Explore the fundamentals, types, and applications of Voltage Source Inverters (VSI), their role in renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and the future prospects.
Introduction to Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
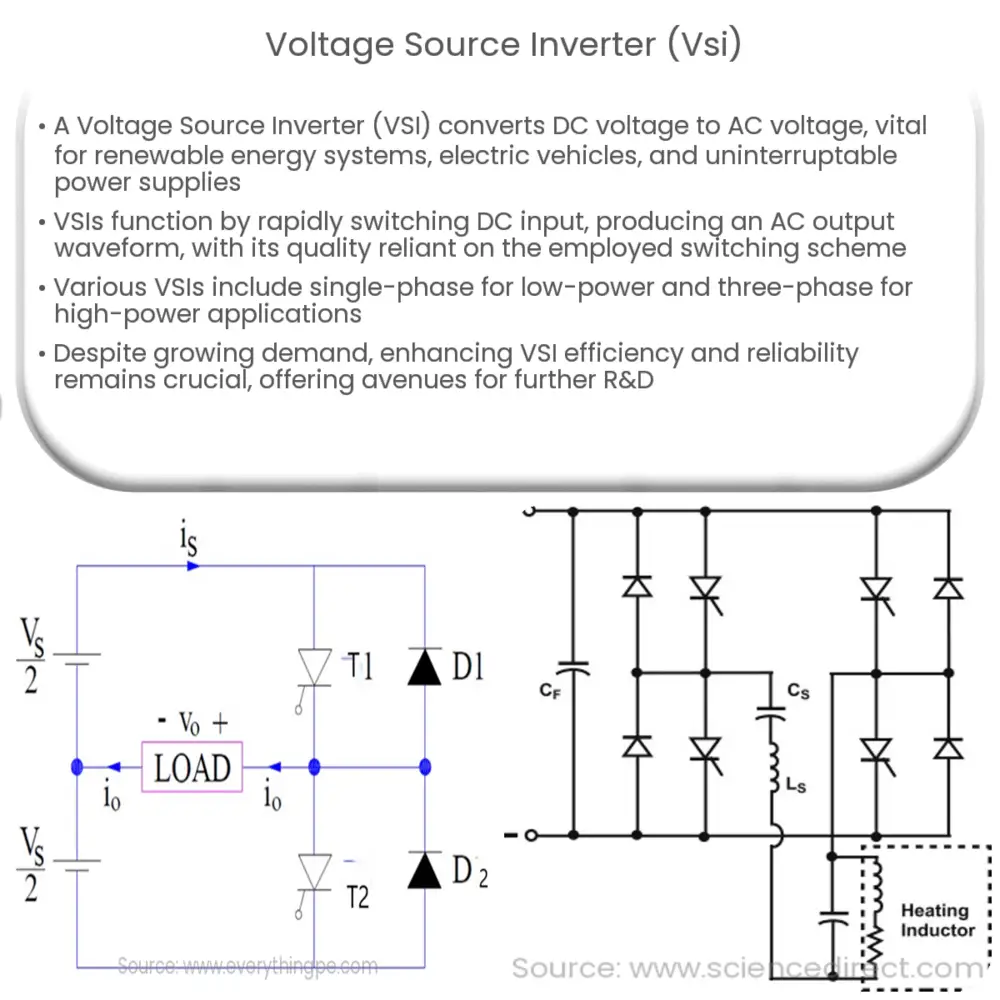
A Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) is a type of power electronic device that converts direct current (DC) voltage to alternating current (AC) voltage. It’s a crucial component in many applications, including renewable energy systems, electric vehicle drive systems, and uninterruptable power supplies.
Principle of Operation
The VSI operates by switching the DC input voltage on and off rapidly, producing a square wave output. This output is then filtered to create a more sinusoidal waveform, suitable for most AC applications. The quality of the output waveform is a critical factor in the operation of a VSI, and it depends on the switching scheme used.
Types of Voltage Source Inverters
Switching Techniques
VSI uses different switching techniques to control the frequency and amplitude of the output voltage. These include:
Regardless of the technique used, it is vital to manage the switching transitions carefully to avoid damaging the VSI or connected devices.
Performance Factors
The performance of a VSI depends on several factors:
Understanding these factors can help to optimize the design and operation of a VSI for a given application.
Applications of Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
Voltage Source Inverters are essential components of many modern systems:
Future Prospects and Challenges
With the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and electric vehicles, the demand for Voltage Source Inverters is expected to grow significantly. However, several challenges need to be addressed:
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) is a key component in a wide range of applications, converting DC power into AC power. Its role in renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, UPS systems, and variable frequency drives highlights its significance in today’s technology landscape. However, ongoing challenges in efficiency and reliability present opportunities for further research and development. The future of VSI technology is promising, with its increasing importance in the evolving energy landscape and electric vehicle market.

