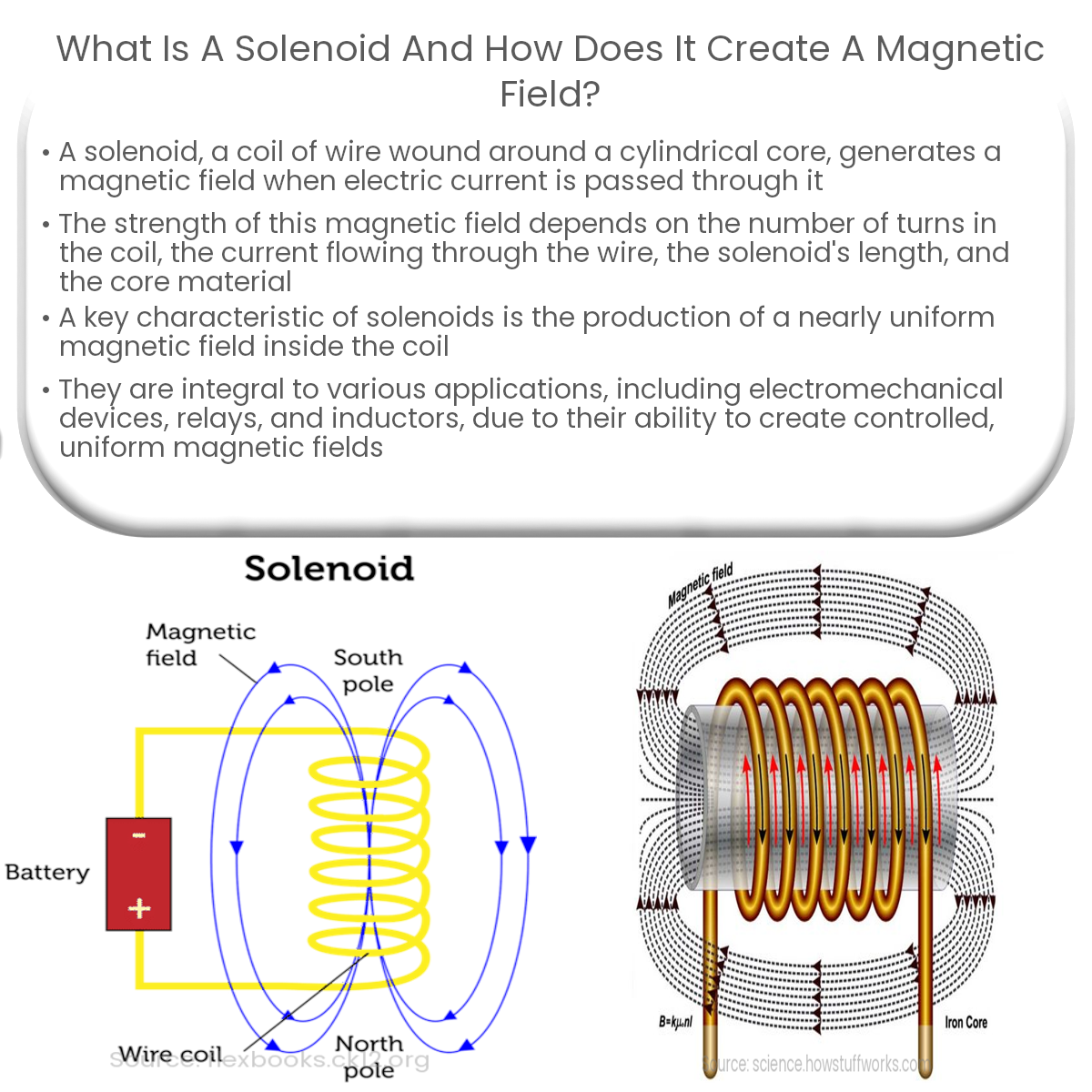
A solenoid is a coil of wire that generates a magnetic field when current flows through it. Its uniform field is used in various applications.
Introduction to Solenoids
A solenoid is a coil of wire wound around a cylindrical core, often made of ferromagnetic material. When an electric current is passed through the wire, it generates a magnetic field within and around the coil. Solenoids are widely used in various applications, such as electromechanical devices, relays, and inductors.
Creating a Magnetic Field
The magnetic field created by a solenoid is primarily due to the current flowing through the wire. According to Ampere’s law, a current-carrying wire generates a circular magnetic field around it. When the wire is wound into a coil, the magnetic fields produced by each turn of the wire add up to form a stronger, more concentrated magnetic field inside the solenoid.
In a solenoid, the direction of the magnetic field is determined by the direction of the current flow. This can be found using the right-hand rule: if you curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the current flow, your thumb will point in the direction of the magnetic field.
Uniform Magnetic Field
One of the key characteristics of a solenoid is that it produces a nearly uniform magnetic field inside the coil, while the magnetic field outside the coil is much weaker. This is because the magnetic field lines inside the solenoid are parallel and evenly spaced, whereas the field lines outside the solenoid curve and spread out.
Factors Affecting the Magnetic Field
The strength of the magnetic field inside a solenoid depends on several factors:
- Number of turns: The more turns of wire in the solenoid, the stronger the magnetic field.
- Current: The greater the current flowing through the wire, the stronger the magnetic field.
- Length: The magnetic field strength decreases as the length of the solenoid increases.
- Core material: A ferromagnetic core can significantly increase the magnetic field strength by concentrating the field lines within the core.
Applications of Solenoids
Solenoids are used in a variety of applications due to their ability to generate a controlled, uniform magnetic field. Some common uses include:
- Electromagnetic relays and switches
- Electromechanical actuators and valves
- Electromagnetic locks
- Transformers and inductors
- Medical imaging devices
In conclusion, solenoids are an essential component in many electrical and electromechanical systems, owing to their ability to generate a strong, uniform magnetic field.