Explore the world of Linear Voltage Regulators: their types, working principle, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
Introduction to Linear Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulation is an essential function in electronics. It allows electronic devices to maintain a constant voltage output irrespective of the fluctuations in the input voltage or load. Among the various types of voltage regulators, the Linear Voltage Regulator holds a significant place. This article provides an overview of Linear Voltage Regulators, their types, working principles, and applications.
What is a Linear Voltage Regulator?
A Linear Voltage Regulator is a system that maintains a consistent output voltage level, regardless of changes in the input voltage or load conditions. This consistency is crucial in many electronics applications, as it prevents damage to the device and ensures reliable functionality.
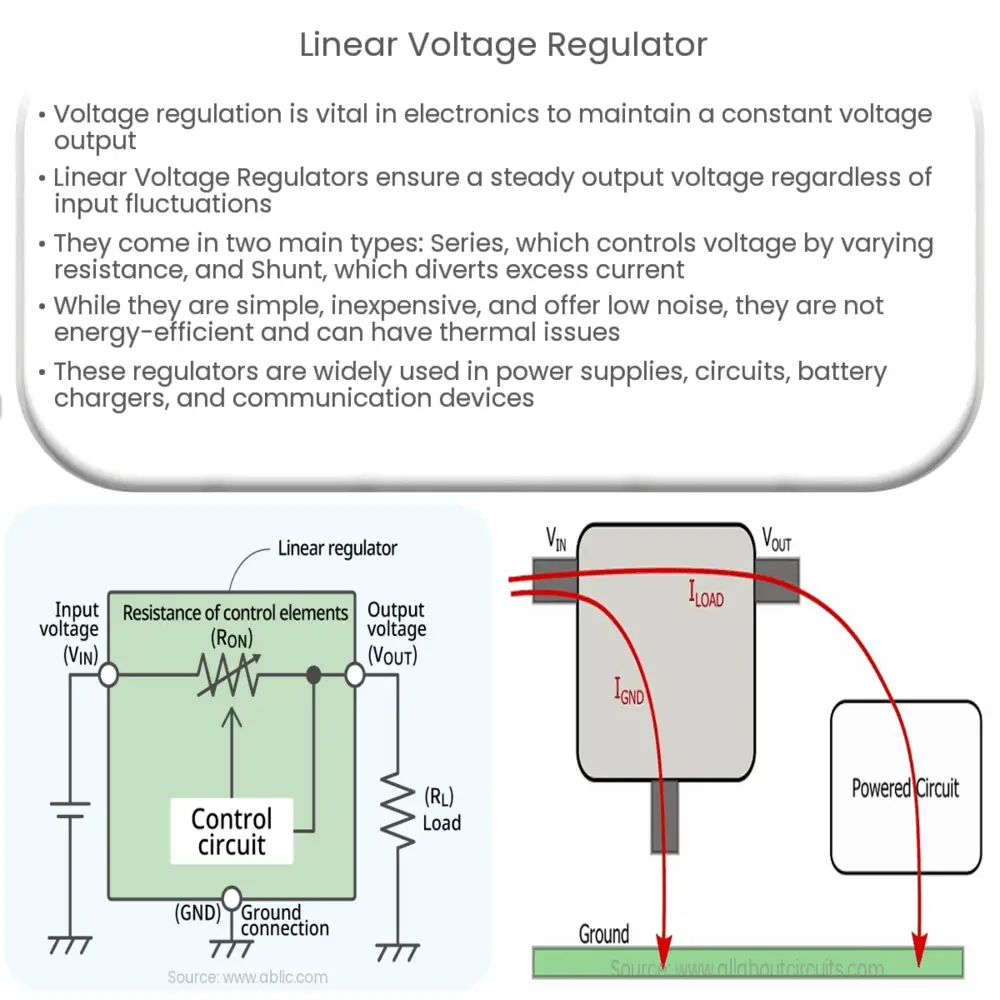
Types of Linear Voltage Regulators
- Series Voltage Regulator: In this type of regulator, the regulating device is in series with the load. The output voltage is controlled by varying the resistance of the series device.
- Shunt Voltage Regulator: In this type, the regulating device is connected in parallel to the load. The shunt regulator works by shunting the excess current away from the load to maintain the desired output voltage.
How does a Linear Voltage Regulator Work?
The working principle of a linear voltage regulator involves the comparison of the output voltage with a fixed reference voltage. The difference between the two voltages is amplified and used to control the regulation element. This process ensures that the output voltage is always maintained at the desired level.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Linear Voltage Regulators
- Advantages: Linear voltage regulators are simple in design, inexpensive, and offer low noise output. They also have a fast response time, making them ideal for applications requiring immediate response to changes in the input voltage or load conditions.
- Disadvantages: Despite their advantages, linear voltage regulators are not energy efficient, especially when there is a large difference between the input and output voltage. This is because the excess energy is dissipated as heat, leading to thermal issues. They also have a limited power handling capacity.
Applications of Linear Voltage Regulators
Linear voltage regulators find extensive use in various applications due to their simplicity and effectiveness. Here are a few significant areas of their use:
- Power Supplies: They are used in power supplies for providing a stable output voltage.
- Electronic Circuits: Linear voltage regulators are used in electronic circuits that require a constant voltage.
- Battery Chargers: These regulators play an essential role in battery chargers where a steady voltage is necessary for efficient charging.
- Communication Devices: They are used in communication devices to prevent signal distortion that can be caused by voltage fluctuations.
Selection Criteria for Linear Voltage Regulators
While selecting a linear voltage regulator, a few critical factors need to be considered:
- Input Voltage: The regulator should be able to handle the maximum input voltage.
- Output Voltage: The regulator should provide the required output voltage.
- Load Current: It should be able to supply the maximum load current.
- Power Dissipation: The power dissipation should be within acceptable limits to prevent overheating.
Conclusion
In conclusion, linear voltage regulators play an essential role in numerous electronic applications. They maintain a consistent output voltage, ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of electronic devices. Despite their limitations, such as poor energy efficiency and power handling capacity, their simplicity, low cost, and fast response time make them a popular choice. Therefore, understanding their functionality, advantages, disadvantages, and selection criteria are crucial in designing and maintaining robust electronic systems.

