Snubber circuits are energy-absorbing circuits used to eliminate voltage spikes and limit the rate of change in current and voltage in electrical systems.
Introduction to Snubber Circuits
In the world of electronics, managing voltages and currents efficiently is vital to the successful operation of a system. That’s where snubber circuits come in. Snubber circuits are energy-absorbing circuits used to eliminate voltage spikes and limit the rate of change in current and voltage in electrical systems.
The Need for Snubber Circuits
When switching devices like transistors or thyristors are used in circuits, they can generate sudden voltage or current spikes due to parasitic inductance and capacitance within the circuit. These spikes can damage sensitive components or cause unwanted electromagnetic interference. Snubber circuits are designed to protect against these issues.
How Snubber Circuits Work
A snubber circuit absorbs excess energy by providing a path for the current to follow, either dispersing it as heat or storing it for later use. This operation limits the rate of voltage change (dV/dt) and current change (dI/dt) and clamps voltage spikes.
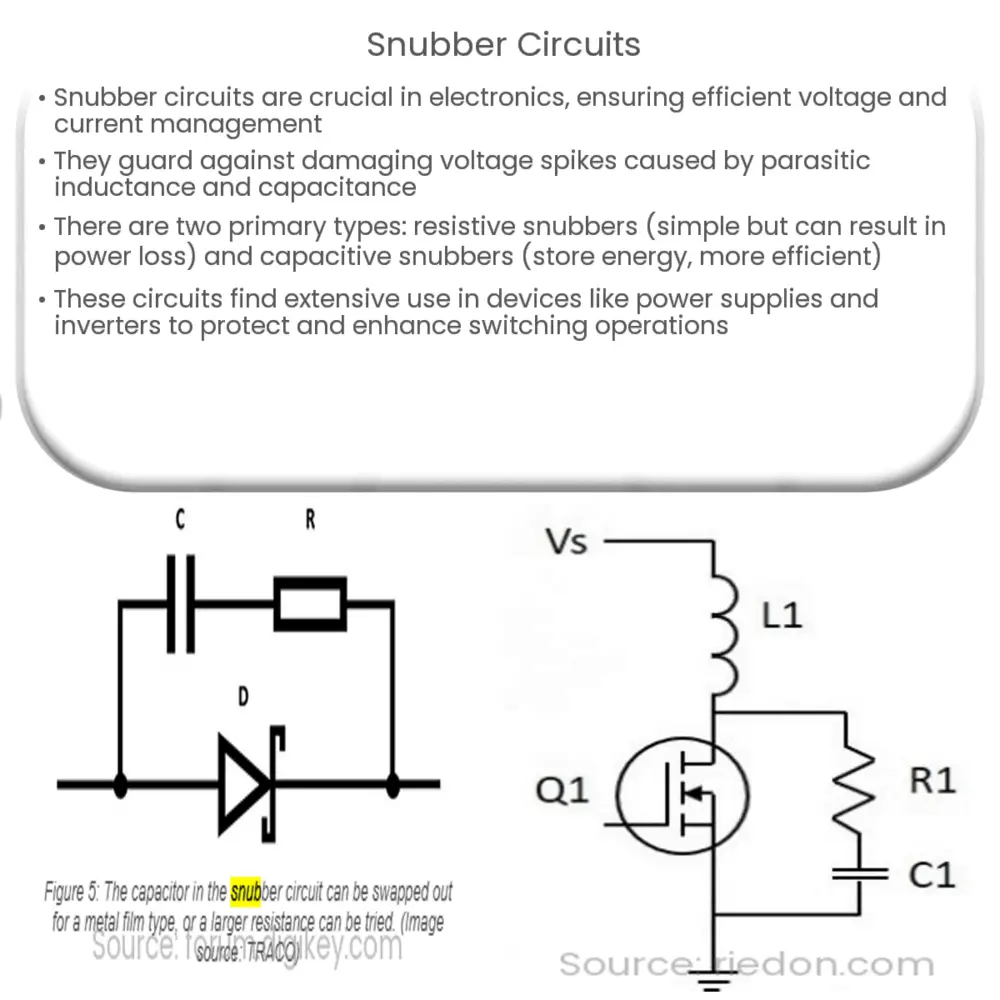
Types of Snubber Circuits
There are mainly two types of snubber circuits – resistive snubbers and capacitive snubbers:
- Resistive snubbers are the simplest type, composed of a resistor and capacitor in series. They are used for their simplicity and reliability but can result in power loss due to the resistor.
- Capacitive snubbers consist of a capacitor and diode. They are more efficient than resistive snubbers as they store energy instead of dissipating it as heat.
Key Applications of Snubber Circuits
Snubber circuits find use in various applications, especially where switching devices are extensively used. These include power supply units, inverters, electric motor drives, and power amplifiers. They protect these systems from harmful voltage spikes and ensure smoother switching operations.
Design Considerations for Snubber Circuits
When designing a snubber circuit, several factors need to be considered:
- The type of switching device and its voltage and current ratings.
- The nature of the load and the source.
- The operational frequency of the system.
Detailed Design Factors
Expanding on the design considerations:
- Type of Switching Device: Certain devices are more sensitive to voltage spikes or rapid changes in voltage and current, requiring the use of snubber circuits for protection.
- Load and Source Characteristics: The presence of inductive or capacitive loads may necessitate the use of snubber circuits to prevent unwanted voltage or current spikes.
- Operational Frequency: At higher frequencies, parasitic inductance and capacitance can become significant, making snubber circuits more critical.
The Components of a Snubber Circuit
The primary components of a snubber circuit, regardless of its type, are a resistor and a capacitor.
- The Resistor (R) in a snubber circuit serves the primary function of energy dissipation. Its value is often calculated based on the energy it needs to absorb and the maximum allowable voltage across the switching device.
- The Capacitor (C) plays a crucial role in determining the snubber’s effectiveness. It helps limit the rate of voltage change (dV/dt) across the switching device.
The Role of Diodes in Snubber Circuits
In certain types of snubber circuits, a diode may be added in parallel with the resistor. The diode provides a path for the current when the switching device turns off, preventing a sudden voltage spike across the device.
Practical Considerations for Snubber Circuits
While snubber circuits provide valuable protection for electronic systems, there are some practical considerations:
- Energy dissipated by the snubber circuit can lead to heating. This may require thermal management techniques, especially in high-power applications.
- Properly sizing the components of the snubber circuit is crucial. An incorrectly sized snubber circuit may not provide sufficient protection, or it could adversely affect the operation of the circuit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, snubber circuits are an essential component in many electronic systems. They help protect sensitive components from damage caused by voltage spikes and rapid changes in voltage and current. By understanding their function, the different types, and how to design them properly, one can improve the reliability and performance of electronic systems.

