Explore the world of magnetic position sensors, their working principles, types, applications, recent advancements, and future prospects.
Magnetic Position Sensors: An Overview
Magnetic position sensors are critical components in a variety of industrial and consumer applications. These versatile devices measure the direction and magnitude of magnetic fields to determine the precise position of an object in relation to the sensor. This article will delve into the intricacies of magnetic position sensors, their working principles, applications, and the latest advancements in this field.
Working Principle
The operation of magnetic position sensors is grounded on the principle of magnetoresistance or the Hall Effect. The magnetoresistance-based sensors determine position by detecting changes in resistance due to the influence of a magnetic field. On the other hand, those based on the Hall Effect measure voltage changes across a conductor when it is subjected to a magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of current flow.
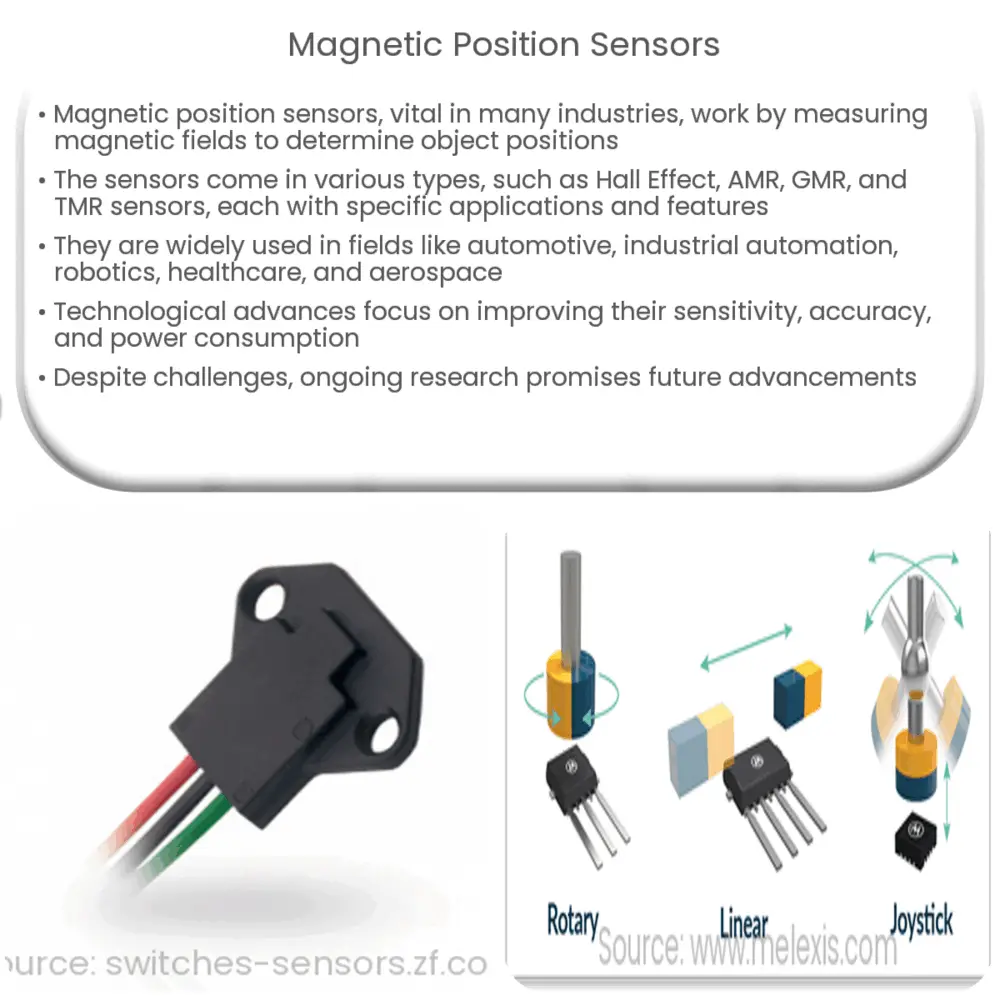
Types of Magnetic Position Sensors
Applications
Magnetic position sensors have broad applications due to their reliability, precision, and versatility. These include automotive systems, industrial automation, robotics, medical devices, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
In the automotive industry, they help in tasks like steering angle detection, pedal position sensing, and gear position detection. In the realm of industrial automation, they are used for precise machine control and monitoring, while in robotics, they assist in complex tasks like robotic arm positioning.
In the healthcare sector, they contribute to applications like surgical robotics and medical imaging, ensuring precise movement and accurate data acquisition. In aerospace, they are employed in flight control systems, ensuring safety and accuracy.
Latest Developments
In recent years, advancements in magnetic position sensor technology have largely focused on improving sensitivity, accuracy, and power consumption. This is driven by the increasing demand for sensors in applications that require high precision and reliability under challenging conditions, such as autonomous vehicles, drones, and advanced robotics.
For instance, the development of TMR sensors has generated considerable interest. These sensors offer a unique blend of high sensitivity, low power consumption, and excellent temperature stability, making them suitable for a broad range of applications.
Furthermore, the integration of magnetic position sensors with microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) is another promising development. This combination allows for the creation of more compact and efficient sensors, which are ideal for applications with stringent space and power constraints, such as wearable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the significant advancements in magnetic position sensor technology, there are still several challenges to overcome. These include improving the sensors’ robustness to environmental variations, reducing their size and cost, and enhancing their resolution and accuracy.
Moreover, the increasing miniaturization of devices and the rise of IoT have created a demand for smaller, more efficient, and more versatile sensors. Thus, research in this field is likely to focus on developing new materials and technologies to meet these requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, magnetic position sensors play a vital role in various industries and applications, offering precise, reliable measurements under diverse conditions. The continuous advancements in this field, driven by evolving application requirements and technological innovation, promise to make these sensors even more versatile and efficient in the future.
Whether it’s enhancing the safety and performance of vehicles, improving the precision of industrial machinery, or enabling breakthroughs in medical technology, magnetic position sensors are at the forefront of innovation. As we look ahead, we can anticipate these humble yet powerful components to continue making significant contributions to the technology landscape.

