Explore the functioning, benefits, types, and considerations of Motor Capacitor Banks in this detailed guide, enhancing electrical efficiency.
Understanding Motor Capacitor Banks
Motor capacitor banks are a crucial element in many electrical systems. They are primarily used to improve the power factor of an electrical system, which in turn leads to more efficient energy usage. Understanding how they work and their benefits is crucial for any electrical engineer or technician.
What are Motor Capacitor Banks?
Motor capacitor banks, also known as power factor correction capacitor banks, are groups of capacitors that are wired together in a bank or array. These capacitors are used in conjunction with electrical motors and other inductive loads to increase the power factor, which is a measure of how effectively incoming power is used in the system.
How do Motor Capacitor Banks Work?
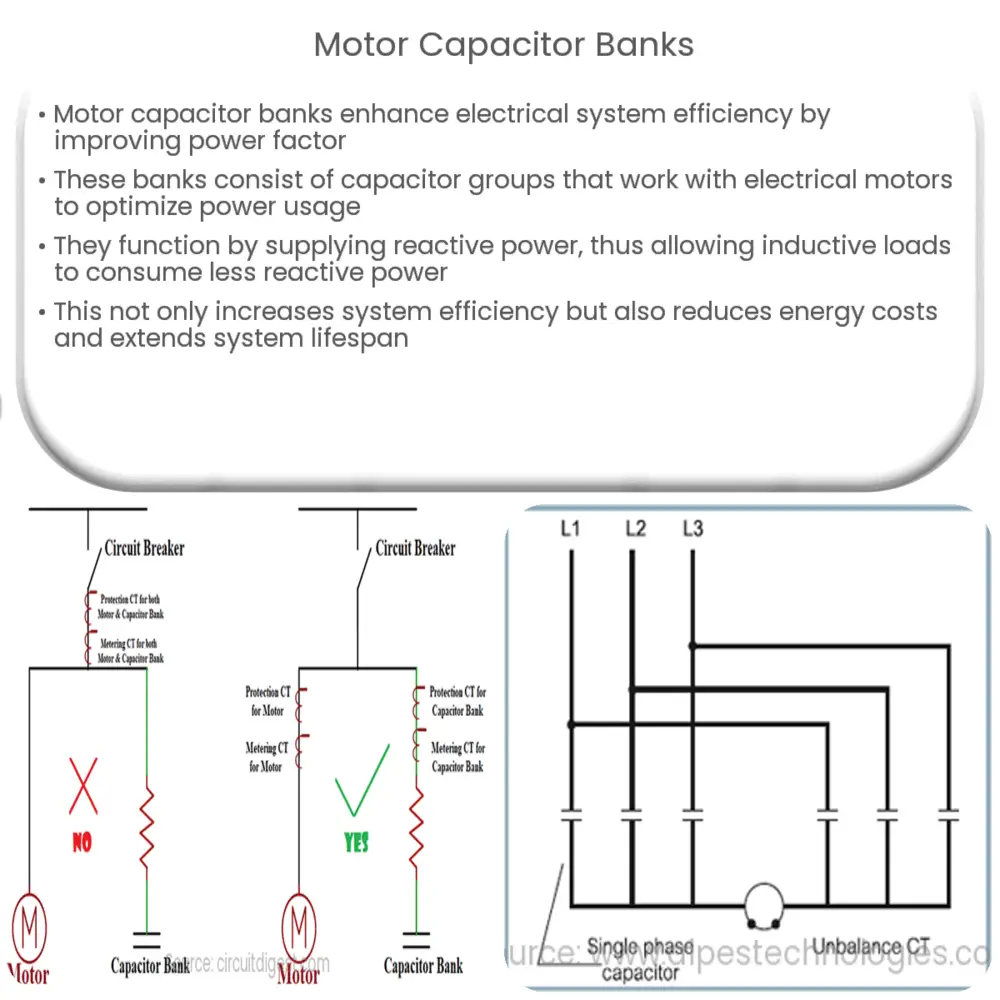
Motor capacitor banks operate by supplying reactive power to the electrical system. Reactive power is essentially the power that is stored and then released by the inductive loads (like motors) in the system. By supplying this reactive power, the capacitor bank allows the inductive loads to draw less reactive power from the power source, which improves the power factor and overall efficiency of the system.
- Inductive Load: Inductive loads, such as electric motors, create a lag between the current and voltage in an electrical system, which can lower the system’s power factor.
- Reactive Power: Reactive power is the power that oscillates between the source and load, which is not converted into useful work. Instead, it is stored and then released back into the system.
- Capacitor Bank: The capacitor bank supplies this reactive power, reducing the amount that the load needs to draw from the power source.
Benefits of Motor Capacitor Banks
There are numerous benefits associated with the use of motor capacitor banks in an electrical system. They can improve system efficiency, reduce power consumption, and lower electricity costs. By improving the power factor, they can also reduce strain on the electrical system and increase its lifespan. The energy savings can be substantial, particularly in industrial settings where large motors are common.
Types of Motor Capacitor Banks
There are different types of motor capacitor banks, each designed for specific applications. The two main types are fixed and automatic capacitor banks.
- Fixed Capacitor Banks: These are typically used in situations where the load and power factor are relatively constant. They provide a fixed amount of reactive power to the system.
- Automatic Capacitor Banks: These are used in situations where the load and power factor fluctuate. An automatic capacitor bank can adjust the amount of reactive power it supplies based on the current power factor.
Considerations for Using Motor Capacitor Banks
While motor capacitor banks can provide significant benefits, it’s essential to consider several factors when implementing them. The size of the bank needs to match the reactive power demand of the system. Overcompensating can lead to a power factor that is too high, which can be just as problematic as a low power factor.
Additionally, the physical placement of the capacitor bank in the system can impact its effectiveness. Ideally, the bank should be placed as close as possible to the inductive loads. This placement minimizes the length of the power lines between the loads and the bank, which reduces power loss.
Conclusion
In conclusion, motor capacitor banks are a vital component in many electrical systems. They improve the power factor and efficiency of a system, leading to lower energy consumption and costs. By understanding the basics of how they work, their benefits, and considerations for their use, one can optimize the performance of electrical systems and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.

