Explore the evolution, types, usage, and pros & cons of twisted pair cables, a crucial element in modern data transmission.
Understanding Twisted Pair Cables
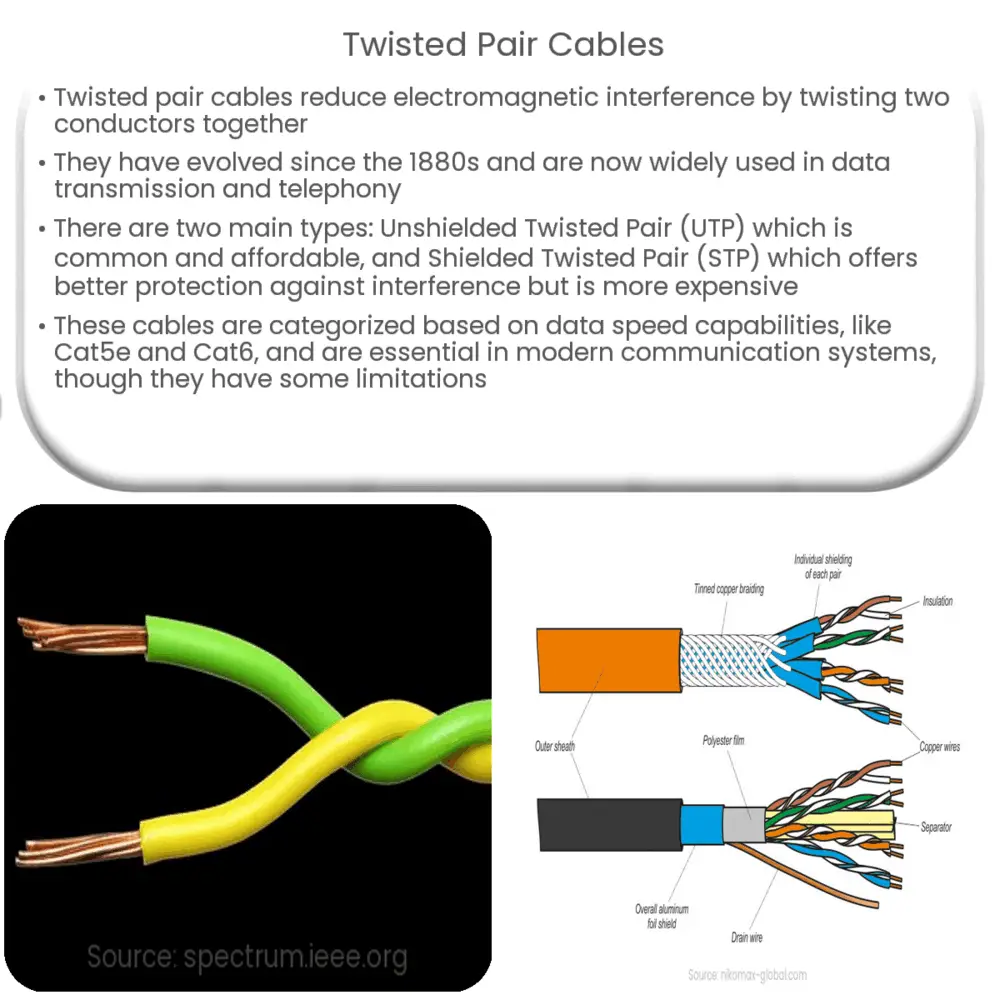
Twisted pair cable is a type of wiring in which two conductors are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources and cross talk from neighboring cables. The pair of wires carry equal and opposite signals, and the destination device reads the difference between the two.
The Evolution of Twisted Pair Cables
The use of twisted pair cabling dates back to the telegraph era of the 1880s. Since then, it has become the most popular method for data transmission and telephone line wiring. Over the years, the design and build of these cables have evolved significantly to meet the increasing demands for higher bandwidth and noise reduction.
Types of Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables fall under two primary categories: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP).
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): This is the most common type of twisted pair wiring, used primarily for telephone and computer networking because of its affordable pricing and ease of installation. Despite not having a protective shielding, it relies on the twisting design to reduce noise and maintain signal quality.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): This type of cable includes a layer of insulation and an outer protective shield around each pair or around the group of pairs. STP is designed to offer more protection against interference, making it ideal for environments with potential EMI. However, STP is more expensive and difficult to install compared to UTP.
Categories of Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables are also classified based on their capabilities in terms of data transmission speeds and bandwidth, usually referred to as “Categories”.
- Category 3 (Cat3): Once widely used for Ethernet networks, now largely obsolete.
- Category 5 (Cat5): Provides performance up to 100 MHz, suitable for most varieties of Ethernet.
- Category 5e (Cat5e): An enhanced version of Cat5 that reduces crosstalk.
- Category 6 (Cat6): Supports bandwidth frequencies of up to 250 MHz, more tightly wound and often comes with a plastic core.
Usage of Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables are prevalent in various sectors due to their versatility and efficiency in data transmission. Here are some common uses:
- Telecommunications: Twisted pair cables are extensively used in telephone networks where signals are transmitted digitally.
- Computer Networks: In local area networks (LANs), twisted pair cables are used for data transmission, connecting computers, and other network devices.
- Video Applications: Twisted pair cables are also utilized in video surveillance systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Twisted Pair Cables
Like all technologies, twisted pair cables come with their own set of pros and cons.
- Advantages:
- They are more affordable compared to other types of cables.
- They are lightweight, flexible, and easy to install.
- They offer a good range of distance on a single cable run.
- Disadvantages:
- They are more vulnerable to interference if not properly shielded.
- Their data transfer speed is lower compared to optical fiber cables.
- Signal quality can degrade over long distances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, twisted pair cables are a critical element in modern data transmission and telecommunication systems. Their relatively low cost, ease of installation, and versatility make them a popular choice for a variety of applications, from home internet connections to large-scale business networks. However, like all technologies, they have their limitations. While the disadvantages are worth noting, the widespread use and continued development of twisted pair cables indicate their advantages and usefulness in many scenarios. As the demand for high-speed data transmission continues to grow, we can expect further advancements and improvements in twisted pair cable technology.



