Explore the workings, types, applications, advantages, and future of inductive position sensors in this comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Inductive Position Sensors
Inductive position sensors have become a crucial component of today’s technologically advanced world. These innovative devices operate on a principle that leverages the power of electromagnetism to detect the position of a metallic object in proximity.
The Working Principle of Inductive Position Sensors
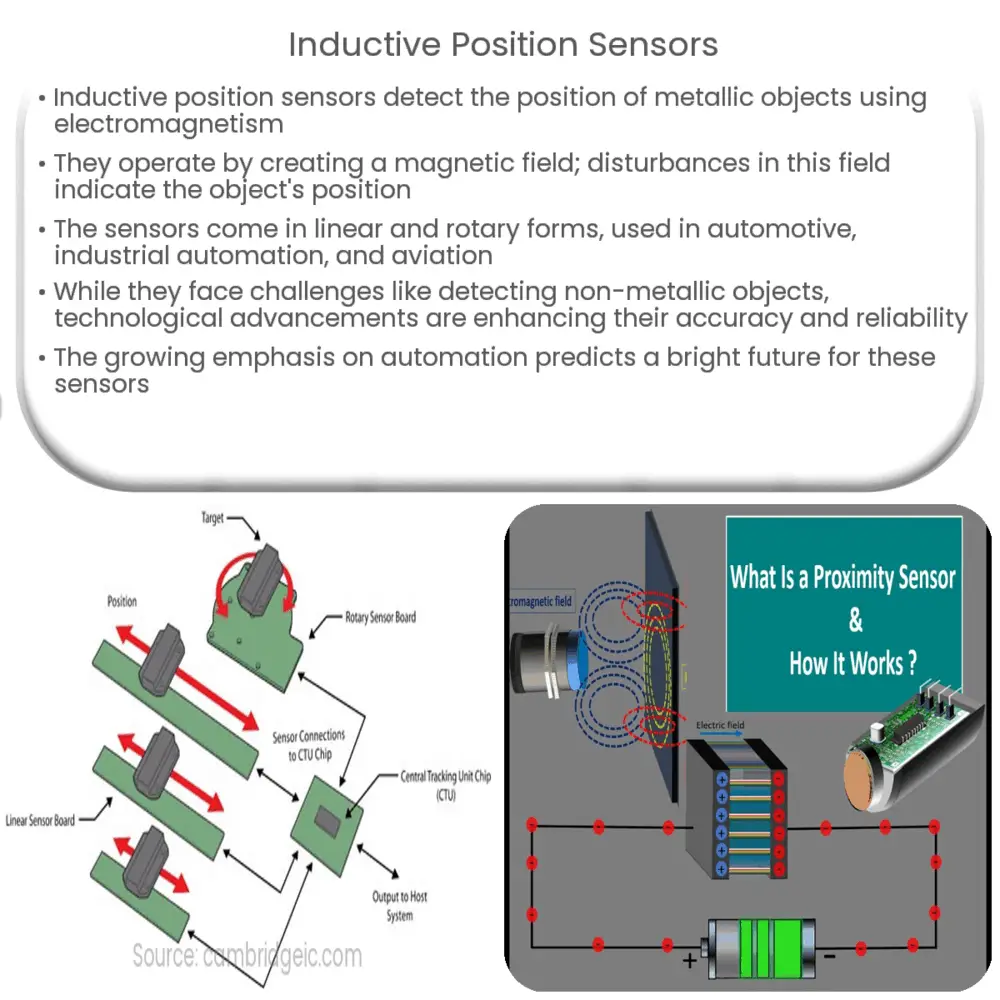
The core operating principle of an inductive position sensor involves creating a magnetic field via an inductor, typically a coil of wire. When a metal object enters this magnetic field, it disrupts the field’s current flow. The sensor then measures this disturbance, which serves as an indicator of the position of the object.
Types of Inductive Position Sensors
- Linear Inductive Sensors: As the name suggests, these sensors measure the position of objects in a linear path. They are most commonly used in industrial automation processes, robotics, and vehicular applications.
- Rotary Inductive Sensors: These sensors determine the angular position of a metal object. Their main applications are in the field of robotics and aerospace systems.
Applications of Inductive Position Sensors
Inductive position sensors are employed in numerous domains due to their robustness, reliability, and non-contact nature. They find extensive applications in sectors like automotive, industrial automation, and aviation. Let’s delve deeper into some of the primary applications:
- Industrial Automation: Sensors are used for process control, equipment calibration, and system monitoring in various industries.
- Automotive: Here, they play a key role in applications like throttle control, steering angle detection, and gear position monitoring.
- Aviation: They contribute to flight controls, engine controls, and landing gear systems.
Advantages of Inductive Position Sensors
There are several benefits to using inductive position sensors, the most notable of which are their non-contact operation and robustness against environmental conditions. As non-contact devices, they offer a long lifespan without any wear and tear. Moreover, these sensors can function effectively even in adverse conditions like dust, humidity, and high temperatures, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
The Challenges
Despite the numerous advantages, inductive position sensors are not without their limitations. Some of the challenges include difficulty in detecting non-metallic objects and sensitivity to changes in the target’s material properties.
Overcoming the Challenges
While there are indeed challenges in implementing inductive position sensors, progress in technology has led to the development of more sophisticated sensors capable of overcoming these limitations. For instance, advancements in sensor design and software algorithms have made it possible to compensate for the effects of changes in target material properties, improving sensor accuracy and reliability.
Future of Inductive Position Sensors
As technology advances, the future of inductive position sensors seems bright. With the rise of Industry 4.0, the Internet of Things (IoT), and autonomous vehicles, the demand for these sensors is set to grow exponentially. Researchers are also exploring the potential of combining inductive sensors with other sensing technologies to improve detection capabilities and increase application domains. The advent of miniaturized and low-power sensors is also expected to boost their use in portable and battery-operated devices.
Conclusion
In summary, inductive position sensors are a pivotal component in modern technology, contributing significantly to various sectors, including industrial automation, automotive, and aviation. While they present certain challenges, continuous advancements in sensor technology are steadily mitigating these issues, paving the way for more efficient and versatile applications.
As the world continues to lean towards automation and digitalization, the relevance and demand for these sensors are anticipated to rise even further. The future developments in the realm of inductive position sensors promise exciting prospects that will continue to revolutionize the world of technology and beyond.

