Explore the science behind magnetic field generators, their types such as permanent magnet and electromagnetic generators, and their diverse applications.
Magnetic Field Generators: A Comprehensive Overview
The concept of magnetic fields is an essential one in both basic and advanced physics. With their invisible force and ability to interact with various materials, magnetic fields are key to many technological applications. At the heart of these applications, we find magnetic field generators. These devices are central to various scientific and industrial applications, playing a crucial role in our day-to-day life.
Understanding Magnetic Fields
Before we dive into the specifics of magnetic field generators, it’s important to have a foundational understanding of magnetic fields. These fields exist in any space where magnetic forces are observed. They flow from the magnetic north pole to the south pole of a magnet. The field strength, measured in Tesla (T), is the force that a magnetic field exerts on moving charged particles.
What are Magnetic Field Generators?
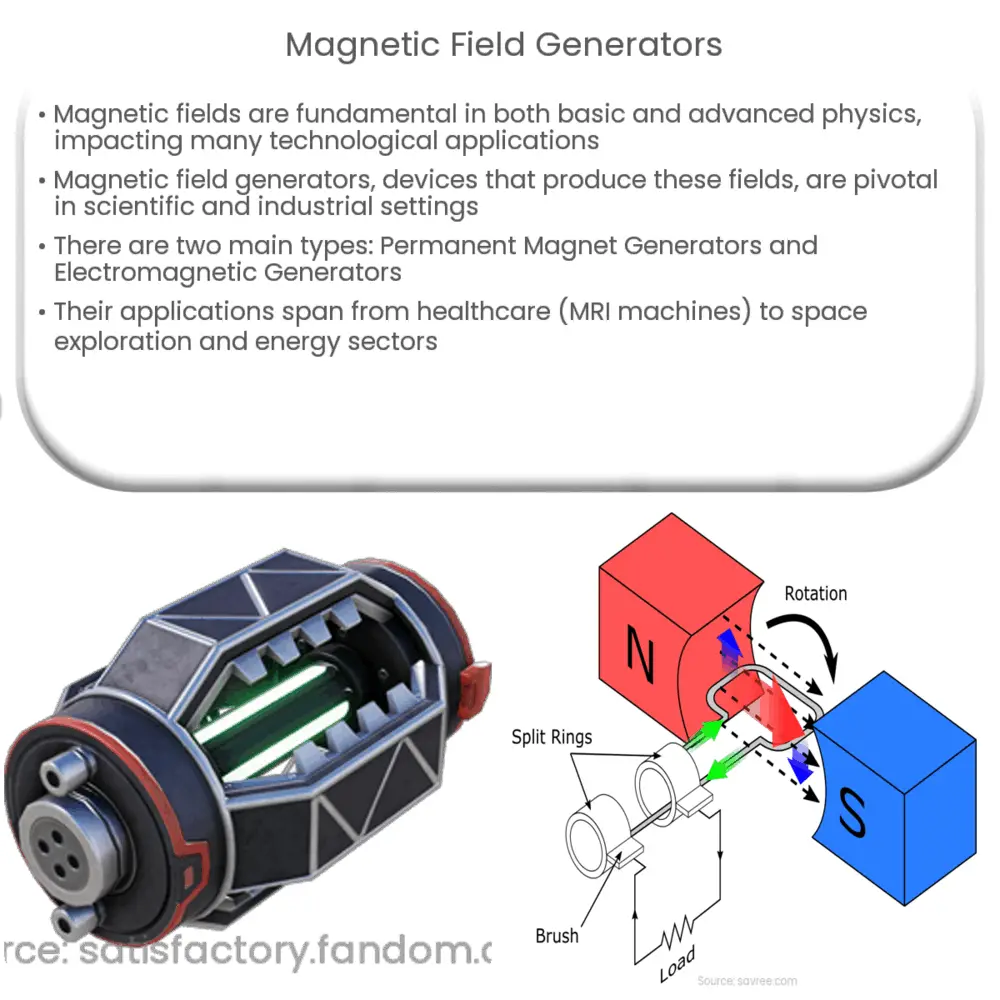
A magnetic field generator is a device used to create a magnetic field. This field can be static (as in a permanent magnet) or dynamic (as in an electromagnet). A magnetic field generator typically includes a magnet or an electrical current source, and a magnetic core that concentrates the magnetic field. The size, strength, and design of the generator can vary greatly depending on its intended use.
Types of Magnetic Field Generators
- Permanent Magnet Generators: These generators use permanent magnets to produce a magnetic field. They are simple, reliable, and require no external power source. However, the strength of the magnetic field they produce is not adjustable.
- Electromagnetic Generators: Also known as electromagnets, these generators produce a magnetic field when an electric current is applied. The strength of the electromagnetic field can be adjusted by changing the magnitude of the electric current.
Applications of Magnetic Field Generators
Magnetic field generators have a wide range of applications across various industries. From healthcare to technology and even space exploration, the scope of these devices is vast and multidimensional. In the next section, we will delve deeper into the specific uses of magnetic field generators in different fields and the impact they have on our lives.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of magnetic fields and the devices that generate them is essential as we continue to progress technologically. In the second part of this article, we will explore in detail the different types of magnetic field generators, their workings, and their multifaceted applications.
Detailed Examination of Magnetic Field Generators
Permanent Magnet Generators
Permanent Magnet Generators (PMGs) are perhaps the most straightforward type of magnetic field generator. They rely on the intrinsic magnetic properties of certain materials—like iron, nickel, cobalt, and rare-earth metals—to generate a constant magnetic field. The key advantage of PMGs is their reliability and simplicity. Since they don’t require an external power source, they can operate indefinitely without maintenance. However, their inability to adjust the magnetic field strength can be a limiting factor in some applications.
Electromagnetic Generators
Unlike PMGs, Electromagnetic Generators create magnetic fields using electricity. When an electrical current flows through a coil of wire—often wound around a magnetic core—it generates a magnetic field. By varying the strength of the current, the magnetic field’s intensity can be adjusted. This adjustability makes electromagnetic generators particularly useful in applications where variable field strength is necessary, such as in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines in the healthcare sector.
Applications of Magnetic Field Generators
- Healthcare: Magnetic field generators are integral to the functioning of MRI machines, which use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the human body.
- Technology: Magnetic fields play a crucial role in data storage devices like hard disk drives. They are also employed in magnetic levitation technology, used in high-speed trains.
- Space Exploration: NASA uses magnetic fields to study the properties of planets and protect spacecraft from harmful solar radiation.
- Energy: Magnetic field generators are key components in generators and electric motors used in the energy sector.
Conclusion
In conclusion, magnetic field generators are incredibly versatile devices that have become indispensable in various industries. From the healthcare sector’s reliance on MRI machines to the technology industry’s use in data storage and transfer, magnetic field generators’ significance is inarguable. As we continue to explore and develop new technologies, it is clear that understanding and harnessing the power of magnetic fields will remain a critical part of scientific advancement.

