Magnetic induction is used in electricity generation by inducing a voltage in conductors when the magnetic field around them changes, as in generators.
Introduction to Magnetic Induction and Electricity Generation
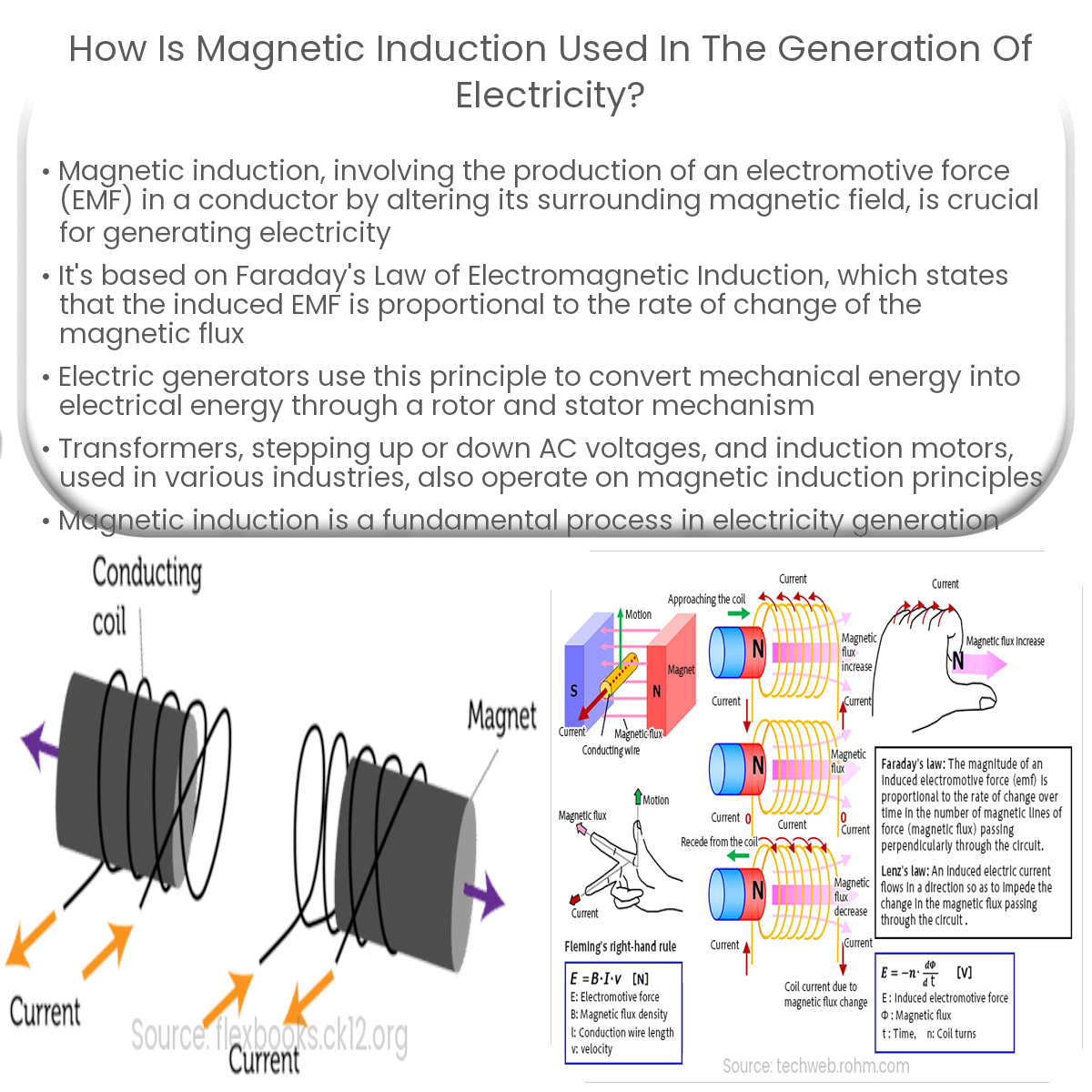
Magnetic induction plays a crucial role in generating electricity. This process involves the production of an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in a conductor by altering the magnetic field around it. In this article, we’ll explore how magnetic induction is utilized in electricity generation.
Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
The foundation of magnetic induction in electricity generation is Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. Faraday’s Law states that the induced EMF in a closed loop is directly proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the loop. Mathematically, it can be represented as:
EMF = -dΦB/dt
where ΦB is the magnetic flux and t represents time.
Electric Generators
Electric generators are the most common application of magnetic induction in electricity generation. These devices convert mechanical energy into electrical energy using the principles of electromagnetic induction. The main components of a generator are a rotor, stator, and an external power source.
- Rotor: The rotor contains magnets, which create a magnetic field when rotated. This rotation can be driven by various sources, such as water turbines, steam turbines, or internal combustion engines.
- Stator: The stator consists of conductive wire coils that are wound around an iron core. When the magnetic field created by the rotor changes, an EMF is induced in the stator windings, producing an electric current.
Transformers
Transformers are another application of magnetic induction in the electric power industry. These devices are used to step up or step down AC voltages. Transformers consist of two or more coils of wire wound around a common iron core. When an alternating current passes through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil, resulting in a stepped-up or stepped-down voltage.
Induction Motors
Induction motors are widely used in industrial and household applications. These motors operate on the principle of magnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field induces a current in the motor’s rotor. This induced current generates a magnetic field in the rotor, which interacts with the stator’s magnetic field to produce torque and cause the rotor to rotate.
In conclusion, magnetic induction is a fundamental principle in the generation of electricity. It plays a significant role in the operation of electric generators, transformers, and induction motors, enabling the efficient conversion and distribution of electrical energy in various applications.