Electromagnetic waves are used in GPS for tracking, radar for air traffic control, maritime navigation, and LIDAR for mapping and autonomous vehicles.
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves in Navigation and Positioning Systems
Electromagnetic waves play a crucial role in various navigation and positioning systems, offering numerous applications in different fields. This article will discuss the applications of electromagnetic waves in some of the most commonly used navigation and positioning technologies, such as GPS, radar, and LIDAR.
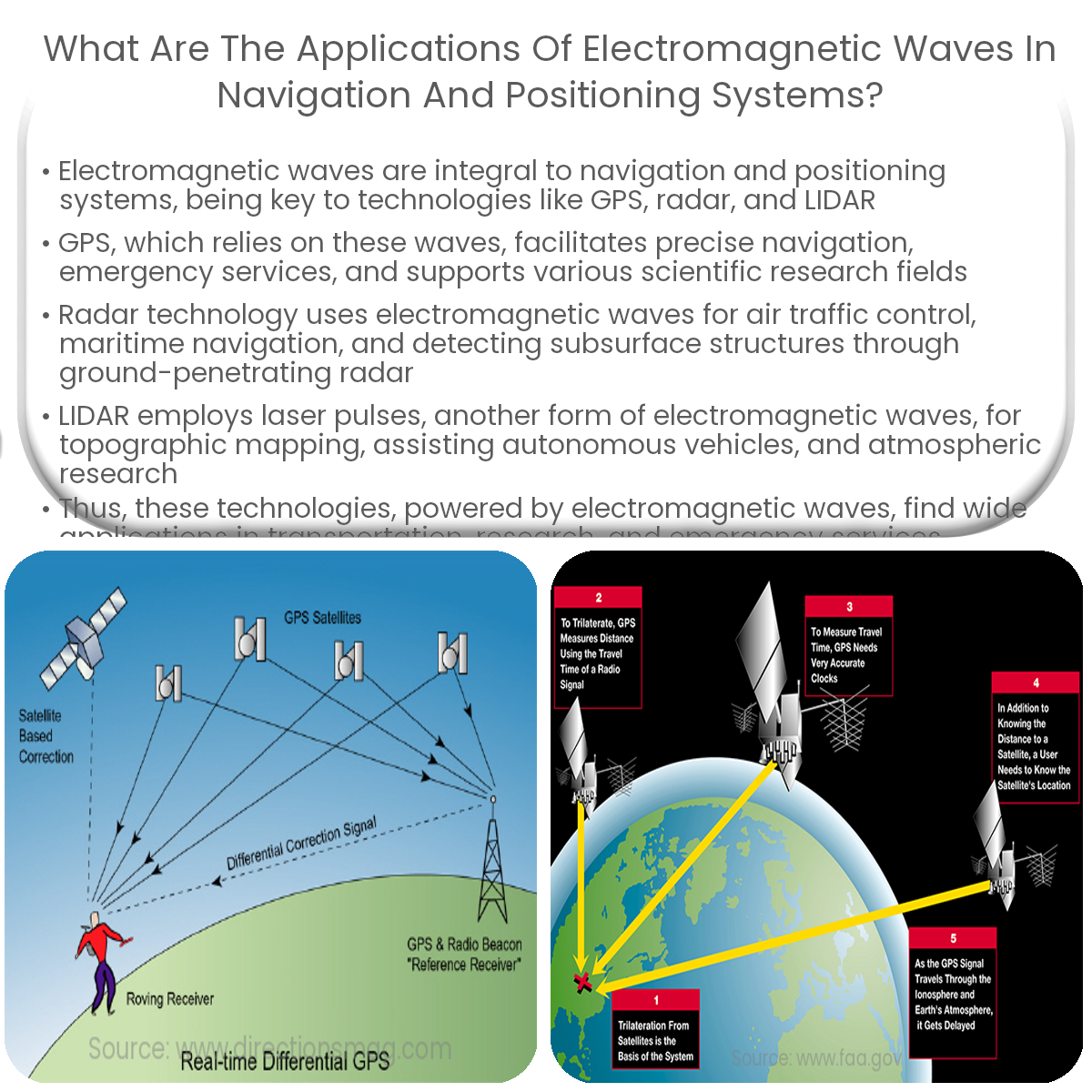
1. Global Positioning System (GPS)
- Navigation and Tracking: GPS, which relies on electromagnetic waves, enables precise navigation and tracking of vehicles, vessels, and individuals. GPS receivers calculate the user’s position by analyzing the time delay between the transmitted and received signals from multiple satellites.
- Emergency Services: GPS plays a vital role in emergency services, helping locate and reach people in need. It is used in search and rescue operations, as well as tracking and coordinating emergency vehicles.
- Scientific Research: GPS data is used in various scientific fields, such as geophysics, meteorology, and environmental monitoring. Researchers use GPS to study earthquakes, volcanic activity, and climate change by tracking the movement of tectonic plates and monitoring atmospheric conditions.
2. Radar
- Air Traffic Control: Radar technology uses electromagnetic waves to determine the position, speed, and direction of aircraft. It helps in the efficient management of air traffic, ensuring safe and organized flights.
- Maritime Navigation: Radar is essential for ships to navigate safely through crowded waters, avoid collisions, and detect potential obstacles. It can also be used for weather monitoring and the detection of approaching storms.
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR): GPR uses electromagnetic waves to detect and map subsurface structures and objects. It has applications in archaeology, geology, and utility detection.
3. LIDAR
- Topographic Mapping: LIDAR technology uses electromagnetic waves in the form of laser pulses to create accurate, high-resolution maps of the Earth’s surface. It is widely used in geology, forestry, and urban planning.
- Autonomous Vehicles: LIDAR sensors are used in self-driving vehicles to detect and avoid obstacles, providing real-time data for safe navigation.
- Atmospheric Research: LIDAR systems can measure atmospheric properties, such as aerosol concentration and wind speed, contributing to our understanding of climate change and air quality.
In conclusion, electromagnetic waves play a vital role in various navigation and positioning systems, from GPS to radar and LIDAR. These technologies have a wide range of applications in transportation, scientific research, and emergency services, showcasing the importance and versatility of electromagnetic waves.