A rectifier is an electronic component that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by allowing current to flow in only one direction.
Introduction to Rectifiers
A rectifier is an essential component in electronic circuits that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). The conversion process is called rectification, and rectifiers are used in various applications, such as power supplies, battery charging, and signal processing.
How Rectifiers Work
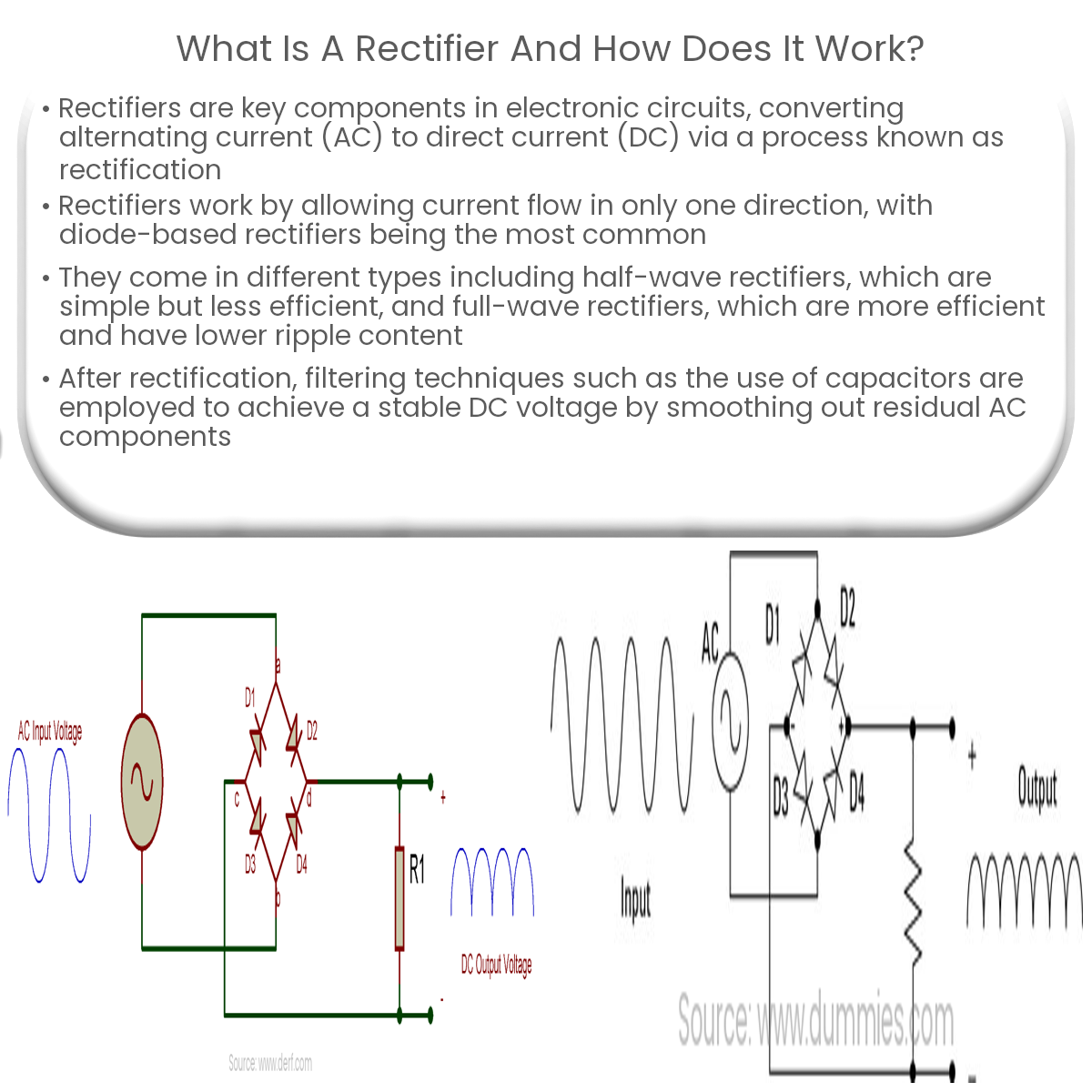
Rectifiers work by allowing current to flow in only one direction, thereby effectively filtering out the negative or positive half of the AC waveform. The most common types of rectifiers are diode-based, where the diodes’ inherent property of allowing current flow in one direction is utilized for rectification.
Types of Rectifiers
- Half-Wave Rectifier: This type of rectifier uses a single diode that allows only the positive or negative half of the AC waveform to pass through. It is the simplest form of rectifier but has low efficiency and high ripple content.
- Full-Wave Rectifier: A full-wave rectifier uses two or more diodes to allow both the positive and negative halves of the AC waveform to pass through. It offers higher efficiency and lower ripple content compared to half-wave rectifiers. There are two main types of full-wave rectifiers:
- Center-Tapped Full-Wave Rectifier: This rectifier uses a center-tapped transformer and two diodes connected to the center tap. The diodes conduct alternately, allowing both halves of the AC waveform to pass through.
- Bridge Rectifier: A bridge rectifier consists of four diodes connected in a bridge configuration. It does not require a center-tapped transformer and offers higher efficiency and better voltage regulation compared to the center-tapped full-wave rectifier.
Filtering and Smoothing
After rectification, the output DC voltage still contains ripples, which are residual AC components. To achieve a smooth and stable DC voltage, capacitors or inductors are used as filters. The most common method is using a capacitor connected in parallel with the load, which stores energy during voltage peaks and releases it during voltage dips, effectively smoothing the voltage waveform.
Conclusion
Rectifiers are crucial components in electronic circuits, responsible for converting AC to DC. They come in various types, such as half-wave and full-wave rectifiers, with different efficiency levels and ripple content. Filtering techniques, like using capacitors, further enhance the output, providing a smooth and stable DC voltage for various applications.