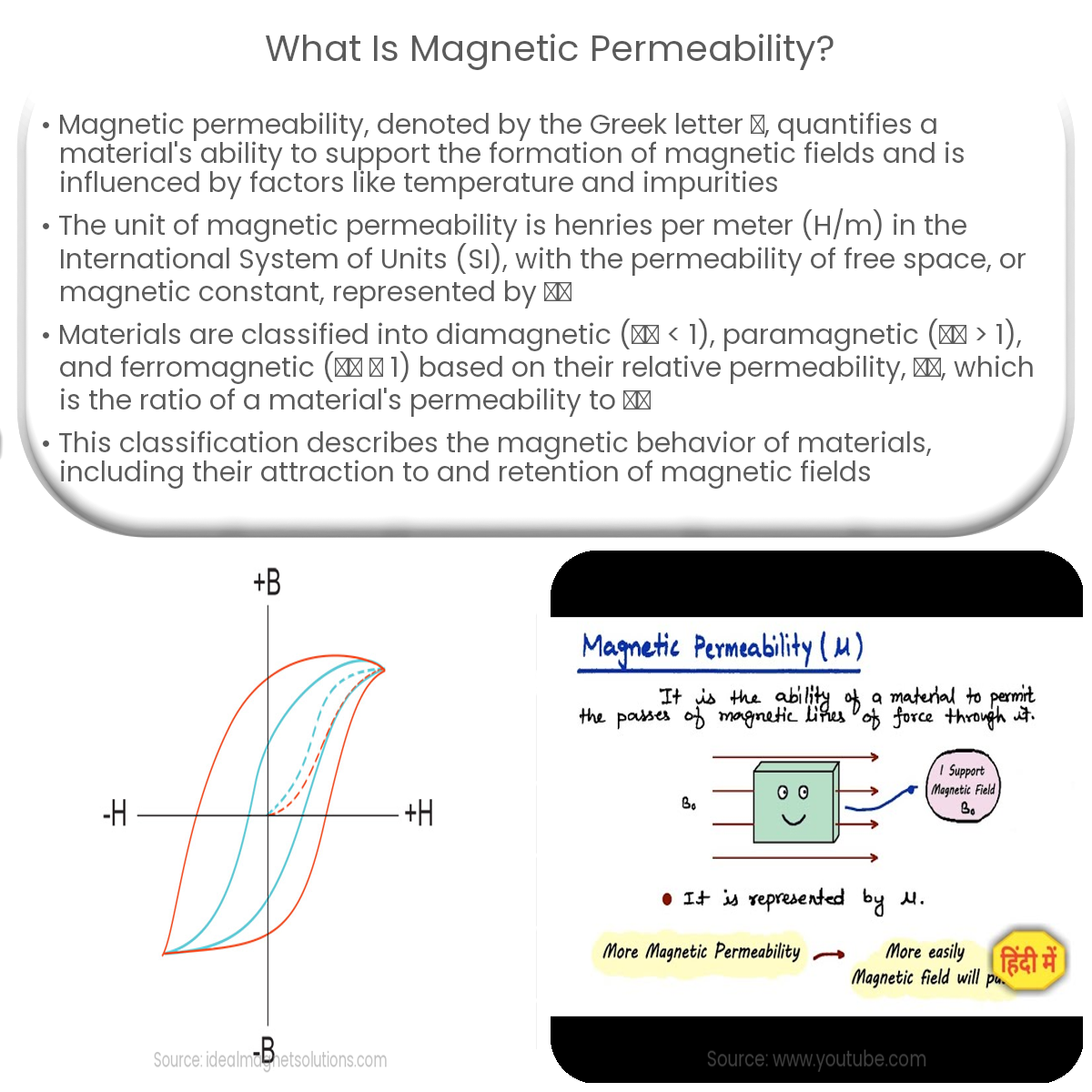
Magnetic permeability is a material’s ability to support magnetic field formation, measured in henries per meter. It varies based on material type.
Understanding Magnetic Permeability
Magnetic permeability is a property of materials that quantifies their ability to support the formation of magnetic fields. In other words, it measures how easily a magnetic field can penetrate a material. The permeability of a material is highly dependent on its composition and structure, which determine its response to an applied magnetic field.
Factors Influencing Permeability
There are several factors that influence the magnetic permeability of a material, including its temperature, impurities, and structural changes. As the temperature of a material increases, its magnetic permeability generally decreases. Similarly, the presence of impurities can disrupt the alignment of magnetic domains, leading to a reduction in permeability.
Units and Dimensions
The magnetic permeability is typically denoted by the Greek letter μ (mu) and has the unit of henries per meter (H/m) in the International System of Units (SI). The permeability of free space, also known as the magnetic constant, is represented by μ0 and has a value of approximately 4π × 10-7 H/m.
Relative Permeability and Types of Materials
Materials can be classified into three categories based on their magnetic permeability: diamagnetic, paramagnetic, and ferromagnetic. The relative permeability (μr) is a dimensionless quantity that represents the ratio of a material’s permeability (μ) to the permeability of free space (μ0). It is used to describe the magnetic behavior of different materials:
- Diamagnetic materials have a relative permeability less than 1 (μr < 1), meaning they have a lower permeability than free space. These materials weakly repel magnetic fields.
- Paramagnetic materials have a relative permeability slightly greater than 1 (μr > 1). They are weakly attracted to magnetic fields but do not retain any magnetization after the field is removed.
- Ferromagnetic materials possess a relative permeability much greater than 1 (μr ≫ 1), which results in a strong attraction to magnetic fields. These materials can retain their magnetization even after the applied field is removed, forming permanent magnets.
In summary, magnetic permeability is a crucial property that helps to understand the interaction of materials with magnetic fields. It is influenced by various factors and is used to categorize materials based on their magnetic behavior.