Explore the world of Inductive Touchscreens, understanding their workings, applications, advantages, limitations, and future innovations.
Understanding the Inductive Touchscreen Technology
While we interact with touchscreen devices on a daily basis, the technology behind this convenient feature is diverse and often overlooked. One such technology is the inductive touchscreen system, a powerful yet underappreciated tool in the realm of touch interfaces.
The term ‘inductive’ might be familiar to those with a background in physics or electronics, as it pertains to the generation of an electric current by a changing magnetic field. This principle is at the heart of inductive touchscreen technology.
How Inductive Touchscreens Work
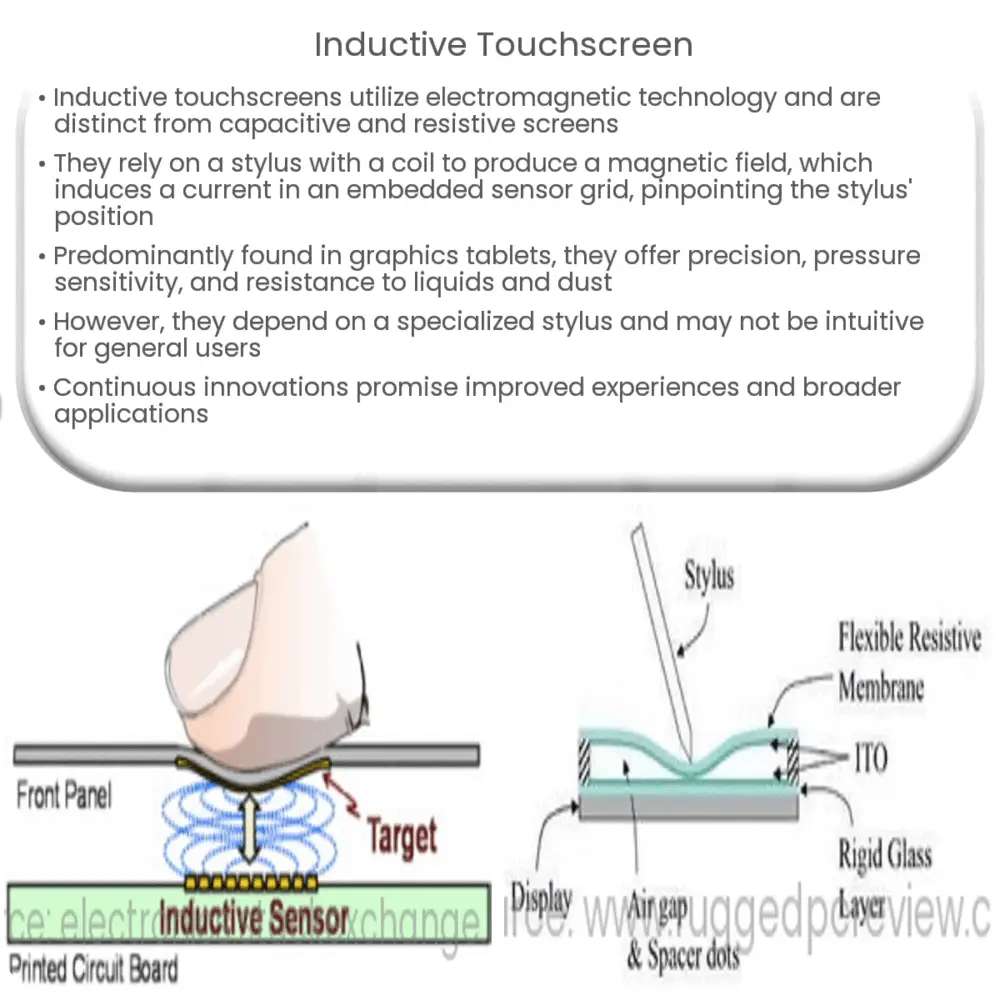
Inductive touchscreens work differently from capacitive or resistive touchscreens, which rely on the human body’s electrical properties or mechanical pressure, respectively. Instead, inductive touchscreens are based on electromagnetic technology.
These screens consist of a sensor grid embedded behind the display and a pointer, often a stylus, equipped with a coil and circuitry to generate an electromagnetic field. When the stylus is brought near the screen, the magnetic field it produces induces a current in the sensor grid. The system then calculates the position of the stylus based on the strength and location of this induced current.
Applications of Inductive Touchscreens
-
Graphics Tablets: Inductive touchscreens are predominantly found in graphics tablets, where they enable precise and responsive inputs. Artists and designers appreciate this technology because it allows for the use of a stylus with pressure sensitivity, tilt recognition, and sometimes even rotation recognition.
-
Specialized Devices: Some specialized devices such as medical equipment and industrial control systems also employ inductive touchscreens. These devices often require a higher level of precision and durability that inductive touchscreens can provide.
Advantages of Inductive Touchscreens
One of the main advantages of inductive touchscreens is their high level of precision. Unlike capacitive touchscreens, which may not differentiate between intentional touches and accidental ones (like a palm resting on the screen), inductive touchscreens only respond to the stylus.
Another significant advantage is the ability to incorporate pressure sensitivity. This feature allows users to create nuanced digital artwork or handwriting that would be impossible with other touch technologies.
Furthermore, inductive touchscreens are not affected by the presence of liquids or dust on the screen, making them suitable for use in a variety of environments.
Limitations of Inductive Touchscreens
Despite their many advantages, inductive touchscreens also have certain limitations. The most prominent is their dependency on a specialized stylus for interaction. Losing or damaging the stylus can render the device unusable until a replacement is obtained.
Additionally, while these screens excel at precision, they may not be the most intuitive for general users. Unlike capacitive touchscreens, which can be operated with a simple touch of a finger, inductive touchscreens require more specific, stylus-based interaction.
Innovations and Future Directions
Inductive touchscreen technology is continually evolving. Recent advancements include the development of passive styluses that do not require batteries or charging. Another exciting development is the integration of inductive technology with other touchscreen types to create hybrid systems. These hybrids can offer the precision of an inductive touchscreen while also supporting finger touch inputs, similar to capacitive screens.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inductive touchscreens represent a unique and powerful facet of touch interface technology. With their high precision, resistance to environmental factors, and potential for nuanced input, they serve as indispensable tools in sectors such as digital artistry, industrial control, and medical equipment.
Despite some limitations, the continuous evolution and innovation in this field promise to further improve user experiences and broaden the range of applications for inductive touchscreens. As consumers and technologists, understanding this technology enables us to better appreciate and harness the power at our fingertips.

