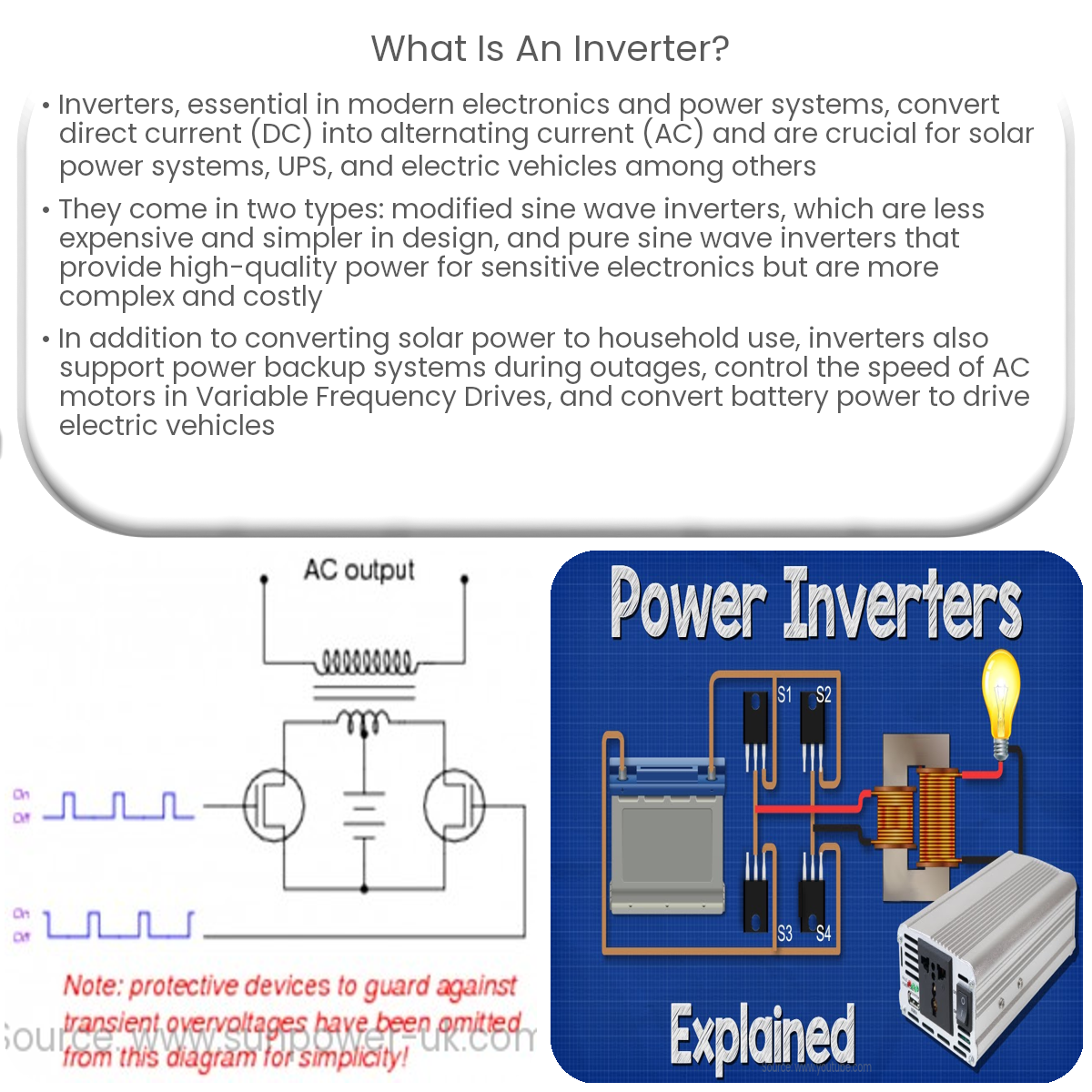
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), used in solar power systems, UPS, and electric vehicles.
Introduction to Inverters
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). Inverters play a crucial role in various applications, including solar power systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and electric vehicles. This article will provide an overview of inverters, their types, and their applications.
Types of Inverters
There are two primary types of inverters: modified sine wave inverters and pure sine wave inverters. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages.
Modified Sine Wave Inverters
Modified sine wave inverters generate an AC output waveform that approximates a sine wave. The output waveform consists of a series of steps, which creates a waveform that is not as smooth as a pure sine wave. These inverters are less expensive and more straightforward to design, making them a popular choice for many applications.
Pure Sine Wave Inverters
Pure sine wave inverters generate an AC output waveform that closely resembles a perfect sine wave. This type of inverter provides a smooth and continuous output, making it ideal for sensitive electronic equipment that requires high-quality power. Pure sine wave inverters are more complex and expensive compared to modified sine wave inverters.
Applications of Inverters
Inverters have a wide range of applications, including:
- Solar power systems: Inverters are used in solar power systems to convert the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power, which can be used by household appliances or fed back into the power grid.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): In the event of a power outage, a UPS uses an inverter to convert the DC power stored in a battery into AC power, ensuring continuous operation of critical equipment.
- Electric vehicles: Inverters are utilized in electric vehicles to convert the DC power from the battery pack into AC power, which drives the electric motor.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Inverters are used in VFDs to control the speed of AC motors by varying the frequency of the supplied voltage.
- Power backup systems: Inverters are employed in power backup systems to supply AC power to appliances and devices during power outages.
Conclusion
Inverters are essential electronic devices that convert DC power into AC power for various applications, such as solar power systems, UPS, and electric vehicles. The two primary types of inverters, modified sine wave and pure sine wave, cater to different requirements and budgets. With their ability to provide continuous power in various situations, inverters play a critical role in modern electronics and power systems.