Explore the workings, applications, advantages, and future of Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulators in our comprehensive guide.
Understanding Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulators
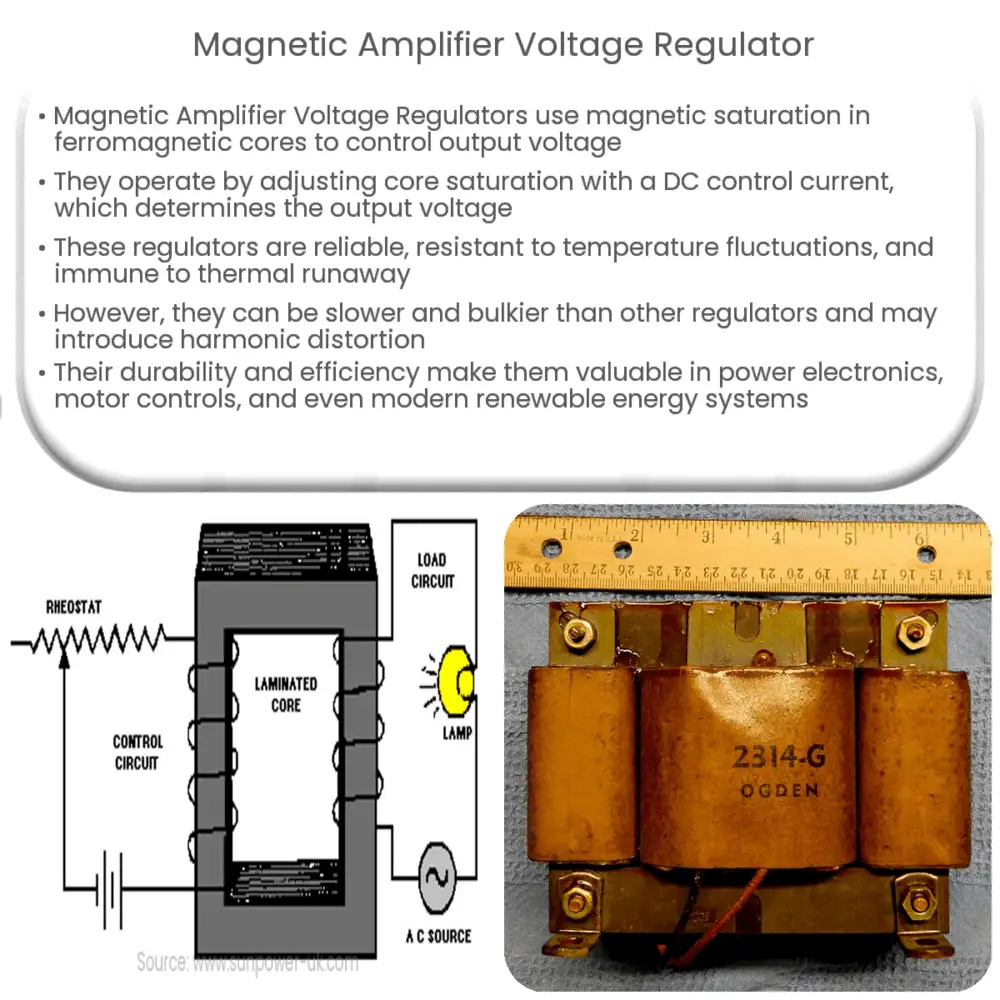
The Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulator is an intriguing piece of technology that has been widely used in power electronics and control systems. It’s a type of voltage regulator that utilizes the principle of magnetic saturation in a ferromagnetic core to control the output voltage. In essence, it can be described as a self-saturating transformer, where the degree of saturation is controlled by the dc control current.
Working Principle of Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulators
The principle behind the operation of a magnetic amplifier voltage regulator is fairly straightforward. The core of the amplifier is designed to become saturated upon the application of a certain level of current. When the core becomes saturated, it can no longer effectively transmit magnetic fields. By controlling the level of current, we can control the saturation of the core and, as a result, the output voltage.
- Control Winding: This is the part of the device where the DC control current is applied. The control winding modifies the magnetic field in the core, which in turn alters the amplifier’s output.
- AC Winding: This part of the device is where the AC input is applied. The alternating current induces a magnetic field in the core, and depending on the level of saturation controlled by the control winding, the output voltage is determined.
- Output Winding: This winding delivers the regulated output voltage. The AC voltage is transformed according to the degree of saturation in the magnetic core.
Applications of Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulators
Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulators find numerous applications in industries due to their robustness, reliability, and insensitivity to temperature variations. They are predominantly used in power electronics, where they provide a cost-effective and efficient solution for regulating voltage in power supplies. Additionally, they are extensively used in motor controls, industrial heating, and lighting systems due to their resistance to electrical noise and ability to handle high power levels.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulators
The magnetic amplifier voltage regulators come with a host of advantages. They are highly reliable, possess a long life span, and demonstrate an excellent tolerance to harsh environmental conditions. Furthermore, these devices are immune to thermal runaway, an undesirable phenomenon in electronic devices where excessive heat leads to device failure.
Despite these merits, magnetic amplifier voltage regulators are not without their downsides. They have a relatively slower response time compared to other types of voltage regulators, and they can be bulkier due to the need for magnetic cores. Lastly, they can introduce harmonic distortion in the output voltage due to the magnetic saturation phenomenon.
Components of a Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulator
A typical Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulator is composed of two main parts: the saturable reactor and the biasing unit.
- Saturable Reactor: This is the main component of the regulator, consisting of a magnetic core and windings. The core material is usually iron, as it easily reaches magnetic saturation. The windings include the control, AC, and output windings, as discussed previously.
- Biasing Unit: The biasing unit’s function is to provide a biasing magnetic field in the core. This biasing field keeps the core in a near-saturated state under no-load conditions, which helps maintain the stability of the output voltage.
Modern Day Uses and Developments
While magnetic amplifier voltage regulators may seem like an outdated technology, they are finding new life in modern applications. For instance, they are being explored for use in renewable energy systems, like solar power converters, where they can offer efficient voltage regulation without the need for complex control circuits. Also, due to their robustness and longevity, they are also considered for use in aerospace and defense applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Magnetic Amplifier Voltage Regulator is a unique piece of technology that leverages the principle of magnetic saturation to regulate voltage. Despite its age, it continues to be relevant due to its numerous advantages, such as robustness, insensitivity to temperature variations, and immunity to thermal runaway. While it may not be the fastest or the most compact voltage regulator available, its reliability and efficiency make it a viable choice for many applications, especially in environments where durability and longevity are prioritized. As we continue to explore new frontiers in power electronics and control systems, the magnetic amplifier voltage regulator’s role is expected to evolve and adapt, ensuring its place in our technological future.

