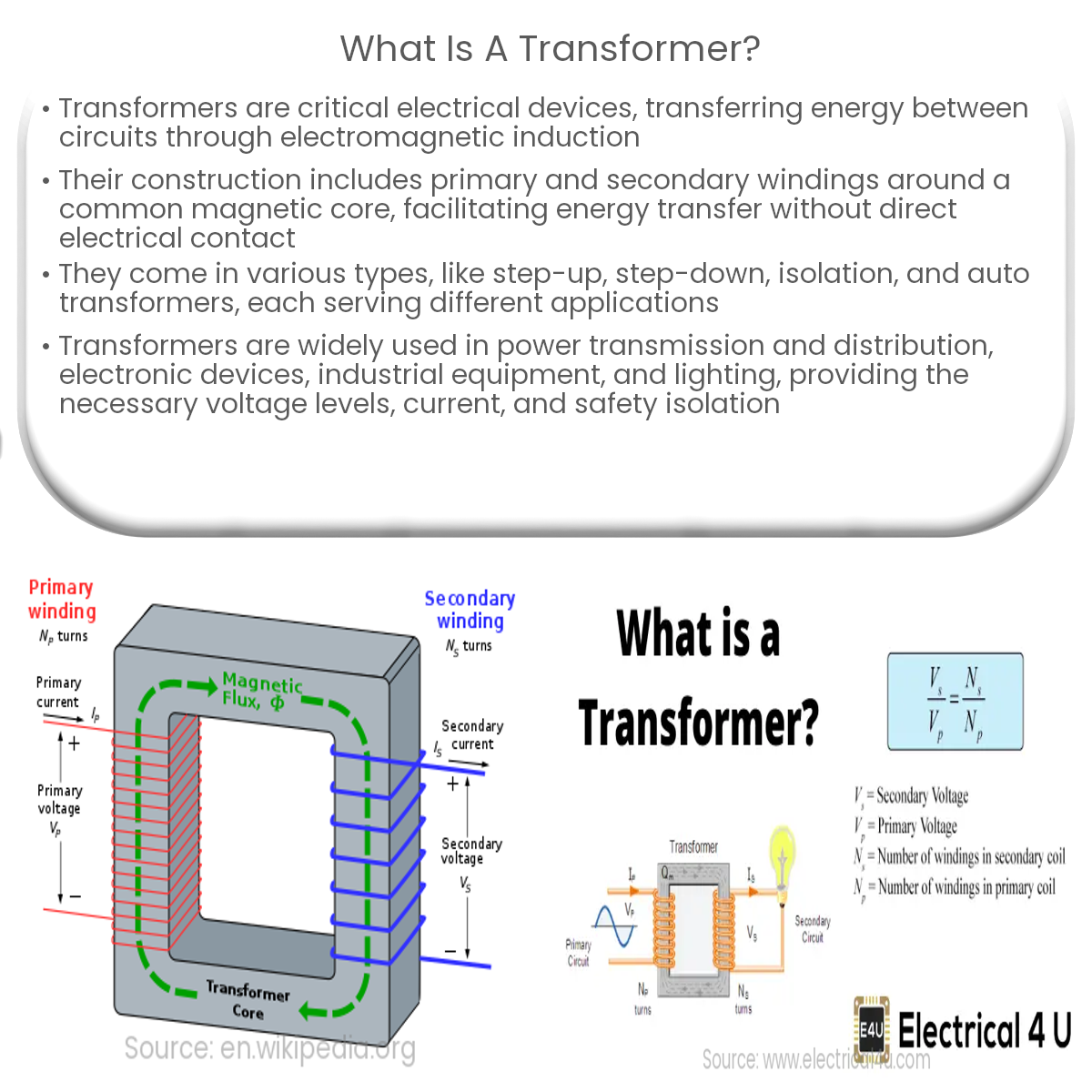
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction, used in power transmission, distribution, and electronics.
Introduction to Transformers
A transformer is an essential electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. It plays a critical role in power transmission and distribution systems, as well as in various electronic applications.
Construction and Principle
Transformers consist of two or more coils, known as primary and secondary windings, wound around a common magnetic core. The primary winding is connected to the input power source, while the secondary winding is connected to the output circuit. When an alternating current (AC) passes through the primary winding, it creates a varying magnetic field, which induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary winding. This process enables the transfer of electrical energy between the primary and secondary circuits without direct electrical contact.
Types of Transformers
Transformers can be classified based on various parameters, such as construction, voltage level, and application. Some common types include:
- Step-up Transformers: These transformers increase the output voltage while decreasing the current, commonly used in power transmission systems.
- Step-down Transformers: They decrease the output voltage while increasing the current, typically used in power distribution systems and electronic devices.
- Isolation Transformers: These transformers have the same input and output voltage but provide galvanic isolation between the primary and secondary circuits, offering protection and noise reduction in sensitive applications.
- Auto Transformers: A single winding serves as both the primary and secondary windings in these transformers, which are more compact and efficient than traditional transformers, but do not provide isolation between input and output.
Applications
Transformers are used in a wide range of applications, such as:
- Power transmission and distribution: Transformers help in stepping up and stepping down voltage levels for efficient power transmission and local distribution.
- Electronic devices: Transformers provide the required voltage levels and isolation for various devices, including computers, televisions, and audio equipment.
- Industrial equipment: Transformers are employed in machine tools, motor control systems, and welding equipment to supply appropriate voltage and current levels.
- Lighting: Transformers are used in halogen and LED lighting systems to regulate voltage and provide isolation for safety purposes.
Conclusion
Transformers are vital electrical devices that transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. Available in various types, transformers are integral to power transmission, distribution, and countless electronic applications, ensuring efficient and safe operation of electrical systems.