A galvanometer is a sensitive instrument used to measure small electric currents or detect the presence of a current by utilizing magnetic fields.
Introduction
A galvanometer is a sensitive instrument used to measure small electric currents or to detect the presence of an electric current. It is an essential tool in electrical and electronic measurements, with applications in various fields such as physics, engineering, and telecommunications. This article will discuss the principles, types, and applications of galvanometers.
Operating Principle
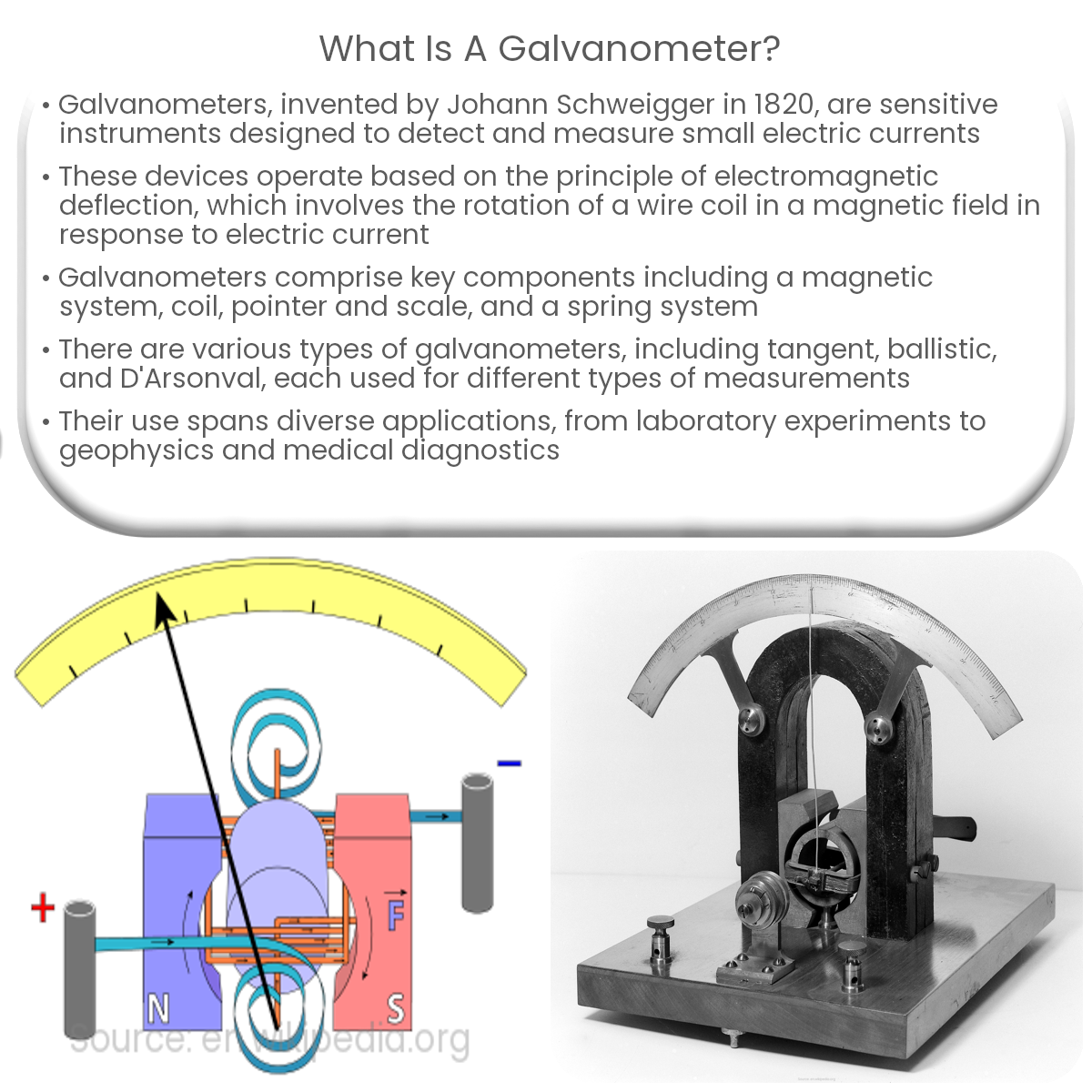
The fundamental principle behind the operation of a galvanometer is the interaction between a magnetic field and an electric current. When an electric current flows through a coil placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a torque, which causes the coil to rotate. This rotation is proportional to the current flowing through the coil, allowing the galvanometer to measure the current by displaying the rotation on a calibrated scale.
Types of Galvanometers
There are several types of galvanometers, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. The most common types include:
- Tangent Galvanometer: This device uses a circular coil and a compass needle to measure the tangent of the angle between the magnetic field of the coil and Earth’s magnetic field. The tangent of this angle is proportional to the current flowing through the coil.
- D’Arsonval Galvanometer: Also known as a moving coil galvanometer, this instrument consists of a small coil of wire suspended in a permanent magnetic field. When current flows through the coil, it experiences a torque and rotates, with the rotation being measured by a calibrated scale.
- Vibration Galvanometer: This type of galvanometer is designed to measure alternating currents (AC). It uses a coil suspended between two magnets, which vibrates when current flows through it. The frequency of vibration is proportional to the current amplitude.
Applications of Galvanometers
Galvanometers have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Current Measurement: Galvanometers are used to measure small electric currents in circuits or to detect the presence of an electric current.
- Voltage Measurement: By connecting a galvanometer in series with a known resistance, it can be used to measure voltage across a circuit element.
- Physics Experiments: Galvanometers are employed in many physics experiments to measure the magnetic fields produced by electric currents or to investigate the properties of conductors and insulators.
- Electronics: In electronic applications, galvanometers can be used to calibrate and test electronic components and circuits.
Conclusion
A galvanometer is a sensitive instrument used to measure small electric currents or detect the presence of an electric current. It operates based on the interaction between a magnetic field and an electric current. With various types and applications, galvanometers are essential tools in electrical and electronic measurements across multiple fields.