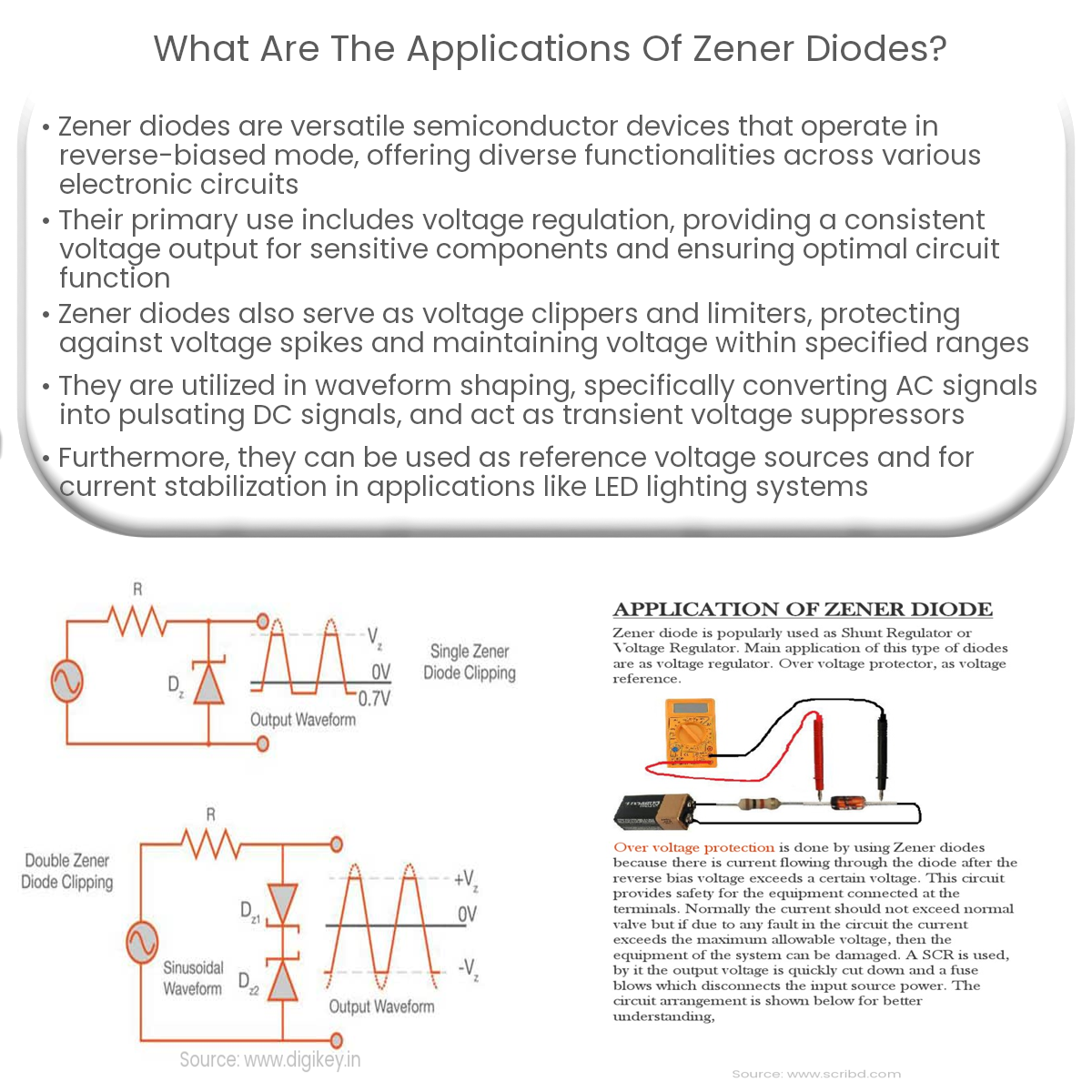
Zener diodes are used in voltage regulation, clipping and limiting, waveform shaping, transient voltage suppression, reference voltage, and current stabilization.
Applications of Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are unique semiconductor devices that offer versatile and reliable functionality in various electronic circuits. They are designed to operate in the reverse-biased mode and maintain a constant voltage over a wide range of current. This article discusses some common applications of Zener diodes.
Voltage Regulation
One of the primary uses of Zener diodes is voltage regulation. By maintaining a stable voltage across their terminals, they can provide a consistent voltage output to sensitive electronic components, ensuring the proper functioning of the circuit.
Voltage Clipping and Limiting
Zener diodes can be used to clip or limit voltage levels in circuits. When used as a voltage clipper, the diode prevents voltage spikes from damaging other components, while as a voltage limiter, it helps maintain the voltage within a specific range.
Waveform Shaping
Zener diodes are also employed in waveform shaping applications, such as the conversion of AC signals into pulsating DC signals. This is particularly useful in power supply circuits, where a stable DC voltage is required.
Transient Voltage Suppression
Transient voltage spikes can cause significant damage to electronic components. Zener diodes can act as transient voltage suppressors, protecting sensitive components from voltage surges.
Reference Voltage
Due to their ability to maintain a stable voltage, Zener diodes are often used as reference voltage sources in various electronic circuits, including analog-to-digital converters and voltage comparators.
Current Stabilization
Zener diodes can be used in conjunction with other circuit components to stabilize current levels. This is beneficial for maintaining constant current in applications such as LED lighting systems.
Conclusion
Zener diodes are versatile and essential components in modern electronics, serving various roles in voltage regulation, protection, and signal processing. Their unique characteristics and reliable operation make them invaluable in a wide range of applications, ensuring the proper functioning and safety of electronic circuits.