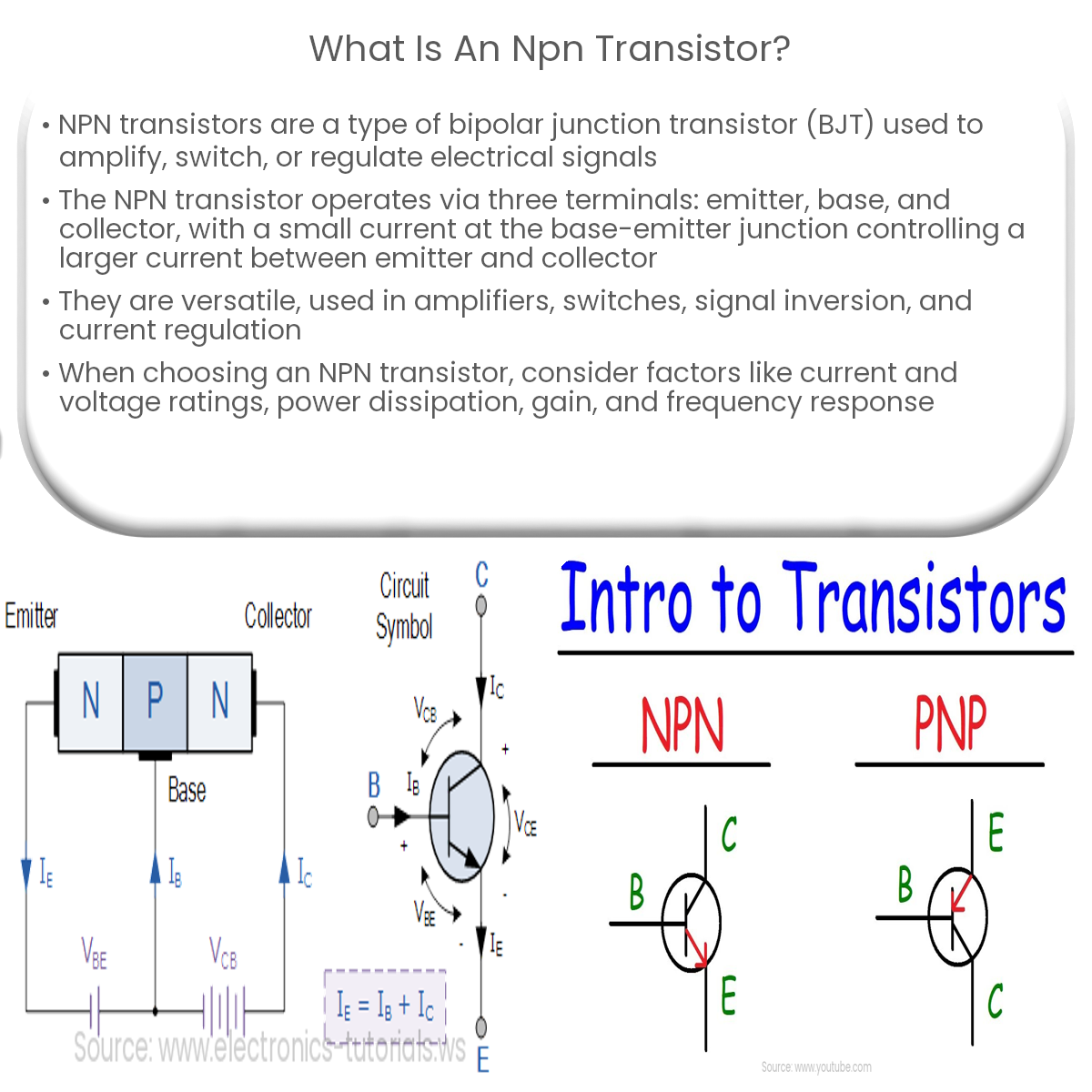
An NPN transistor is a bipolar junction transistor with two N-type semiconductor layers surrounding a P-type layer, used for amplification and switching.
Introduction to NPN Transistors
An NPN transistor is a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT), which is a fundamental component used in electronic circuits to amplify, switch or regulate electrical signals. The NPN transistor is composed of two N-type semiconductor layers sandwiching a P-type semiconductor layer, hence the name NPN.
Structure and Operation
The NPN transistor has three terminals: the emitter, base, and collector. The emitter is the source of majority carriers (electrons in the case of NPN), the base is the controlling terminal, and the collector is the output terminal. In an NPN transistor, a small current applied to the base-emitter junction allows a larger current to flow between the emitter and the collector.
When a positive voltage is applied to the base-emitter junction, the transistor is said to be in the “ON” state, or forward-biased. This allows the majority carriers (electrons) to flow from the emitter to the collector. Conversely, when a negative or zero voltage is applied to the base-emitter junction, the transistor is in the “OFF” state, or reverse-biased, and no current flows between the emitter and collector.
Applications
NPN transistors are versatile and widely used in various electronic applications, including:
- Amplifiers: They can amplify weak input signals, such as audio or radio signals, to produce a stronger output signal.
- Switches: NPN transistors can act as electronic switches to turn circuits ON or OFF, controlling devices like relays and motors.
- Signal inversion: They can be used to invert digital logic signals in circuits, such as in NOT gates or inverters.
- Current regulation: They can be employed in voltage regulators and current sources to provide stable output currents and voltages.
Choosing the Right NPN Transistor
When selecting an NPN transistor for a specific application, consider the following parameters:
- Current rating: Ensure the transistor can handle the required collector current without overheating or damage.
- Voltage rating: The transistor’s collector-emitter and collector-base voltage ratings must be suitable for the circuit’s voltage levels.
- Power dissipation: Check the transistor’s maximum power dissipation to avoid overheating during operation.
- Gain: The transistor’s current gain, or hFE, should meet the amplification requirements of the application.
- Frequency response: For high-frequency applications, select a transistor with a suitable transition frequency (fT).