A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), used in power supplies, battery charging, and more.
Introduction to Rectifiers
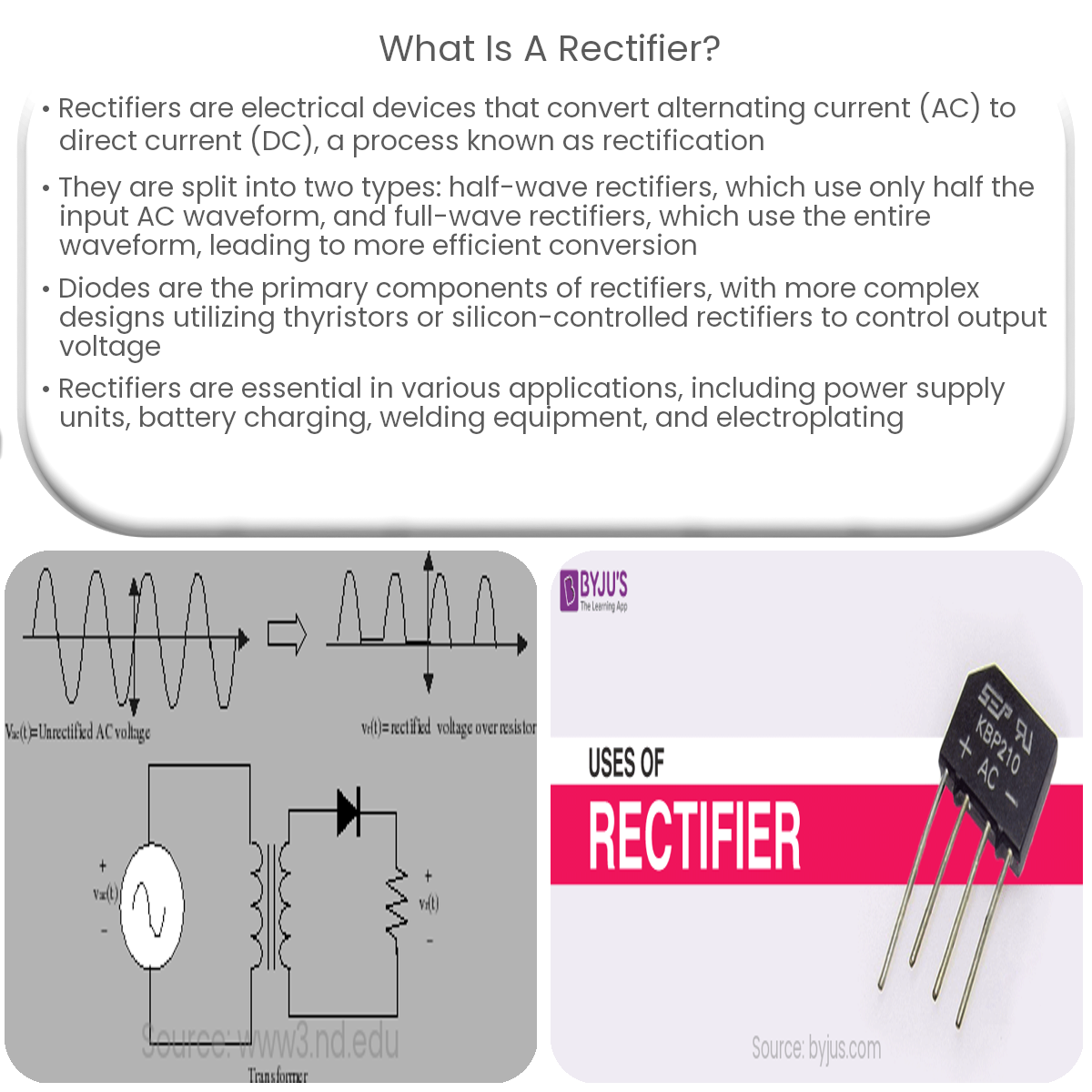
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). The process of converting AC to DC is known as rectification. Rectifiers are essential components in various electronic devices and power supply systems, as many of them require a stable DC voltage to operate correctly.
Types of Rectifiers
Rectifiers can be classified into two main categories: half-wave rectifiers and full-wave rectifiers. Both types are further subdivided into uncontrolled and controlled rectifiers, depending on their ability to control the output voltage.
Rectifier Components
Rectifiers typically employ diodes as their primary components. Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in only one direction, making them ideal for rectification purposes. In more complex designs, thyristors or silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) are used to control the output voltage by varying the conduction angle.
Applications of Rectifiers
Rectifiers are widely used in various applications, including:
In conclusion, rectifiers play a crucial role in the operation of electronic devices and systems by converting AC voltage to DC voltage. Their wide range of applications highlights their importance in modern technology.