Explore the world of logic gates, their types, functions, and key applications in digital electronics and computing systems.
Introduction to Logic Gates
Logic gates are the basic building blocks of any digital system. They are a physical device implementing a Boolean function, essentially performing a basic logic operation, typically on two binary inputs.
Types of Logic Gates
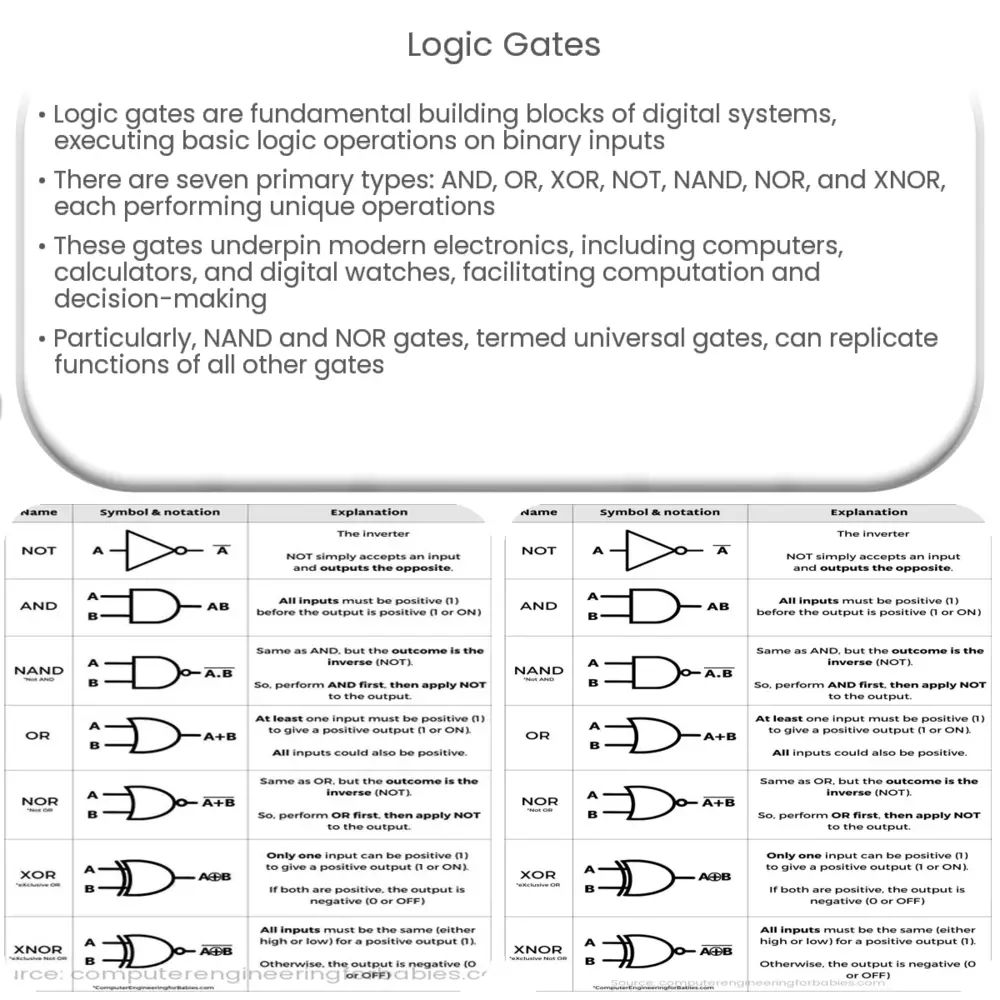
There are seven basic types of logic gates: AND, OR, XOR (Exclusive OR), NOT, NAND (NOT AND), NOR (NOT OR), and XNOR (NOT XOR). Each of these gates is represented by a specific symbol and performs a distinct operation.
1. AND Gate
The AND gate produces an output of 1 if and only if all its inputs are 1. If any of the inputs are 0, the output will be 0.
2. OR Gate
An OR gate outputs 1 if at least one of the input values is 1. If all inputs are 0, the output will also be 0.
3. XOR Gate
The XOR (Exclusive OR) gate gives an output of 1 only if an odd number of inputs are 1. In the case of two inputs, the output is 1 if one input is 0 and the other is 1.
4. NOT Gate
The NOT gate, also known as an inverter, is a gate that outputs the opposite value to its input. If the input is 1, the output is 0, and vice versa.
5. NAND Gate
The NAND gate is the opposite of an AND gate. It outputs 0 only if all its inputs are 1. For any other combination of inputs, the output is 1.
6. NOR Gate
The NOR gate is the reverse of an OR gate. It outputs 1 only if all its inputs are 0. For any other combination, the output is 0.
7. XNOR Gate
The XNOR gate outputs 1 only if the number of 1 inputs is even. With two inputs, it outputs 1 when both inputs are the same, and 0 when they are different.
Applications of Logic Gates
Logic gates are integral to the functioning of modern electronics. They form the basis of digital computation, enabling complex operations in devices such as computers, calculators, and digital watches. A closer look at their uses and practical applications will be discussed in the next section.
Uses and Practical Applications of Logic Gates
The functions of logic gates extend across a wide array of electronic devices. Here are some of their main applications:
-
Computers: Logic gates are the foundation of digital circuits like processors and memory modules. They facilitate arithmetic operations, data storage, and data processing.
-
Calculators: They play a crucial role in calculators, enabling the execution of complex mathematical operations.
-
Digital Watches: In digital watches, logic gates are used to count time and display it digitally.
-
Telecommunication Systems: Logic gates help in the digital processing of data and signals in telecommunication devices.
-
Control Systems: They are used extensively in control systems such as traffic lights, elevators, and automated machines for decision-making processes.
How Logic Gates Function in Circuits
Logic gates are interconnected to form a digital circuit to achieve a desired output based on the inputs. The output of one gate can serve as the input for another, allowing complex logical functions to be implemented. For example, a combination of logic gates can be used to create a circuit that adds two binary numbers. This is an example of how computers and calculators perform arithmetic operations.
Universal Gates
Of particular interest in the study of logic gates are the NAND and NOR gates, often referred to as universal gates. These gates are termed as such because they can be singly or in combination used to recreate the functions of all other basic logic gates. Understanding the potential of these gates and how they function is crucial in digital electronics and computing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, logic gates are a fundamental component of digital electronics and computing. They are the means by which binary information is manipulated, allowing for the execution of complex logical operations. From basic digital devices to sophisticated computing systems, logic gates play an indispensable role in our modern digital age. With a solid understanding of logic gates and their operations, one can grasp the functioning of the digital world that surrounds us.

