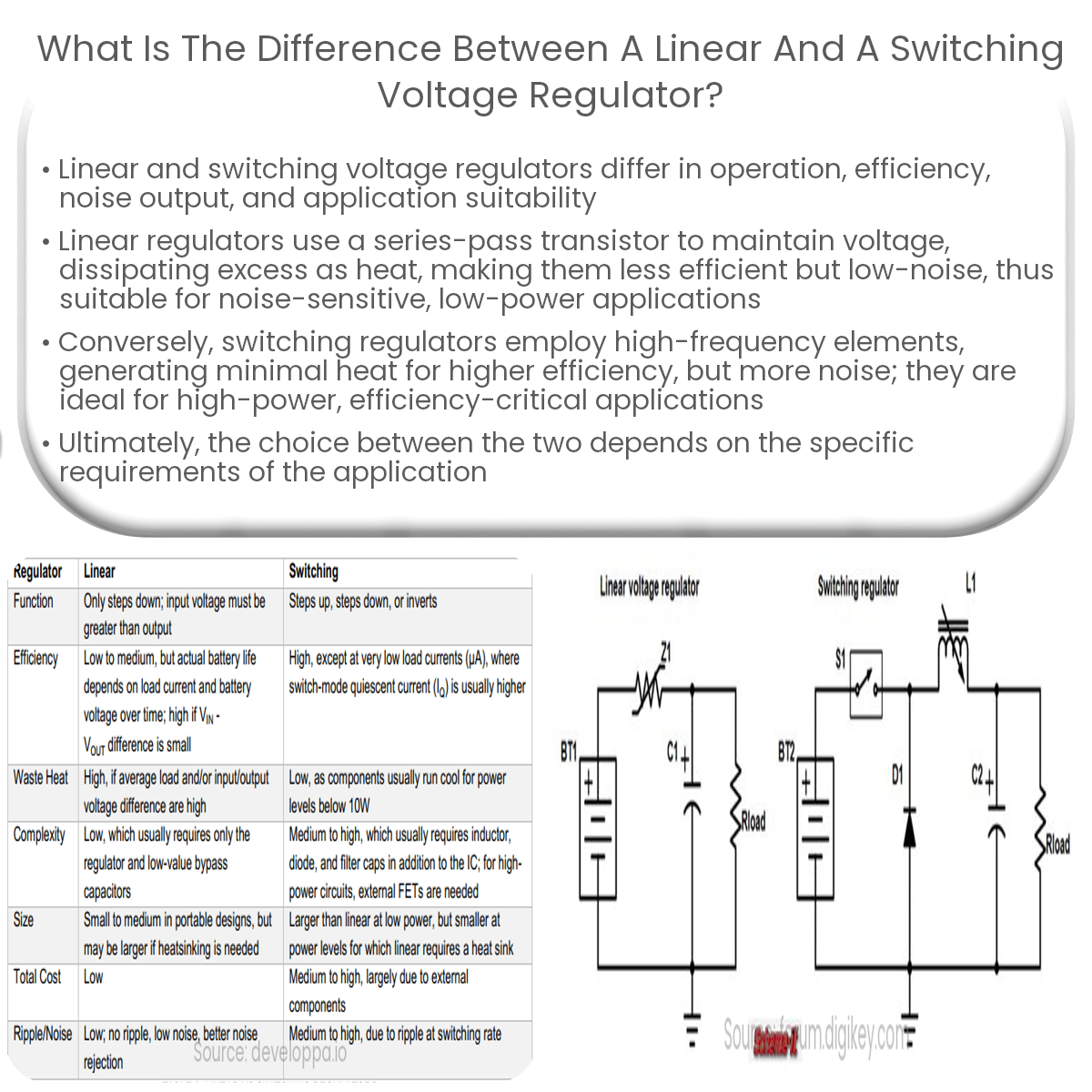
Linear regulators use a series-pass transistor for constant output, while switching regulators use high-frequency elements for higher efficiency.
Linear vs. Switching Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators play a vital role in electronic systems, ensuring a stable and constant output voltage. This article will discuss the differences between linear and switching voltage regulators, focusing on their working principles, efficiency, and applications.
1. Working Principle
Linear and switching voltage regulators employ distinct methods for regulating voltage:
- Linear Voltage Regulators: These regulators use a series-pass transistor to control the output voltage. The regulator adjusts the transistor’s resistance to maintain a constant output voltage, regardless of input voltage fluctuations or load current changes.
- Switching Voltage Regulators: These regulators use a high-frequency switching element, such as a transistor or MOSFET, to control the output voltage. The switching element rapidly alternates between “on” and “off” states, with the duty cycle adjusted to achieve the desired output voltage. The output voltage is then filtered and smoothed using capacitors and inductors.
2. Efficiency
One of the key differences between linear and switching voltage regulators is their efficiency:
- Linear Voltage Regulators: These regulators are less efficient, as they dissipate excess voltage as heat. This can result in significant power loss and may require heat sinks to manage thermal dissipation in some applications.
- Switching Voltage Regulators: These regulators are more efficient, as the switching element generates minimal heat when in its fully “on” or “off” state. This reduces power loss and makes them suitable for applications where power consumption is a concern.
3. Noise and Ripple
Noise and ripple performance are also important factors that differentiate linear and switching voltage regulators:
- Linear Voltage Regulators: These regulators provide a low noise output, making them suitable for noise-sensitive applications, such as audio and precision measurement devices.
- Switching Voltage Regulators: These regulators can generate more noise due to the high-frequency switching. However, careful design and filtering can help minimize noise in many applications.
4. Applications
The choice between linear and switching voltage regulators often depends on the specific application requirements:
- Linear Voltage Regulators: Ideal for low-power, noise-sensitive applications, such as audio equipment, precision instrumentation, and low-current devices.
- Switching Voltage Regulators: Suitable for high-power, efficiency-critical applications, such as portable devices, telecommunications, and automotive systems.
Conclusion
Linear and switching voltage regulators differ in their working principles, efficiency, noise performance, and applications. Linear regulators offer simplicity and low noise output, while switching regulators provide higher efficiency. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the application, with each type offering unique advantages and trade-offs.