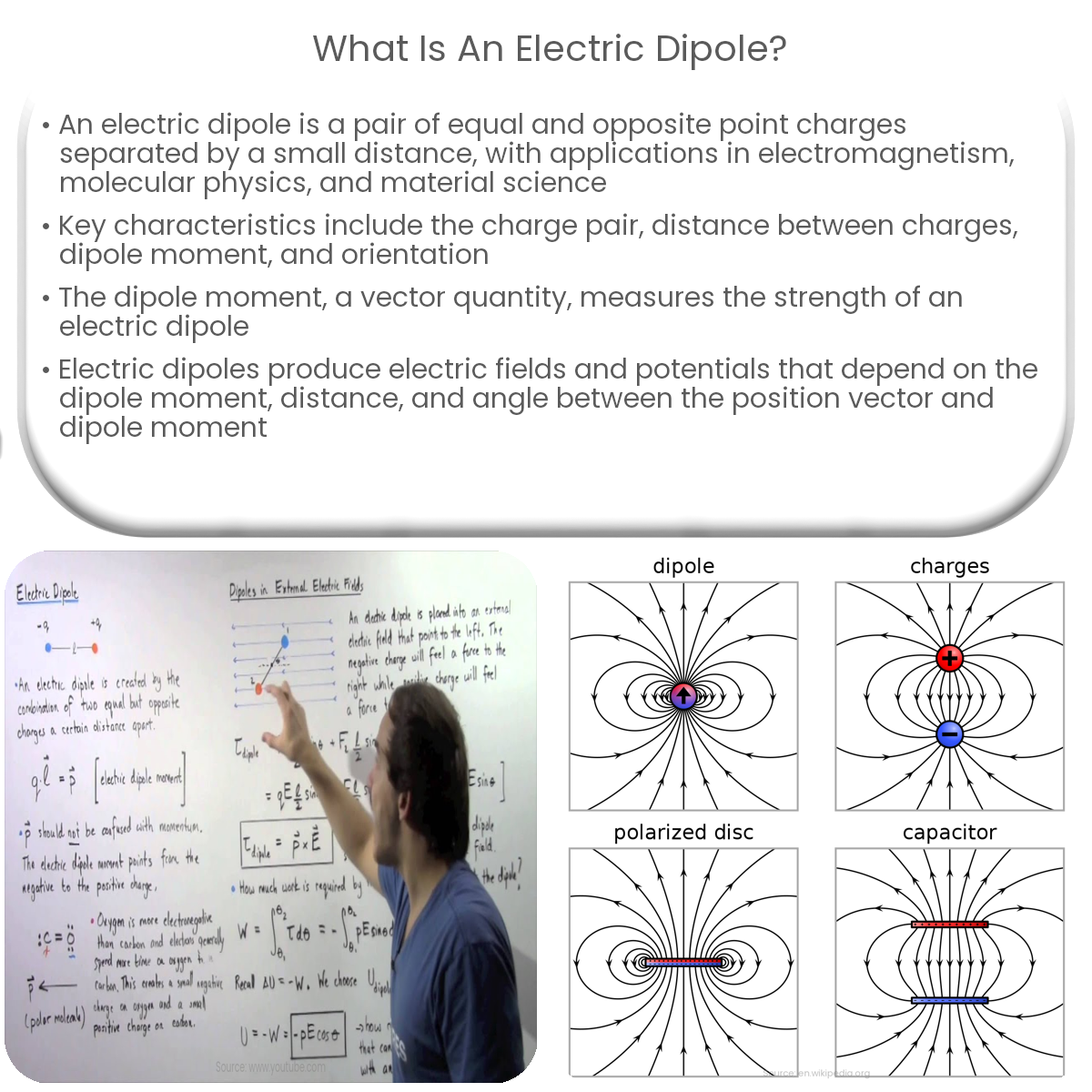
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite point charges separated by a small distance, with a characteristic dipole moment and electric field.
Introduction to Electric Dipoles
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite point charges separated by a small distance. Electric dipoles are important in various areas of physics, including electromagnetism, molecular physics, and material science.
Characteristics of Electric Dipoles
Some key characteristics of electric dipoles include:
Dipole Moment
The dipole moment (p) is a measure of the strength of an electric dipole and is calculated as the product of the charge magnitude (q) and the distance (d) between the charges:
p = q * d
The dipole moment is a vector quantity, with its direction pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge.
Electric Field and Potential Due to an Electric Dipole
An electric dipole produces an electric field in the space surrounding it. The electric field at a point in space due to an electric dipole depends on the dipole moment, the distance between the point and the dipole, and the angle between the dipole moment and the position vector. Calculating the electric field due to an electric dipole involves complex equations, often requiring the use of calculus.
Similarly, the electric potential at a point in space due to an electric dipole depends on the dipole moment, the distance between the point and the dipole, and the angle between the dipole moment and the position vector. The electric potential can be positive, negative, or zero, depending on the point’s location relative to the dipole.
Applications of Electric Dipoles
Electric dipoles are relevant in various applications and scientific fields, such as: