A resistor is an electronic component that controls and regulates electric current flow in circuits by providing a specific level of resistance.
Introduction to Resistors
A resistor is a fundamental electronic component used in electrical circuits to control and regulate the flow of electric current. It is designed to have a specific level of electrical resistance, which is a measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current. In this article, we will explore the function, types, and applications of resistors.
Function of a Resistor
The primary function of a resistor is to limit the flow of electric current through a circuit, following Ohm’s Law, which states that the current (I) flowing through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across it and inversely proportional to its resistance (R). Mathematically, this relationship is expressed as:
I = V / R
Resistors help maintain desired current levels, protect components from excessive current, and control voltage levels in various parts of a circuit.
Types of Resistors
Resistors can be classified into several types based on various factors:
- Fixed Resistors: These resistors have a constant resistance value and are the most common type of resistor. Examples include carbon film, metal film, and wirewound resistors.
- Variable Resistors: Also known as potentiometers or rheostats, these resistors have an adjustable resistance value, allowing them to be tuned for specific requirements.
- Thermistors: These resistors exhibit a change in resistance with temperature, making them suitable for temperature sensing and control applications.
- Light-dependent Resistors (LDRs): Also called photoresistors, LDRs change their resistance based on the intensity of light, making them ideal for light-sensing applications.
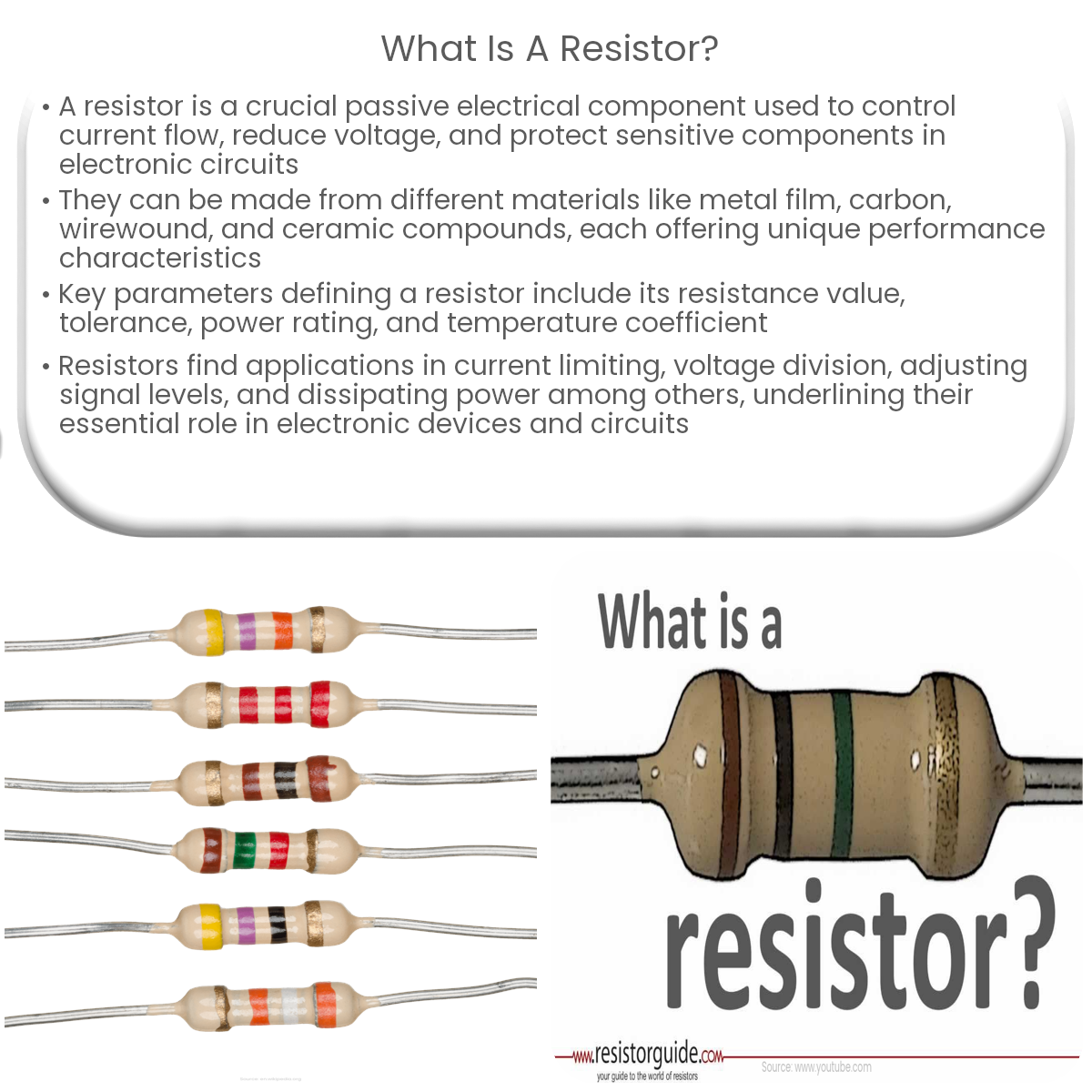
Resistor Color Code and Tolerance
Many fixed resistors use a color-coding system to indicate their resistance value and tolerance. The color code consists of a series of colored bands painted on the resistor’s body. Each color represents a numerical value, and the sequence of colors corresponds to the resistance value and tolerance. Tolerance indicates the range within which the actual resistance value may deviate from the nominal value, expressed as a percentage.
Applications of Resistors
Resistors play a crucial role in a wide variety of electronic circuits and devices. Some common applications include:
- Voltage Division: Resistors can be used to create voltage dividers, which proportionally divide the input voltage to obtain a desired output voltage.
- Current Limiting: Resistors can protect components, such as LEDs, from excessive current by limiting the flow of current in a circuit.
- Timing and Control: Resistors are often used in combination with capacitors to create timing circuits, such as RC oscillators or filters.
- Biasing: In transistor circuits, resistors can help establish proper operating conditions by setting bias voltages and currents.
In conclusion, resistors are essential electronic components that regulate current flow and voltage levels in electrical circuits. Understanding the function, types, and applications of resistors is critical for designing and troubleshooting electronic systems.