A piezoelectric sensor is a transducer that converts mechanical stress or strain into electrical signals, using materials that exhibit the piezoelectric effect.
Introduction to Piezoelectric Sensors
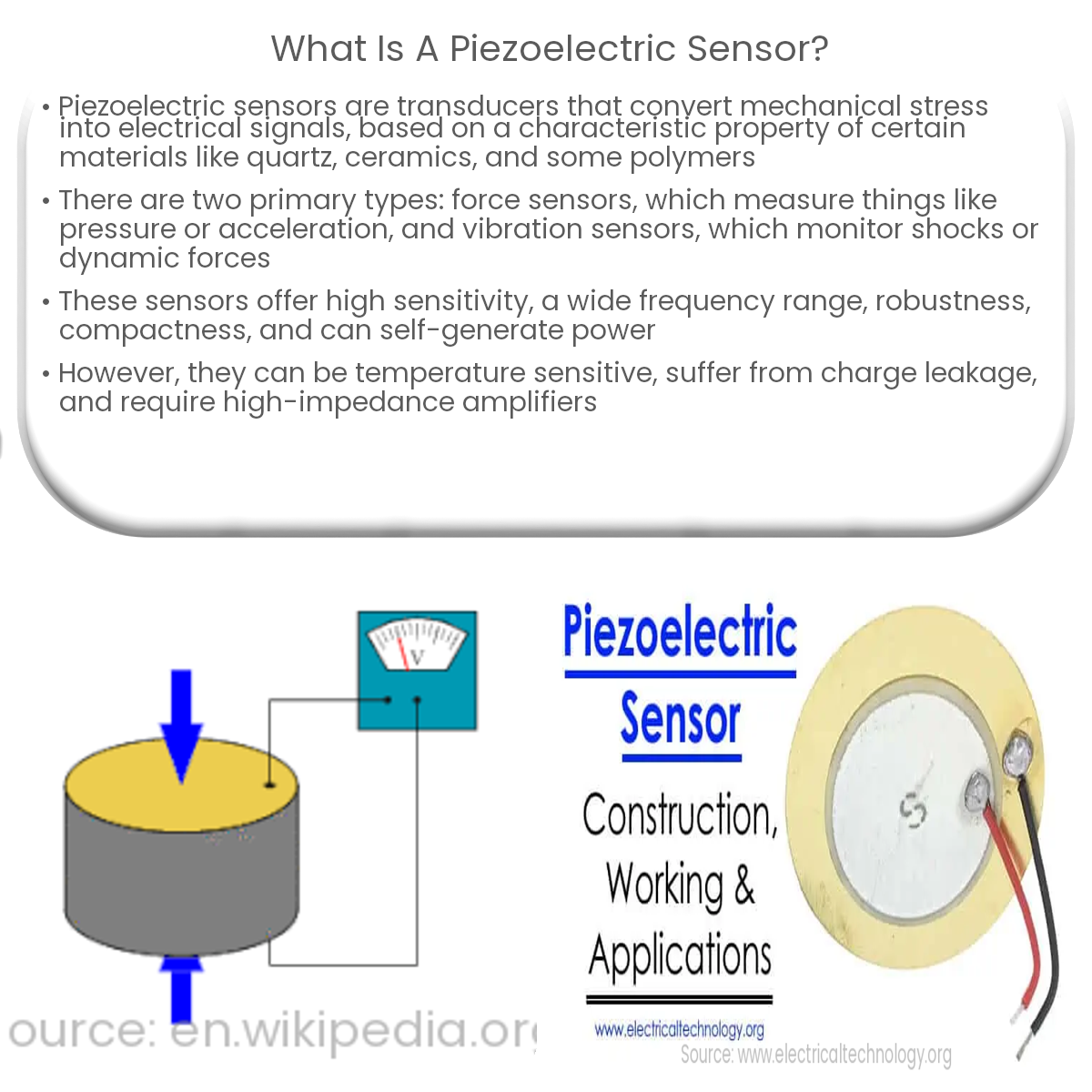
A piezoelectric sensor is a type of transducer that converts mechanical stress or strain into an electrical signal. The term “piezoelectric” is derived from the Greek words “piezo,” which means “to press” or “squeeze,” and “elektron,” meaning “amber” (a material with electrostatic properties). Piezoelectric materials exhibit a unique property where they generate an electric charge in response to applied mechanical stress.
Working Principle of Piezoelectric Sensors
Piezoelectric sensors work based on the piezoelectric effect, a phenomenon observed in certain crystalline materials such as quartz, ceramic, and some polymers. When a mechanical force is applied to these materials, they produce an electric charge proportional to the force applied. Conversely, when an electric field is applied to these materials, they undergo a mechanical deformation. This bidirectional relationship between mechanical stress and electric charge forms the basis for piezoelectric sensors.
Types of Piezoelectric Sensors
There are two main types of piezoelectric sensors:
- Piezoelectric Force Sensors: These sensors measure force, pressure, or acceleration by detecting the charge generated in response to mechanical stress. They are widely used in industrial, automotive, and medical applications, such as pressure sensors, accelerometers, and tactile sensors.
- Piezoelectric Vibration Sensors: Also known as piezoelectric accelerometers, these sensors measure vibrations, shocks, or dynamic forces by converting the mechanical motion into an electrical signal. They find applications in structural health monitoring, machine condition monitoring, and seismic sensing.
Advantages of Piezoelectric Sensors
- High sensitivity: They can detect even minute mechanical changes.
- Wide frequency range: Suitable for detecting a wide range of frequencies, from low-frequency vibrations to high-frequency acoustic waves.
- Robustness: Resistant to harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures, high pressure, and corrosive atmospheres.
- Small size and lightweight: Suitable for integration into compact systems and portable devices.
- Self-generating power: The sensor’s generated charge can be used as a power source, eliminating the need for external power supplies in some applications.
Limitations of Piezoelectric Sensors
- Temperature sensitivity: Output may vary with temperature, requiring additional compensation circuits.
- Charge leakage: Electrical charge may leak over time, leading to signal drift and reduced accuracy.
- High impedance: Requires high-impedance amplifiers to maintain signal integrity.