Electric charge density measures the distribution of electric charges per unit volume, area, or length, and is vital for understanding electromagnetism.
Understanding Electric Charge Density
Electric charge density is an essential concept in the study of electromagnetism, which quantifies the distribution of electric charges in a given region. In this article, we will explore the definition, types, and applications of electric charge density.
Definition of Electric Charge Density
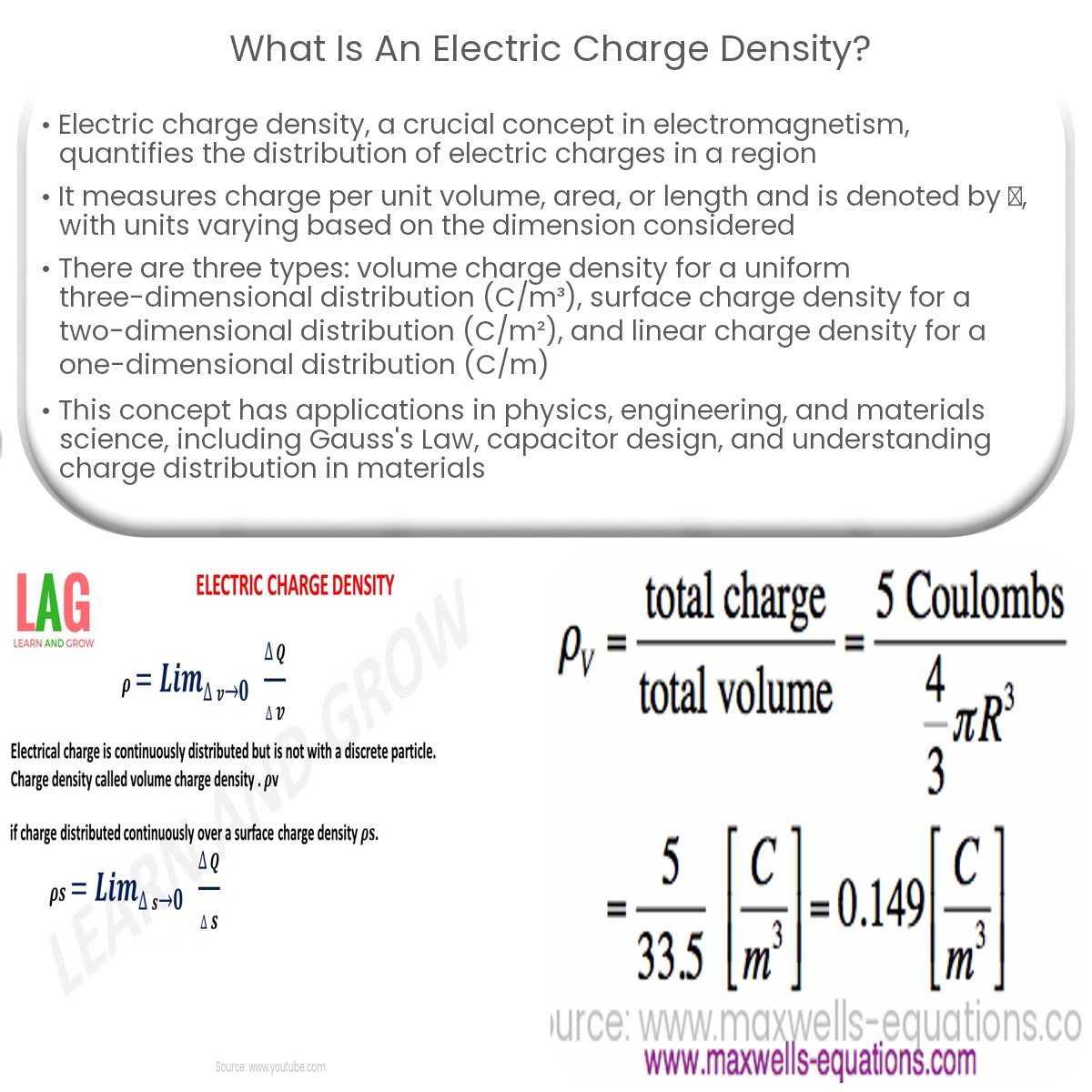
Electric charge density is the measure of the amount of electric charge per unit volume, area, or length. It is generally represented by the symbol ρ (rho) and is expressed in units of coulombs per cubic meter (C/m3), coulombs per square meter (C/m2), or coulombs per meter (C/m) depending on the dimension being considered.
Types of Electric Charge Density
- Volume charge density (ρ): This refers to the amount of electric charge present within a specified volume. It is used when the charge is distributed uniformly throughout a three-dimensional space, and is expressed in units of C/m3.
- Surface charge density (σ): This measures the electric charge per unit area, applicable when the charge is distributed uniformly across a two-dimensional surface. Surface charge density is given in units of C/m2.
- Linear charge density (λ): This describes the electric charge per unit length and is used when the charge is distributed uniformly along a one-dimensional line. Linear charge density is expressed in units of C/m.
Applications of Electric Charge Density
Electric charge density is an essential concept in various fields, including physics, engineering, and materials science. Some applications include:
- Gauss’s Law: Electric charge density plays a crucial role in Gauss’s Law, which relates the electric field surrounding a charged object to the total charge enclosed by the surface. This law is fundamental to understanding the behavior of electric fields and is used extensively in the study of electromagnetism.
- Capacitors: Surface charge density is important in the design and analysis of capacitors, which store electrical energy by accumulating charge on their surfaces. A capacitor’s capacitance is directly related to its surface charge density and the distance between the charged plates.
- Charge distribution in materials: Understanding charge densities is vital in materials science and electronic engineering, as it helps predict the behavior of charged particles within various materials, including conductors, insulators, and semiconductors.
In conclusion, electric charge density is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism, providing a quantitative measure of the distribution of electric charges in various dimensions. It is essential for understanding the behavior of electric fields, designing electronic devices, and studying the properties of materials.