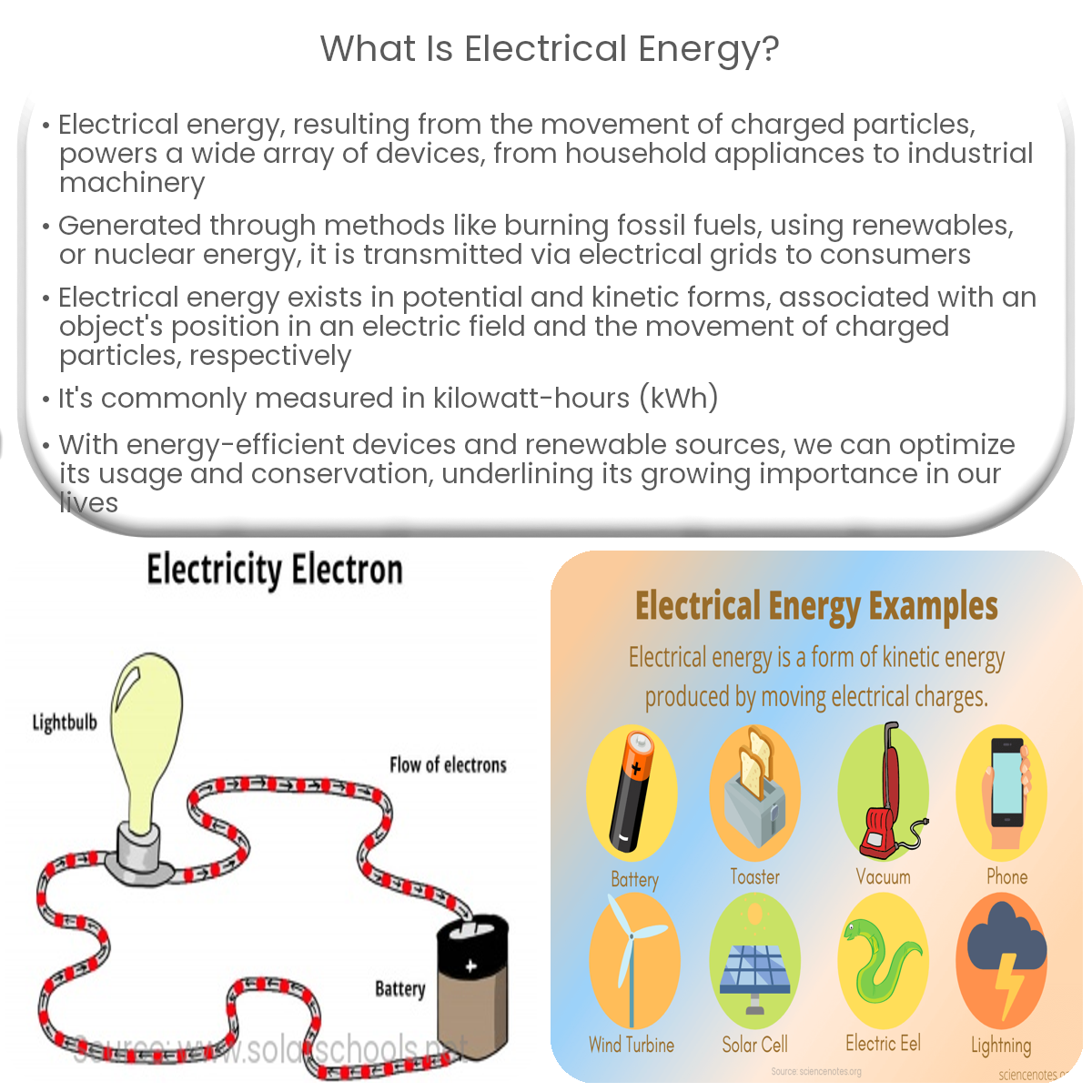
Electrical energy is a form of energy resulting from the movement of charged particles, like electrons, and is widely used to power various devices.
What is Electrical Energy?
Electrical energy is a form of energy that results from the movement of charged particles, such as electrons. It is one of the most widely used and versatile forms of energy in the modern world, powering everything from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Generation and Transmission of Electrical Energy
Electrical energy is generated through various methods, including burning fossil fuels, harnessing renewable resources like solar and wind power, or utilizing nuclear energy. Once produced, the energy is transmitted through electrical grids to reach consumers, where it can be converted into other forms of energy, such as light or heat.
Electrical Energy and Its Forms
Electrical energy can exist in two forms: potential and kinetic. Potential electrical energy, also known as electrostatic energy, is stored in an object when it has an excess of charge. When the charge is allowed to flow, the potential energy is converted into kinetic electrical energy.
- Potential energy: This energy is associated with an object’s position in an electric field. In a capacitor, for example, potential energy is stored when a voltage is applied, causing the separation of charges.
- Kinetic energy: This energy is associated with the movement of charged particles, such as electrons. In an electrical circuit, the kinetic energy of electrons is responsible for powering devices and appliances.
Measuring Electrical Energy
Electrical energy is typically measured in units called joules (J). However, for practical purposes, a more common unit of measurement is the kilowatt-hour (kWh), which represents the amount of energy consumed when one kilowatt of power is used for one hour. This unit is frequently used to measure electrical energy consumption in households and businesses.
Efficiency and Conservation
Efficiency in electrical energy usage is a critical aspect of conserving resources and reducing environmental impact. By using energy-efficient devices and appliances, we can minimize energy loss and reduce overall consumption. Additionally, investing in renewable energy sources and implementing smart grid technology can help optimize the generation, distribution, and utilization of electrical energy.
Conclusion
Electrical energy plays a vital role in our daily lives, powering a wide range of devices and systems. Understanding its generation, transmission, and conversion is essential for efficient usage and conservation. As we continue to develop new technologies and innovative solutions, the importance of electrical energy will only continue to grow.