Explore the basics of square wave inverters, their working principles, applications, advantages, and limitations in this comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Square Wave Inverters
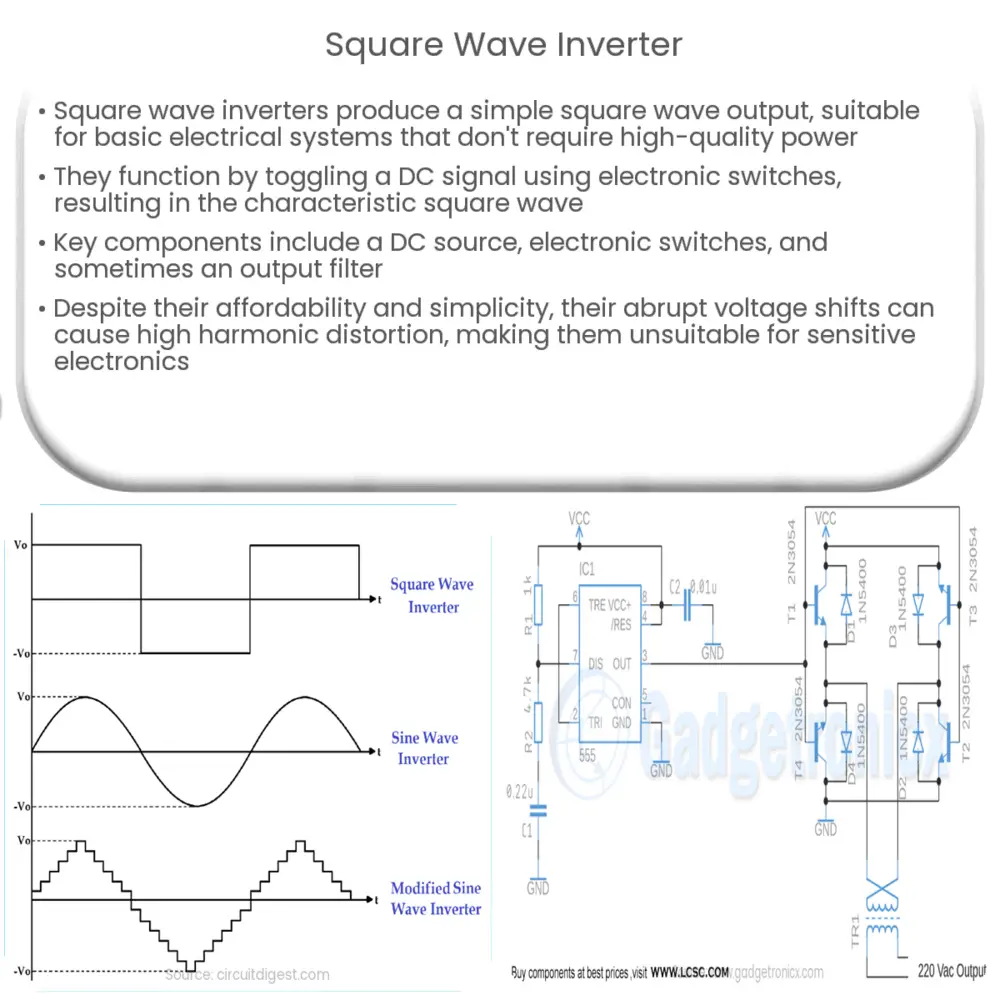
A Square Wave Inverter is a type of inverter that produces a square wave output. It is one of the simplest forms of inverters available in the market. While they may not be as efficient or produce a clean output as other types of inverters, they are straightforward to understand and are often used in simple systems that don’t require high-quality power.
Working Principle
The working principle of a square wave inverter is relatively simple. It mainly involves flipping the DC signal back and forth to create a square wave, hence the name. This operation is carried out using electronic switches that are turned on and off at regular intervals.
Key Components
Applications of Square Wave Inverters
Square wave inverters are typically used in applications that don’t require high-quality, pure sine wave power. They are commonly used in basic power tools, lighting systems, and other simple electrical devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main advantage of square wave inverters is their simplicity and low cost. They are relatively easy to manufacture and understand. However, they also have several disadvantages. The abrupt transitions from positive to negative voltage can cause high harmonic distortion, which can damage sensitive electronics. Furthermore, they are not as efficient as other types of inverters.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into the technical specifications and operational principles of square wave inverters, focusing on the influence of different parameters such as load type, power rating, and harmonic content.
Technical Specifications and Operational Principles
Let’s delve deeper into the specifics of square wave inverters. The operational frequency of these inverters is typically around 50 to 60 Hz, aligning with standard power frequencies. However, the exact frequency can vary depending on the design and purpose of the inverter.
The power rating of a square wave inverter refers to the maximum amount of power it can supply to its load. It’s essential to select an inverter with a power rating that matches the needs of the intended load.
Impact of Load Type
The load type has a significant influence on the performance of a square wave inverter. Resistive loads, like heaters or incandescent lamps, work well with square wave inverters. However, more complex loads such as motors or sensitive electronics may experience problems due to the high harmonic content of the square wave.
Harmonic Content
Square wave inverters have high harmonic content due to their abrupt voltage transitions. Harmonic distortion can cause various issues, including increased heating in electrical devices, malfunctions in sensitive electronics, and degradation of power quality. Therefore, they are not recommended for powering sensitive electronics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, square wave inverters are a simple, cost-effective solution for powering basic electrical devices. They work by flipping a DC signal back and forth to create a square wave output. While they may not be the most efficient or provide the cleanest power output, their simplicity and affordability make them a viable option for certain applications. However, due to the high harmonic content of their output, they are not suitable for powering sensitive electronics. It’s essential to understand these characteristics when considering a square wave inverter for your power needs.
As advancements in technology continue, the performance and efficiency of inverters are likely to improve. However, for now, the square wave inverter remains a testament to the beauty of simplicity in electrical engineering.

