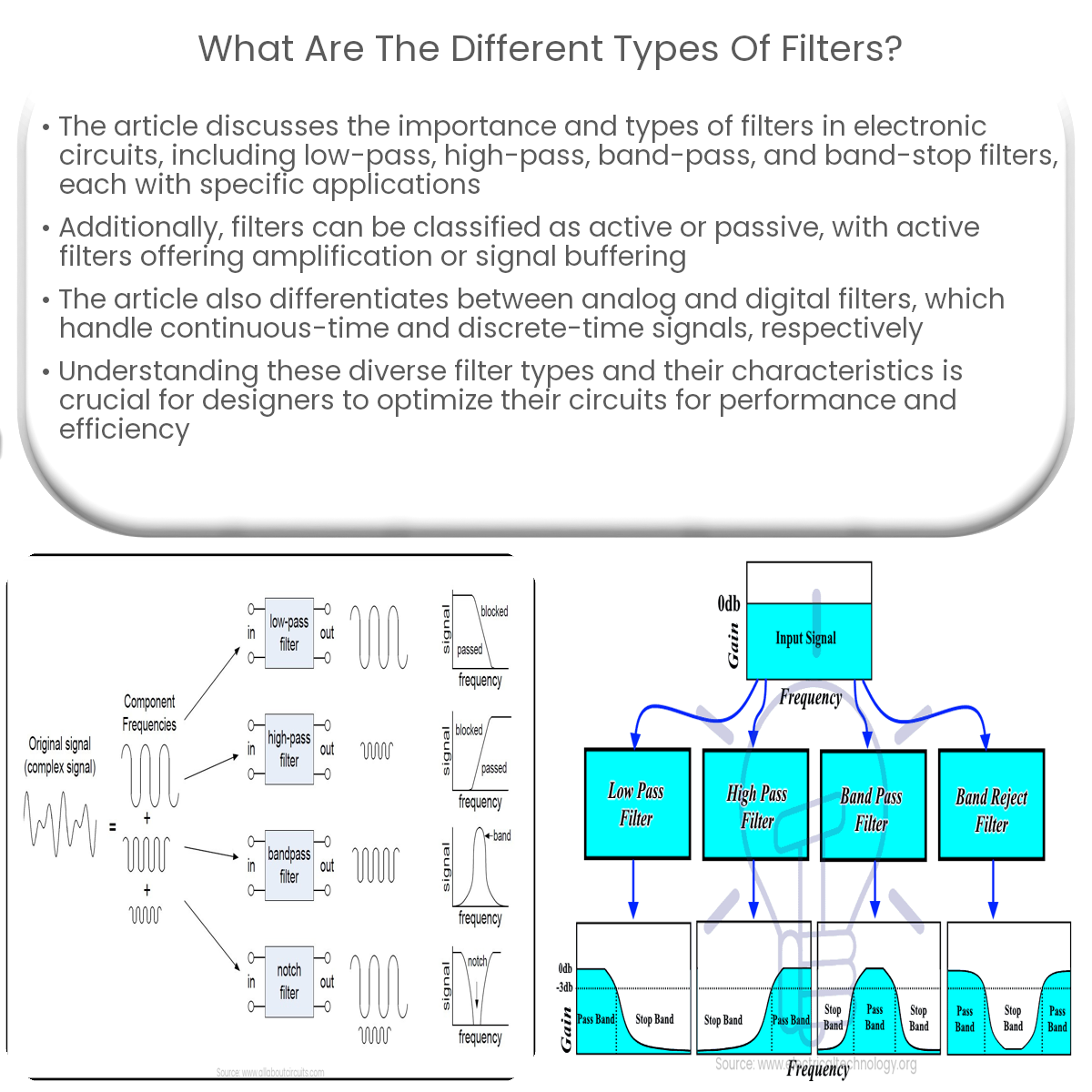
Filters can be low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, band-stop, active, passive, analog, or digital, each with unique characteristics and applications.
Introduction to Filters
Filters are essential components in various electronic circuits, designed to manipulate signals’ frequency content. They are widely used in applications such as audio processing, noise reduction, and communication systems. In this article, we will discuss the different types of filters available and their characteristics.
Low-Pass Filters
Low-pass filters (LPF) are designed to allow signals with frequencies below a specific cutoff frequency to pass through while attenuating higher frequencies. These filters are commonly used in applications where unwanted high-frequency noise must be removed from a signal.
High-Pass Filters
High-pass filters (HPF) work oppositely to low-pass filters. They allow signals with frequencies above a specific cutoff frequency to pass through while attenuating lower frequencies. High-pass filters are often used in applications such as audio systems to remove low-frequency noise or hum.
Band-Pass Filters
Band-pass filters (BPF) are designed to allow a specific range of frequencies to pass through while attenuating frequencies outside that range. These filters are used in applications like radio communication systems, where a specific frequency band must be isolated.
Band-Stop Filters
Band-stop filters, also known as notch filters, are designed to attenuate a specific range of frequencies while allowing other frequencies to pass through. They are often used in applications where a narrow band of frequencies must be removed from a signal, such as eliminating interference in communication systems.
Active and Passive Filters
Filters can also be classified as active or passive, depending on their components. Passive filters are made using passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. These filters do not require an external power source and do not provide amplification. Active filters, on the other hand, use active components such as operational amplifiers (op-amps) in addition to passive components. Active filters require a power source and can provide amplification or signal buffering.
Analog and Digital Filters
Filters can also be divided into analog and digital types. Analog filters work with continuous-time signals and use analog components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Digital filters, however, work with discrete-time signals and are implemented using digital signal processing (DSP) techniques.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of filters and their characteristics is crucial in selecting the appropriate filter for a specific application. By considering factors such as the desired frequency response, filter type, and whether an active or passive filter is needed, designers can optimize their circuits for performance and efficiency.