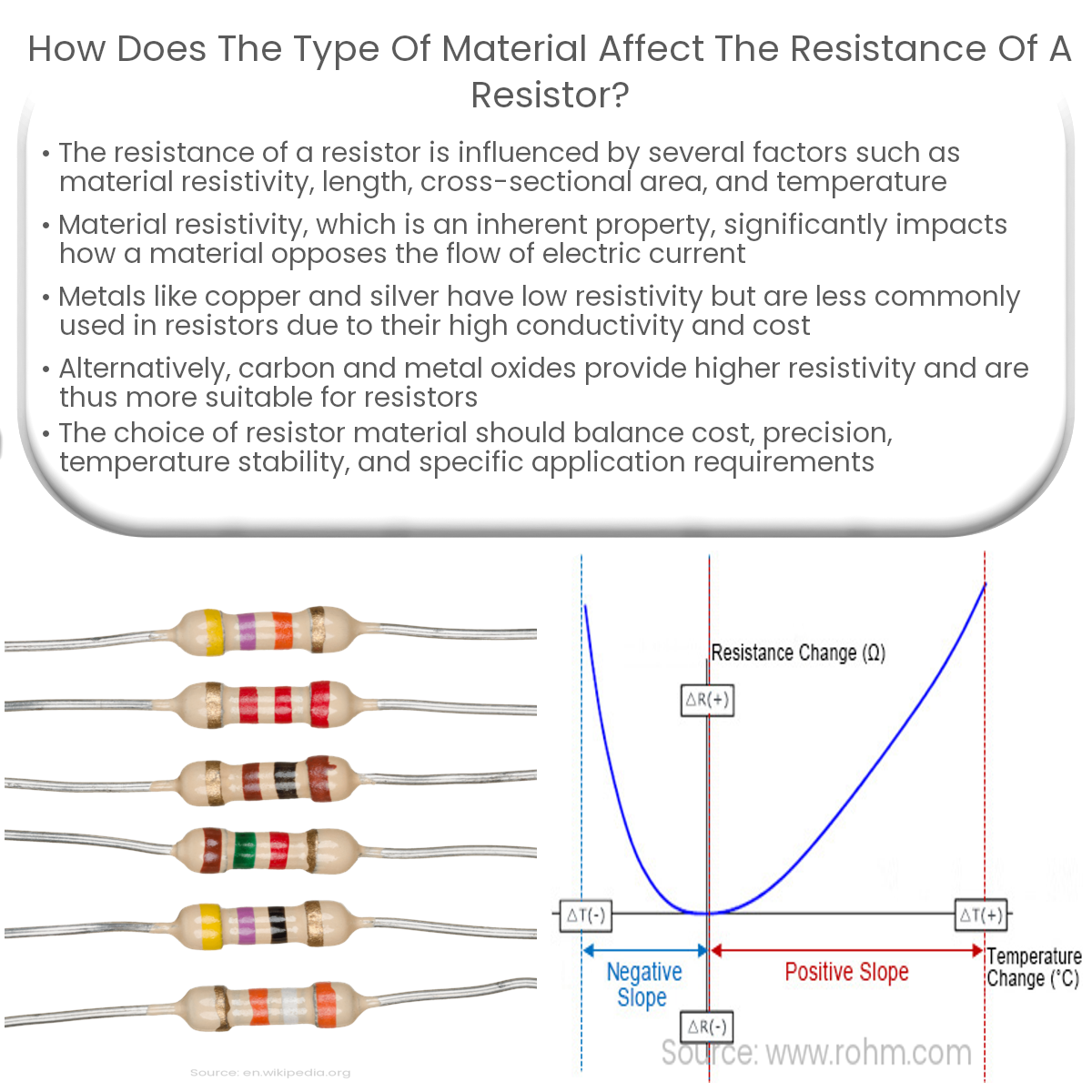
The type of material affects a resistor’s resistance due to differences in resistivity, electron behavior, and other intrinsic properties.
How Does the Type of Material Affect the Resistance of a Resistor?
Resistance is a measure of the opposition a material presents to the flow of electric current. The resistance of a resistor depends on multiple factors, including its material composition. The type of material directly affects the resistance due to differences in the behavior of electrons within various materials.
Factors Influencing Resistance
Several factors influence the resistance of a resistor, including:
- Material resistivity
- Length
- Cross-sectional area
- Temperature
Among these factors, material resistivity is the intrinsic property that determines how a specific material resists the flow of electric current.
Material Resistivity
Resistivity is a material property that quantifies its inherent resistance to electric current flow. Different materials have varying resistivities based on their atomic structures and the behavior of their electrons. Some common materials used in resistors and their characteristics include:
- Metals: Metals such as copper, silver, and gold have low resistivity due to their loosely bound valence electrons, which freely move and conduct current. However, these metals are not commonly used in resistors because they conduct too efficiently and are expensive.
- Carbon: Carbon has higher resistivity than metals, making it suitable for use in resistors. Carbon-based resistors are cost-effective and widely used, but they can have higher temperature coefficients, leading to less stable resistance values at elevated temperatures.
- Metal Oxides: Metal oxides, such as tin oxide and ruthenium oxide, offer higher resistivity and improved temperature stability compared to carbon-based resistors. Metal oxide film resistors are commonly used in applications requiring precision and stability.
- Compound Materials: Compound materials like metal film, thick film, and thin film are used in resistors to achieve specific characteristics. They offer various resistivities, temperature coefficients, and noise performance, depending on the desired application.
Choosing the Right Material
Selecting the appropriate resistor material depends on the requirements of the application, such as precision, temperature stability, power handling, and cost. It is crucial to understand the impact of the material on the resistor’s resistance and consider other factors, like tolerance and temperature coefficient, when designing and optimizing electrical circuits and devices.
In summary, the type of material used in a resistor directly affects its resistance due to the material’s intrinsic resistivity. The choice of material depends on factors such as cost, precision, and temperature stability, with various materials offering unique benefits and trade-offs to meet specific application requirements.