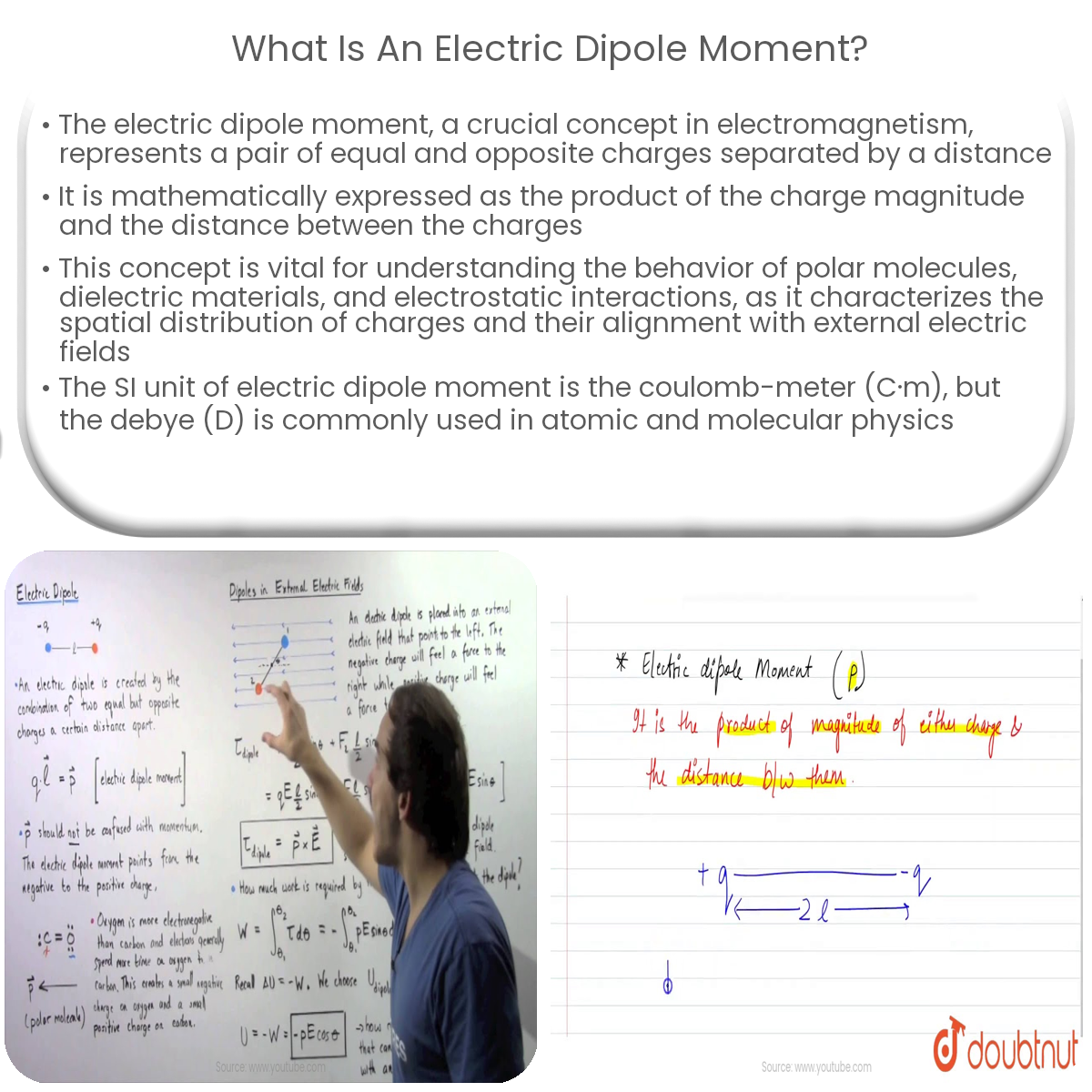
An electric dipole moment is a vector representing equal and opposite charges separated by a distance, crucial for understanding electrostatic interactions.
Introduction to Electric Dipole Moment
An electric dipole moment is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism that helps describe the behavior of charged systems. This article will discuss the definition of electric dipole moment, its mathematical representation, and its significance in various physical phenomena.
Definition of Electric Dipole Moment
An electric dipole moment represents a pair of equal and opposite charges separated by a finite distance. It is a vector quantity that characterizes the spatial distribution of charges and their tendency to align with an external electric field. The electric dipole moment is a critical parameter for understanding the behavior of polar molecules, dielectric materials, and many other electrostatic interactions.
Mathematical Representation of Electric Dipole Moment
Mathematically, the electric dipole moment (p) can be defined as the product of the charge magnitude (q) and the distance (d) between the charges:
p = q · d
The electric dipole moment is a vector directed from the negative charge to the positive charge. Its magnitude is given by the product of the charge and the distance, and its direction is determined by the orientation of the charges.
Significance of Electric Dipole Moment
The electric dipole moment is essential for understanding various physical phenomena, as highlighted below:
- Polar Molecules: Many molecules, such as water, have an inherent electric dipole moment due to the asymmetric distribution of charges within the molecule. This property significantly affects their interactions with other molecules and their behavior in an electric field.
- Dielectric Materials: Dielectric materials contain molecules with electric dipole moments that can be influenced by an external electric field. This property is fundamental to the behavior of capacitors and the polarization of dielectrics.
- Electrostatic Interactions: Electric dipole moments are crucial for understanding various electrostatic interactions, such as dipole-dipole interactions, van der Waals forces, and hydrogen bonding.
Units of Electric Dipole Moment
The SI unit of electric dipole moment is the coulomb-meter (C·m). However, in atomic and molecular physics, the unit debye (D) is commonly used, where 1 D = 3.336 x 10-30 C·m.
In conclusion, the electric dipole moment is a key concept in electromagnetism that characterizes the spatial distribution of charges and their tendency to align with external electric fields. It is essential for understanding the behavior of polar molecules, dielectric materials, and various electrostatic interactions. The electric dipole moment plays a crucial role in the study of electromagnetism and related fields.