Explore the world of inductive energy storage devices, their types, applications, advantages, and future trends in our comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Inductive Energy Storage Devices
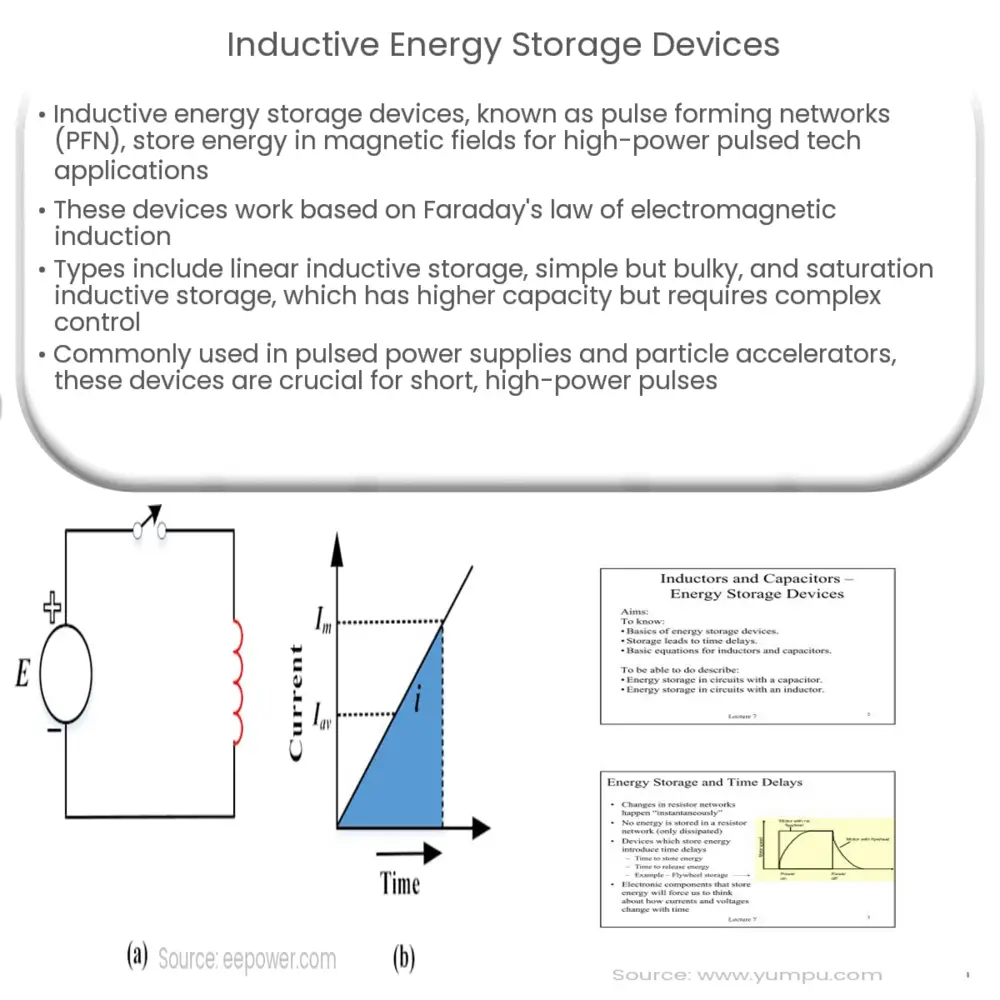
Inductive energy storage devices, also known as pulse forming networks (PFN), are vital in the field of high-power pulsed technology. They store energy in a magnetic field created by electric current flowing through an inductor, or coil. Upon discharge, the stored energy is released in a quick pulse, hence their prominence in pulsed power applications.
Working Principle of Inductive Energy Storage Devices
The operational principle of inductive energy storage devices is rooted in Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. When a current passes through an inductor, a magnetic field is established around it. This magnetic field then stores energy. When the current is interrupted, the collapsing magnetic field induces a voltage in the inductor, releasing the stored energy in a pulse.
Types of Inductive Energy Storage Devices
- Linear Inductive Energy Storage1: Linear inductive energy storage involves the use of linear inductors. It has a simple design and offers better performance compared to other energy storage devices in terms of life cycle and efficiency. However, it suffers from size and weight problems due to the nature of linear inductors.
- Saturation Inductive Energy Storage2: This type utilizes saturable reactors or magnetic switches, which offer increased energy storage capacity compared to linear inductive energy storage. However, they require more complex control strategies to handle the saturable characteristics.
Applications of Inductive Energy Storage Devices
Inductive energy storage devices are commonly used in high-power pulse applications, where they offer advantages over alternative energy storage methods. Some of the most prevalent applications include:
- Pulsed Power Supplies: These devices are utilized in a variety of pulsed power supplies due to their ability to release large amounts of energy in a short time.
- Particle Accelerators: Particle accelerators require short, high-power pulses. Inductive energy storage devices fulfill this requirement effectively, making them an integral part of these systems.
1. David A. Torrey, “Linear Inductive Energy Storage and Compression,” IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 1986.
2. J. R. Bayless and R. W. Lemke, “Saturable reactor energy storage compression circuits,” 1987 2nd IEEE International Pulsed Power Conference, Lubbock, TX, USA, 1987, pp. 145-149.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Inductive Energy Storage Devices
Like any other technology, inductive energy storage devices come with their strengths and weaknesses. Some of the main advantages include:
- High Power and Efficiency: Inductive energy storage devices can release large amounts of power in a short time. This makes them highly efficient, especially for pulsed power applications.
- Long Life Cycle: Inductive energy storage devices have a long life cycle and are very reliable, thanks to their lack of moving parts and mechanical wear.
However, there are also some drawbacks:
- Large Size and Weight: Inductive energy storage devices tend to be large and heavy, particularly in the case of linear inductive energy storage, which can limit their applications.
- Complex Control: Saturation inductive energy storage requires complex control strategies, which can make these devices more challenging to implement and manage.
Recent Developments and Future Trends
Research in the field of inductive energy storage is continually progressing, with numerous advancements and novel applications being explored. Miniaturization techniques are being developed to address the size and weight issue. Furthermore, new materials and fabrication technologies are promising to make these devices even more efficient and adaptable. The potential integration of these devices with renewable energy sources is also a trending topic in current research, pointing towards their broader application in sustainable energy systems in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inductive energy storage devices play a significant role in high-power pulsed technology, offering high power and efficiency. Despite some drawbacks like size, weight, and control complexity, these devices’ potential, especially in the wake of recent developments, is enormous. Their versatility, combined with ongoing advancements, makes them a promising technology for a wide array of applications, including renewable energy systems and beyond.

