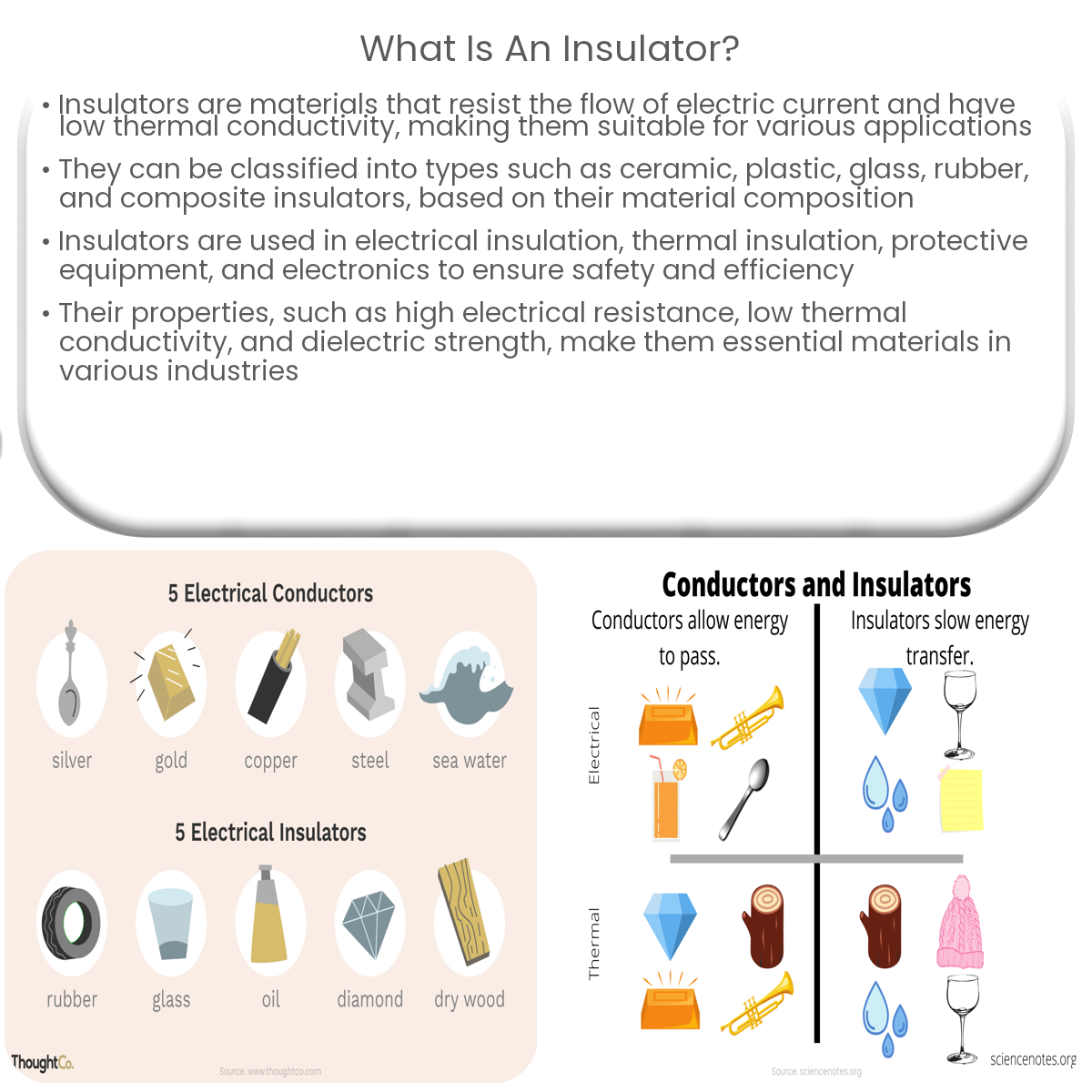
An insulator is a material that doesn’t conduct electric current easily, offering high electrical resistance, low thermal conductivity, and dielectric strength.
Introduction: Understanding Insulators
An insulator is a material that does not easily conduct electric current or allow the flow of electrons. This article will discuss the properties, types, and applications of insulators.
Properties of Insulators
Insulators have certain properties that make them suitable for various applications:
High electrical resistance: Insulators have a high resistance to electric current, which prevents the flow of electrons.
Low thermal conductivity: Insulators do not readily conduct heat, making them useful for thermal insulation in various industries.
Dielectric strength: Insulators can withstand high voltages without breaking down and becoming conductive.
Types of Insulators
Insulators can be classified into different types based on their material composition:
Ceramic insulators: These are made from materials such as porcelain, steatite, and alumina. Ceramic insulators are widely used in high-voltage applications.
Plastic insulators: Plastics like polyethylene, PVC, and Teflon have excellent insulating properties and are used in various electrical and electronic applications.
Glass insulators: Glass insulators are used in high-voltage transmission lines and communication systems due to their high dielectric strength and resistance to environmental factors.
Rubber insulators: Rubber and other elastomeric materials are used as insulators in low-voltage applications and offer flexibility and resilience.
Composite insulators: These insulators are made by combining different materials, such as fiberglass and silicone, to achieve desired electrical and mechanical properties.
Applications of Insulators
Insulators have various applications in the electrical and electronics industry:
Electrical insulation: Insulators are used to separate conductive parts in electrical systems, preventing short circuits and protecting equipment from damage.
Thermal insulation: Insulating materials are used to minimize heat transfer in buildings, appliances, and industrial processes, improving energy efficiency and safety.
Protective equipment: Insulators are used in gloves, boots, and other protective gear to safeguard workers from electrical hazards in high-voltage environments.
Electronics: Insulating materials are used to fabricate printed circuit boards, connectors, and other electronic components to ensure proper functioning and prevent electrical interference.
In conclusion, insulators are essential materials in various industries due to their ability to resist the flow of electric current and provide thermal insulation. They play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical and electronic systems.